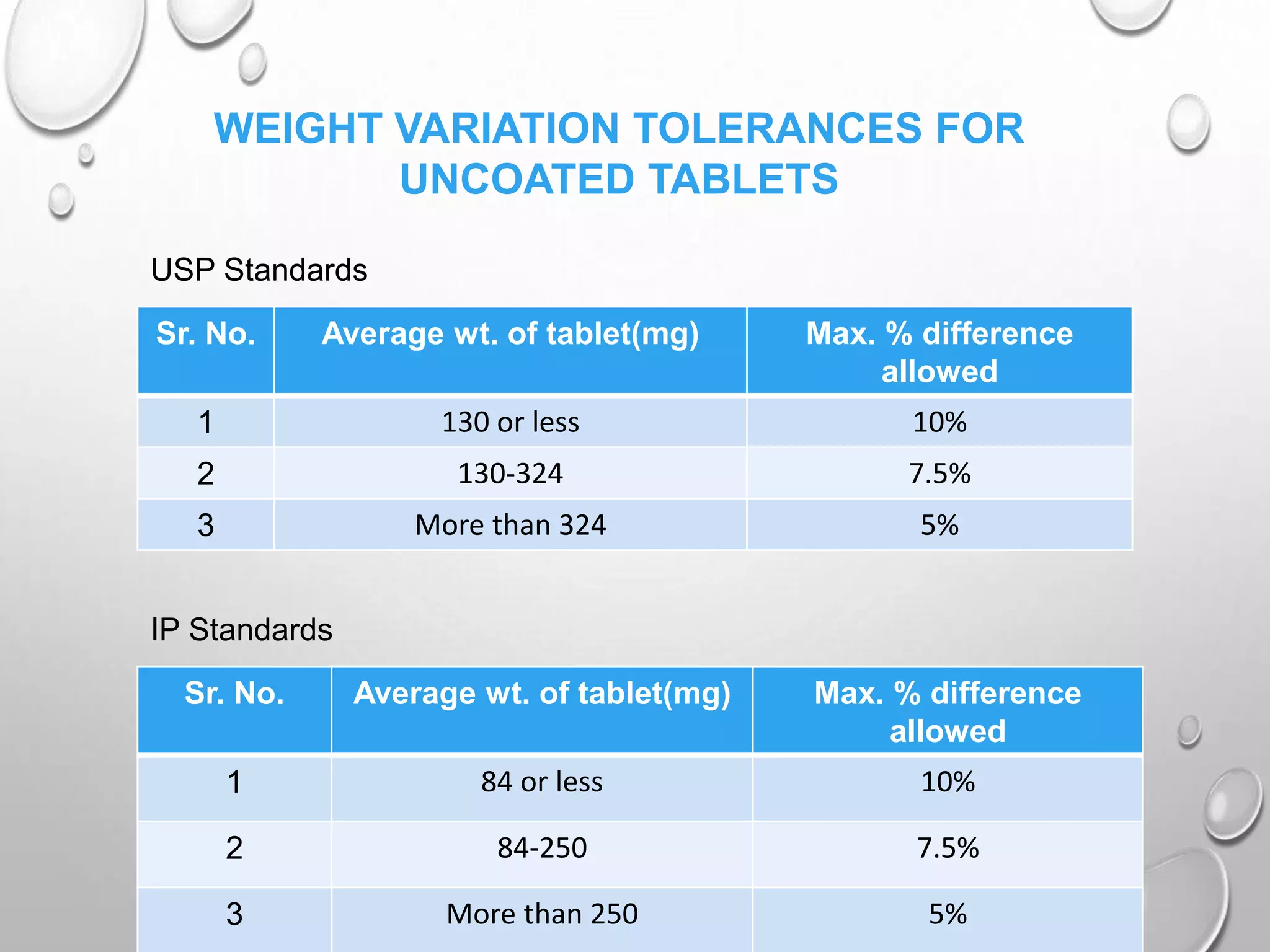
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) is a systematic approach in pharmaceutical manufacturing to ensure product quality by monitoring materials, processes, and personnel from raw material receipt to finished product release. It includes regular testing like hardness, disintegration, and visual inspections tailored to different dosage forms. IPQC is crucial for minimizing errors, enforcing manufacturing rules, and ensuring product specifications are met efficiently.