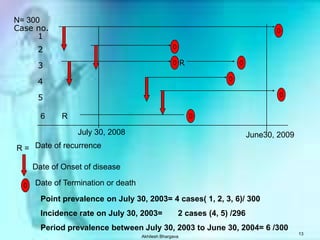
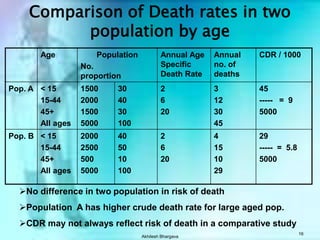
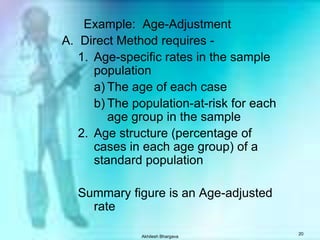
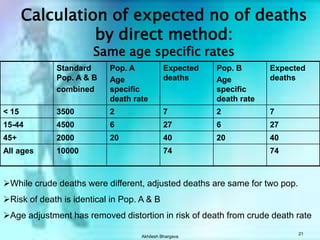
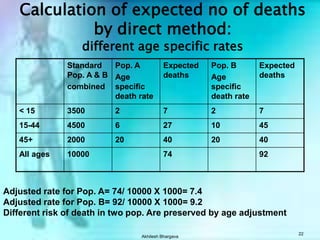
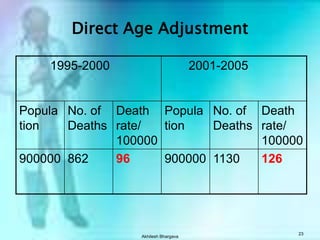
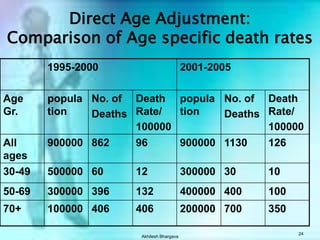
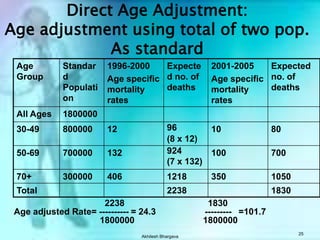
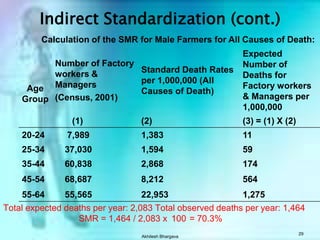
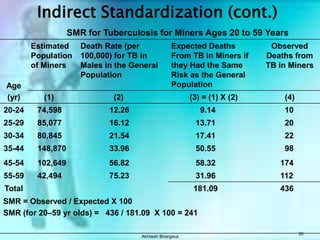
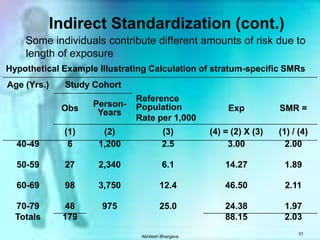
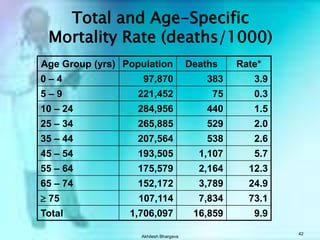
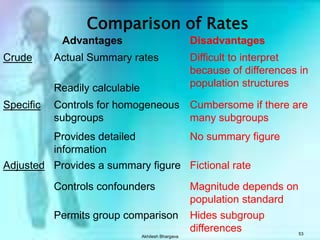
The document discusses various measures used to quantify disease occurrence and mortality rates. It defines key terms like prevalence, incidence, rates, ratios and standardized rates. Prevalence is a snapshot of disease at a point in time while incidence describes new cases occurring over time. Crude rates are calculated for the entire population while specific rates are for subpopulations. Standardized rates allow comparison between populations by adjusting for differences in age or other distributions. Methods like direct and indirect standardization are used to derive adjusted rates. Mortality data from vital statistics provides important public health indicators but has issues like accuracy of documentation and changing disease classifications over time.