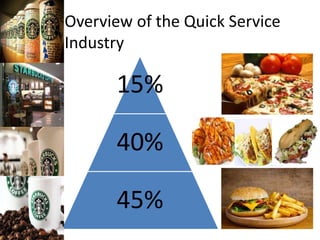
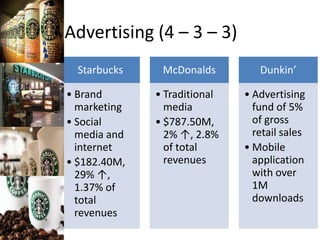
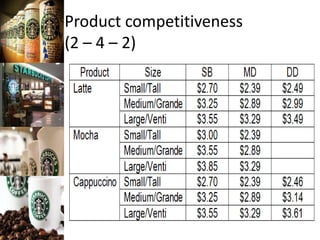
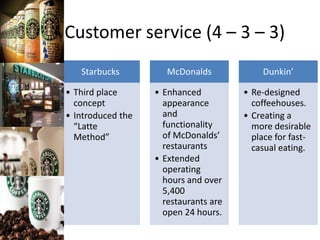
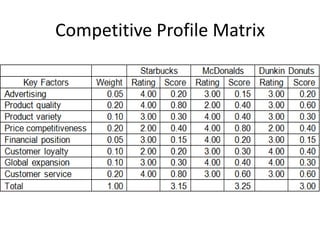
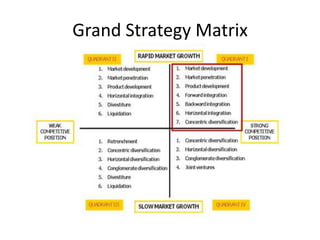
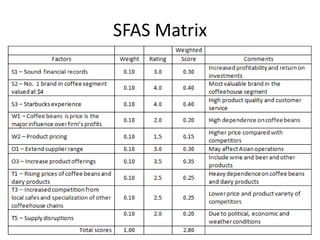
The document provides a competitive profile matrix analysis of Starbucks Corporation relative to its main competitors, McDonald's and Dunkin' Donuts, highlighting strengths, weaknesses, and critical success factors such as advertising, product quality, and customer loyalty. It discusses the quick service industry dynamics and the companies' financial positions, customer loyalty rankings, and global expansion strategies. Additionally, it suggests various strategic initiatives for Starbucks to maintain competitive advantages, such as acquiring businesses for specialized products and increasing market share through targeted store openings.



















![General Strategies
Acquisition or control of brokerage /
logistic firms to support Starbuck’s
supply chain management.
Acquisition or control or coffee bean and
dairy product producers. ;]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starbuckscorporationcpm-130828210534-phpapp02/85/Starbucks-Competitive-Profile-Matrix-27-320.jpg)