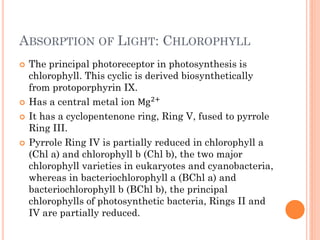
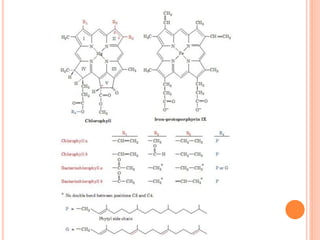
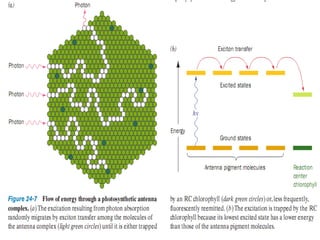
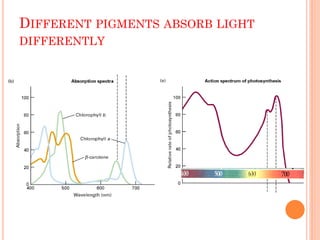
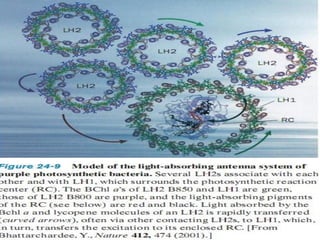
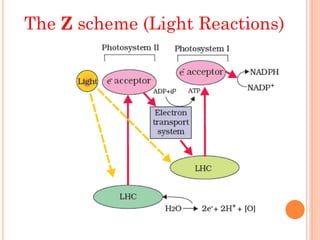
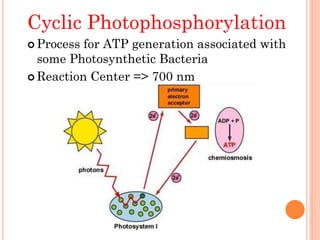
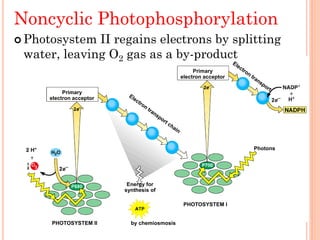
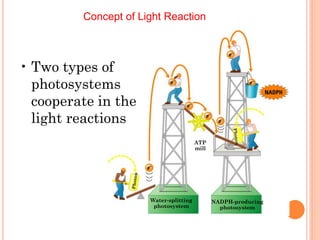
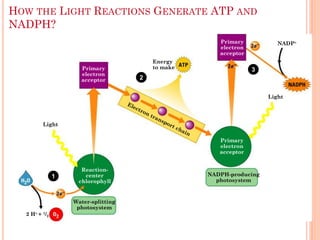
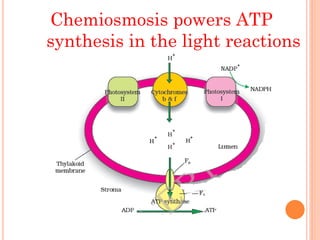
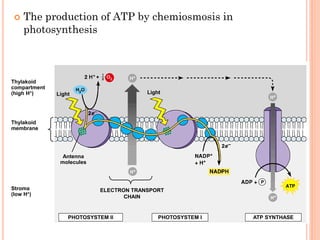
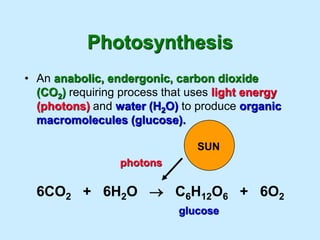
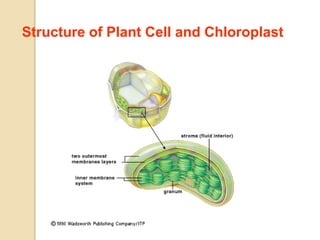
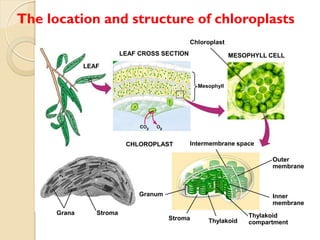
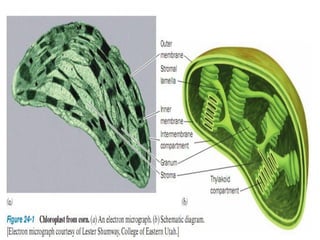
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. It takes place in two stages - the light reactions where light energy is captured to make ATP and NADPH, and the dark reactions where ATP and NADPH are used to incorporate carbon from CO2 into organic compounds like glucose. The chloroplast is the organelle where photosynthesis takes place, containing chlorophyll pigments in the thylakoid membranes which absorb light energy to drive the light-dependent reactions.

















![ photosynthesis is a two-stage process in which light
energy is harnessed to oxidize 2 A (the light
reactions):
and the resulting reducing agent [H] subsequently
reduces C2 (the dark reactions):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/photosynthesis-120109001352-phpapp02/85/Photosynthesis-25-320.jpg)
![VALIDITY OF NEIL HYPOTHESIS
1. Hill reaction :
In 1937,Robert Hill discovered that when isolated chloroplasts that
lack CO2 are illuminated in the presence of an artificial electron
acceptor such as ferricyanide, O2 is evolved with concomitant
reduction of the acceptor [to ferrocyanide]. This demonstrates that
CO2 does not participate directly in the O2 -producing reaction.
It was discovered eventually that the natural photosynthetic
electron acceptor is NADP, whose reduction product, NADPH, is
utilized in the dark reactions to reduce CO2 to carbohydrate.
2. Radioactive O :
In 1941,when the oxygen isotope 18 O became
available,Samuel Ruben and Martin Kamen directly
demonstrated that the source of the O2 formed in
photosynthesis is H2O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/photosynthesis-120109001352-phpapp02/85/Photosynthesis-26-320.jpg)