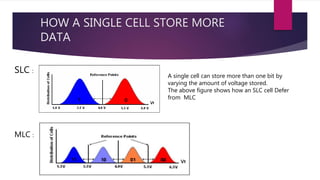
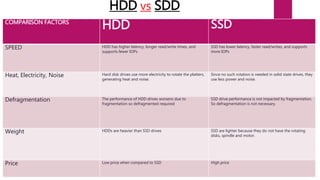
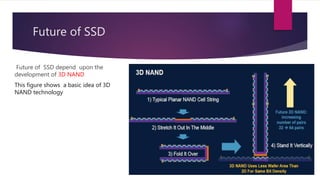
Solid state drives (SSDs) are storage devices that use flash memory instead of spinning disks. They have no moving parts, faster read/write speeds, and better durability than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). SSDs use NAND flash memory chips that can store data in single-level cells (SLC), multi-level cells (MLC), or triple-level cells (TLC). SLC provides the best performance and endurance but at a higher cost, while TLC has the lowest cost but lower endurance. SSDs have advantages over HDDs such as faster speeds, lower power consumption, and insensitivity to fragmentation. However, SSDs also have higher costs per gigabyte and limited