Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times

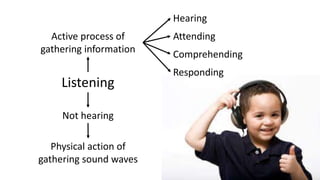


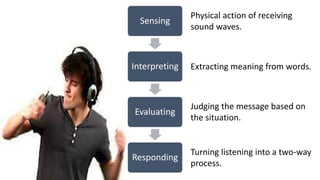



Effective listening skills are important but often underdeveloped. Listening is an active process that involves hearing, attending, comprehending, and responding. It accounts for over 50% of communication skills. However, people often retain only a short message or 25% of what they hear after 48 hours. Barriers to effective listening include environmental distractions, psychological factors like biases, physiological issues, and information overload. Some strategies to improve listening include showing interest, making eye contact, being patient, listening without bias, taking notes, and asking questions.






