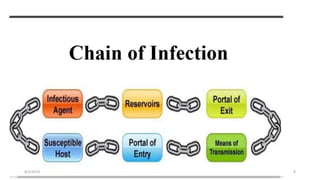
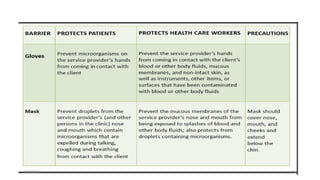
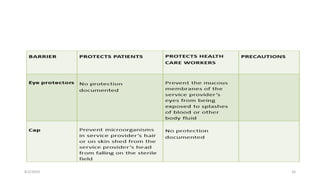
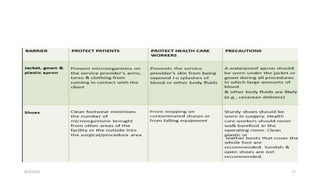
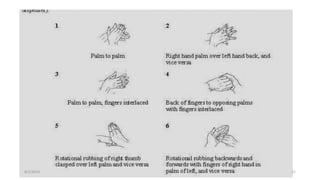
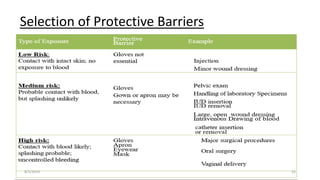
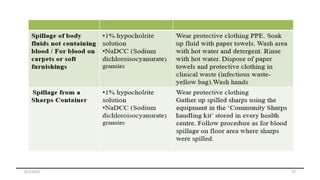
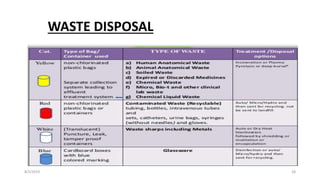
This document outlines universal standard precautions for preventing the transmission of infectious diseases. It discusses the definition of universal precautions, the history of infection control practices, and key aspects of precautions such as proper use of protective equipment, hand hygiene, safe handling of sharps, and waste disposal. The document emphasizes that all human blood and body fluids should be treated as potentially infectious to prevent transmission of bloodborne pathogens like HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C from healthcare workers to patients and vice versa.