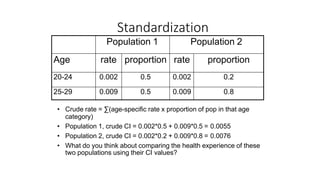
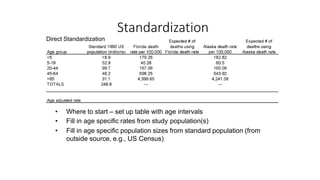
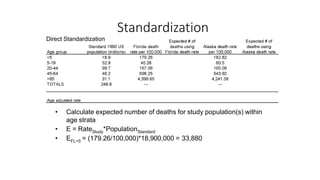
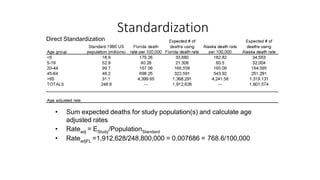
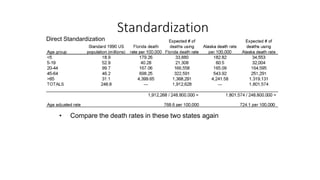
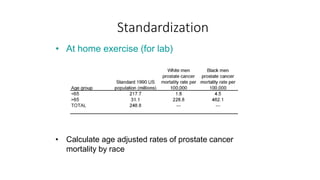
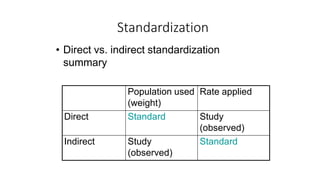
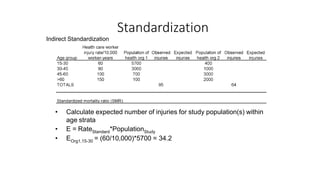
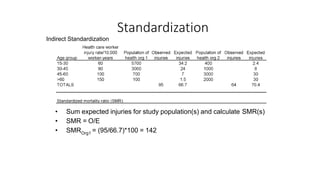
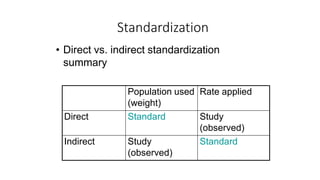
This document discusses different types of rates used to compare disease occurrence between populations and over time. It introduces crude rates, specific rates, and standardized rates. Standardized rates allow for fair comparisons between populations by adjusting for characteristics like age that influence disease risk. The document outlines direct and indirect standardization methods. Direct standardization applies the actual age-specific rates from study populations to a standard population, while indirect standardization applies age-specific rates from a standard population to the age structure of the study populations. Both allow comparison of disease rates between populations after accounting for differences in age distribution.