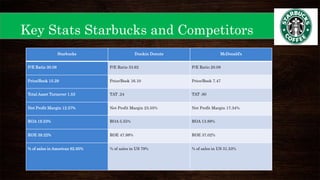
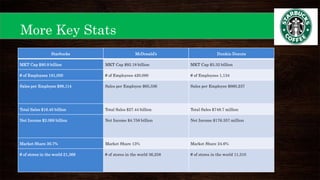
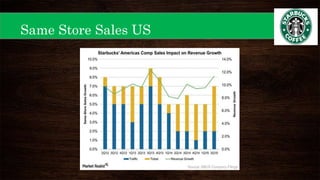
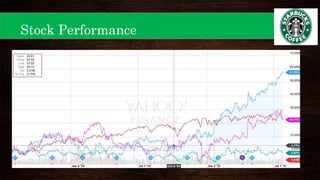
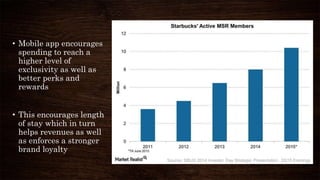
This document provides an overview of Starbucks' strategic management presentation. It discusses Starbucks' history since being founded in 1971, its mission statement, industry, key financial statistics, competitors, and strategies for foreign exchange hedging, commodity hedging, and improving its cash conversion cycle. It also analyzes Starbucks' capital structure, free cash flow, liquidity ratios, same store sales, stock performance, marketing, R&D, personnel practices, and PESTEL factors. Finally, it outlines Starbucks' strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats, and strategies for expanding in the Americas, EMEA, and China-Asia-Pacific regions.