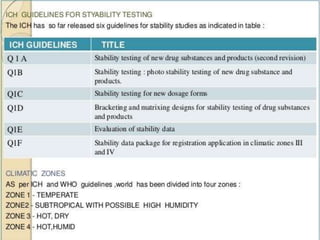
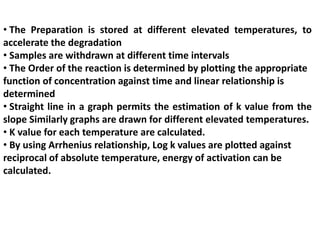
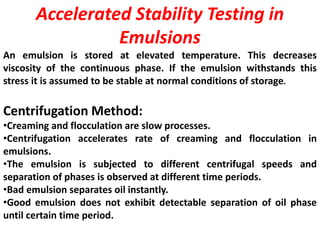
Accelerated stability testing is used to predict the shelf life of pharmaceutical formulations by subjecting them to elevated temperatures and humidity to accelerate any degradation. The key steps involve conducting studies at different temperatures, determining the reaction order, calculating rate constants (k) at each temperature, determining the energy of activation using the Arrhenius equation, and extrapolating to room temperature to estimate shelf life. Limitations include changes in degradation mechanism or order at higher temperatures that limit the accuracy of shelf life predictions.