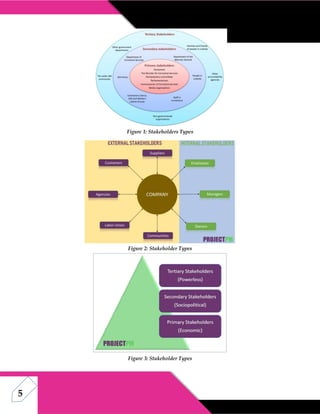
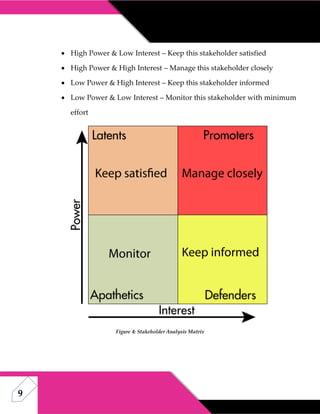
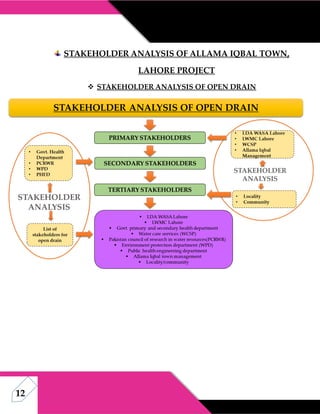
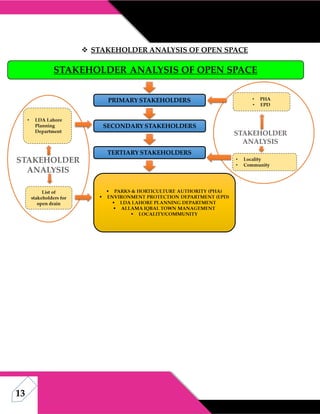
This document discusses stakeholder analysis for community development projects. It defines stakeholder analysis and outlines its aim to understand stakeholders' positions, interests, and influence. It describes primary, secondary, and tertiary stakeholder types and identifies stakeholders for a project in Allama Iqbal Town, Lahore. Benefits of stakeholder analysis include securing support, resources, and managing reactions to change. The power-interest matrix and stakeholder management are also discussed.