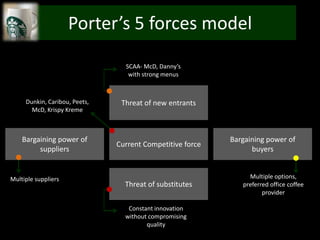
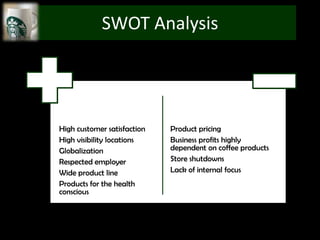
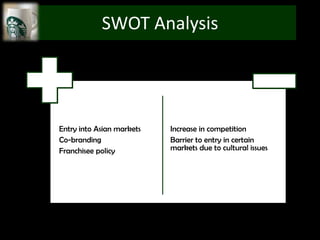
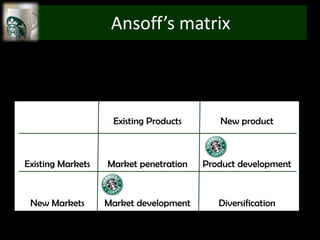
The document provides an overview of Starbucks, including that it opened its first store in 1971 in Seattle and has grown to over 29,972 stores in 60+ countries. It discusses Starbucks' target demographics such as adults ages 25-40, young adults ages 18-24, and kids/teens ages 13-17. The document also performs a Porter's 5 forces analysis, SWOT analysis, and discusses recommendations including concentrated growth strategy and expansion into new markets through Ansoff's matrix.