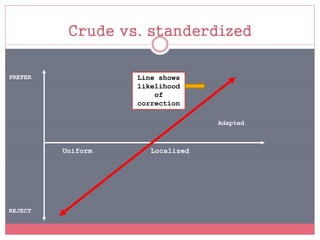
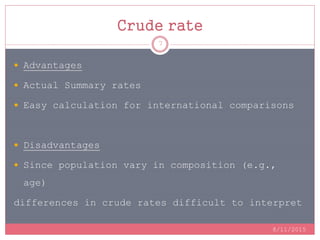
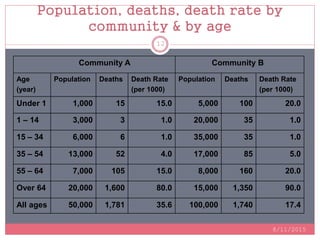
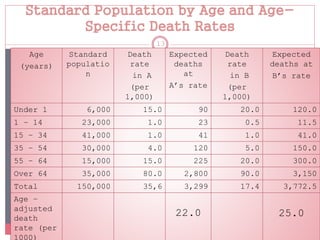
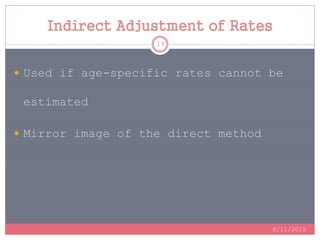
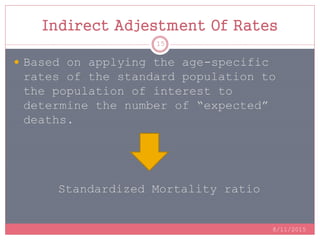
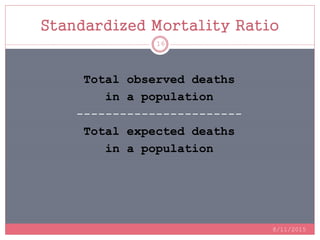
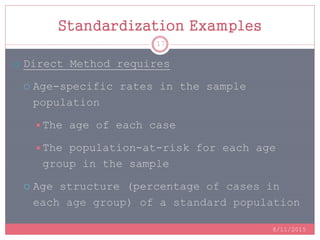
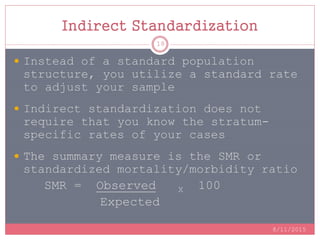
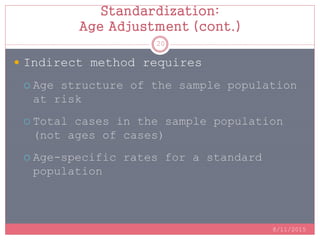
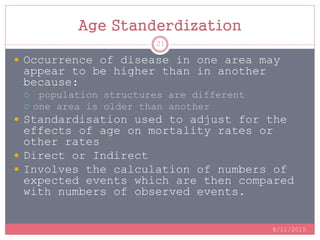
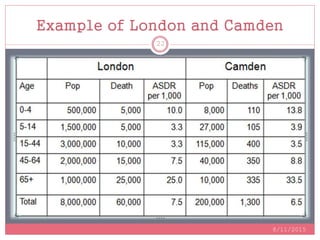
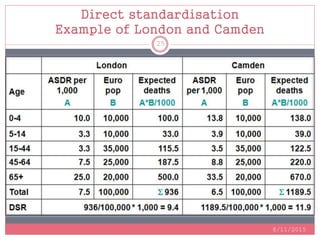
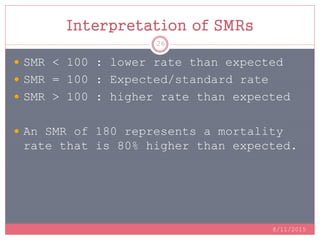
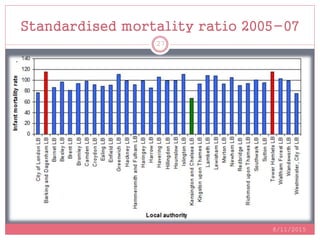
Standardization is a process used to make rates such as mortality rates comparable between populations with different age distributions. There are two main methods: direct standardization which applies the age-specific rates of the populations to a standard population, and indirect standardization which calculates a standardized mortality ratio by taking the ratio of observed to expected deaths based on a standard population's rates. Standardization allows unbiased comparison of health outcomes between groups after removing the effect of differences in age composition.