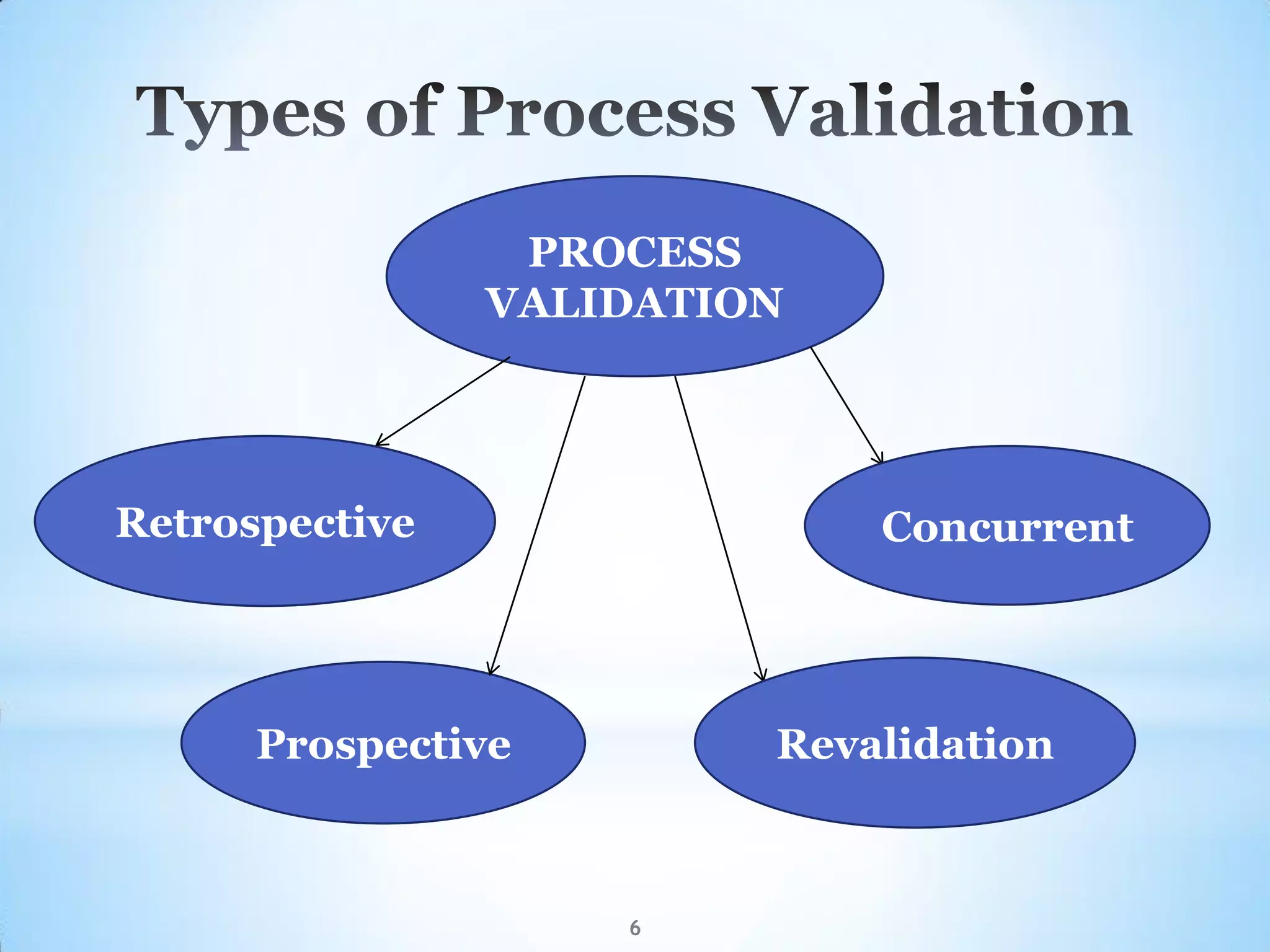
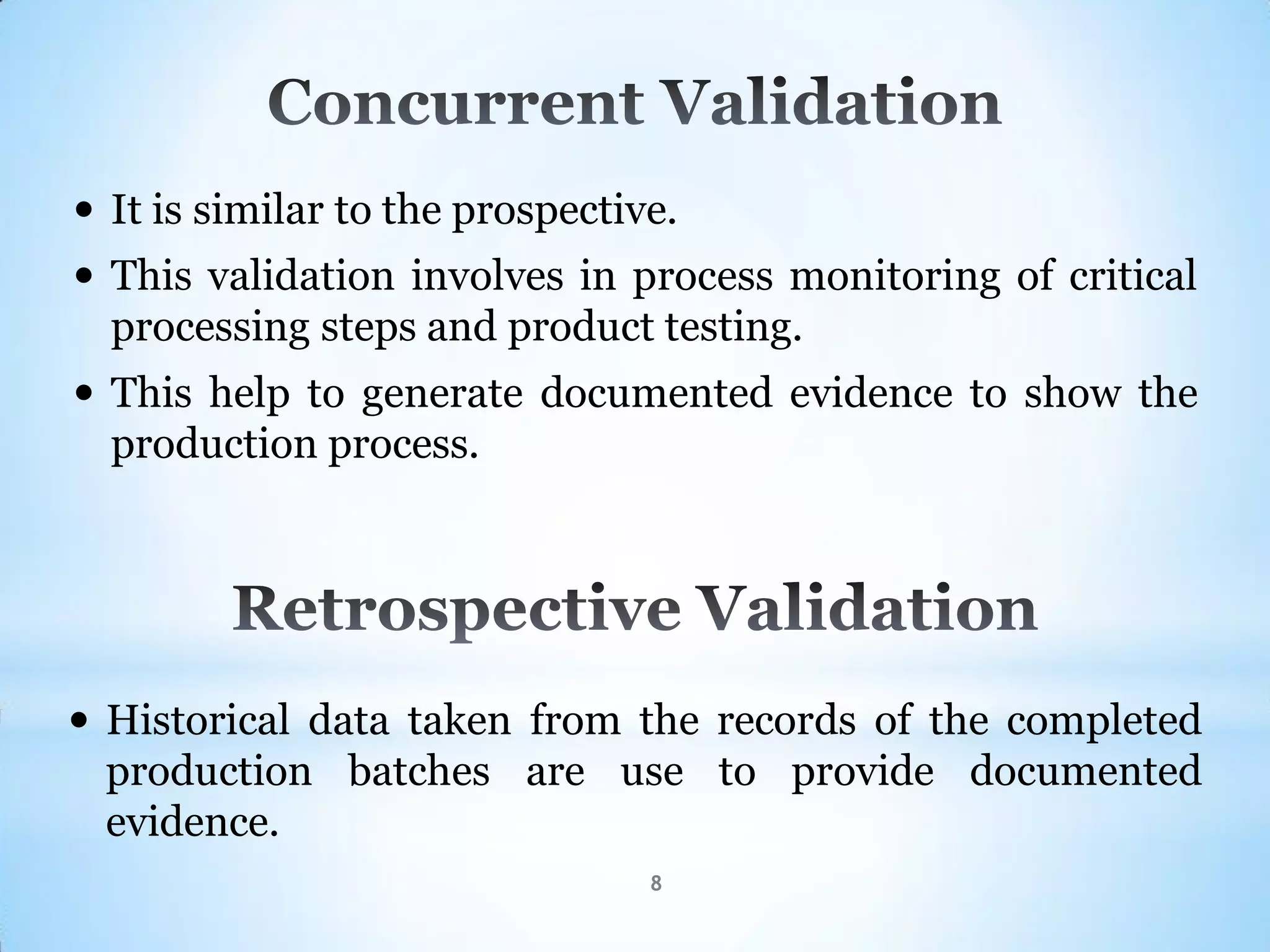
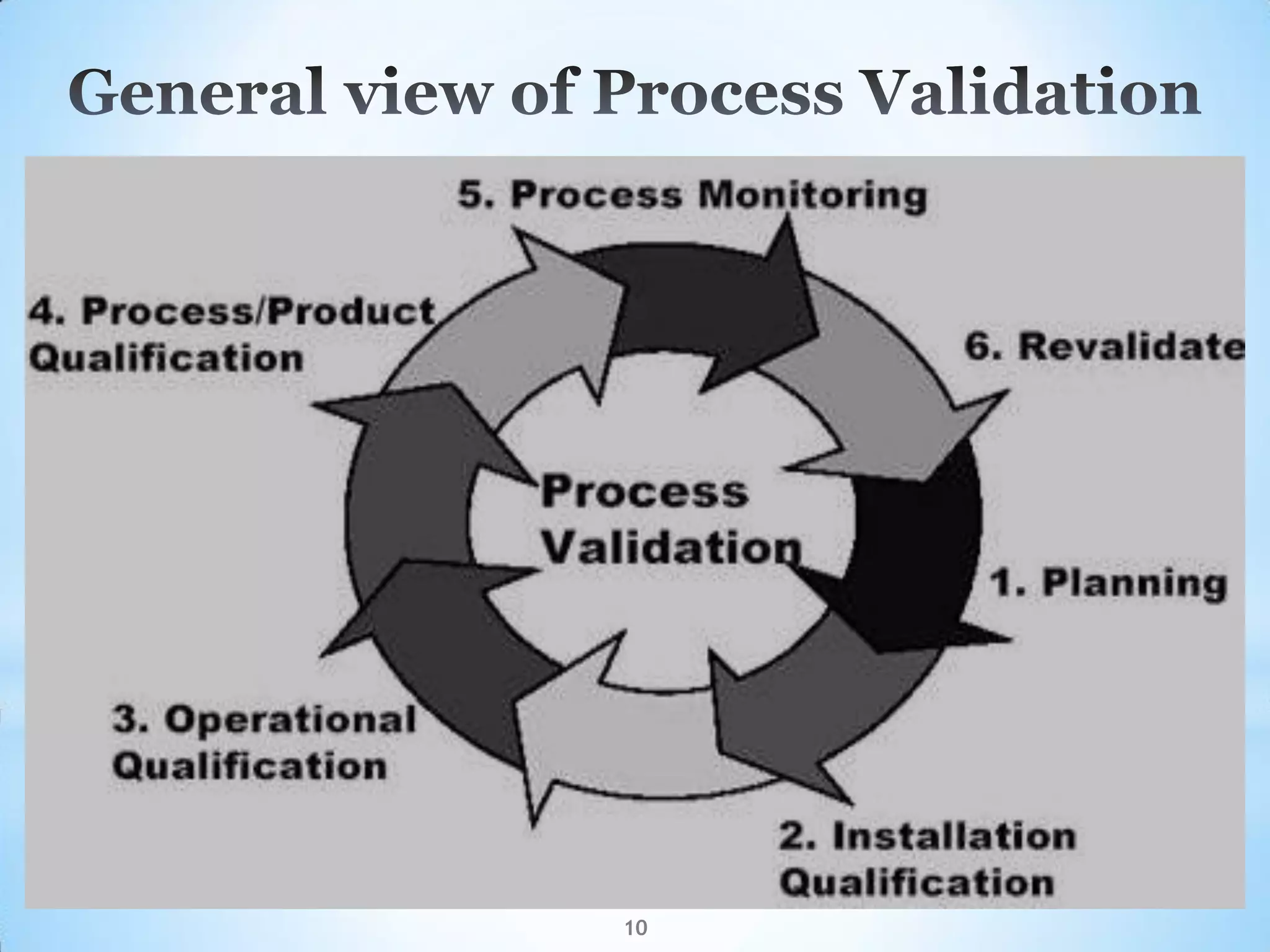
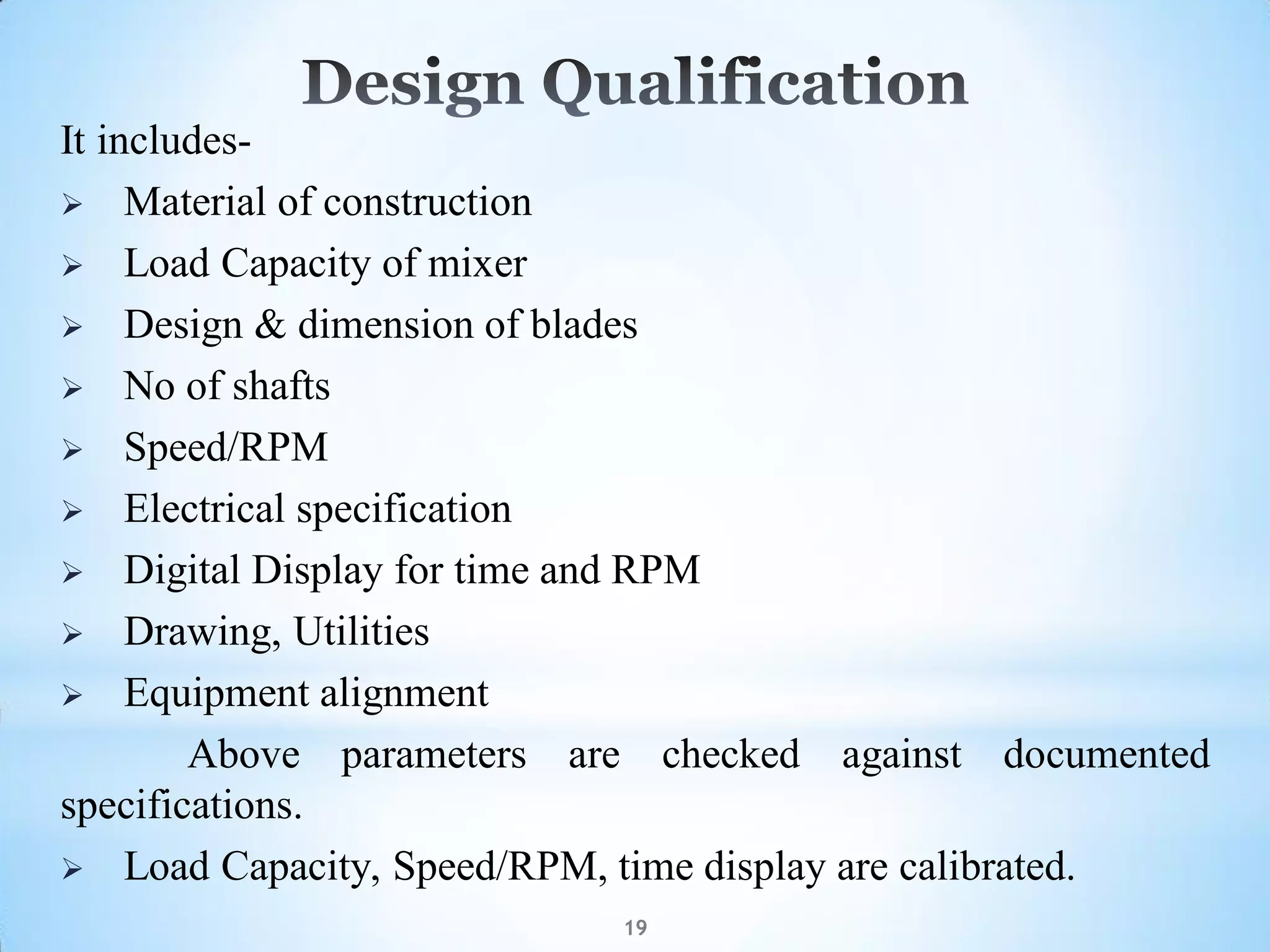
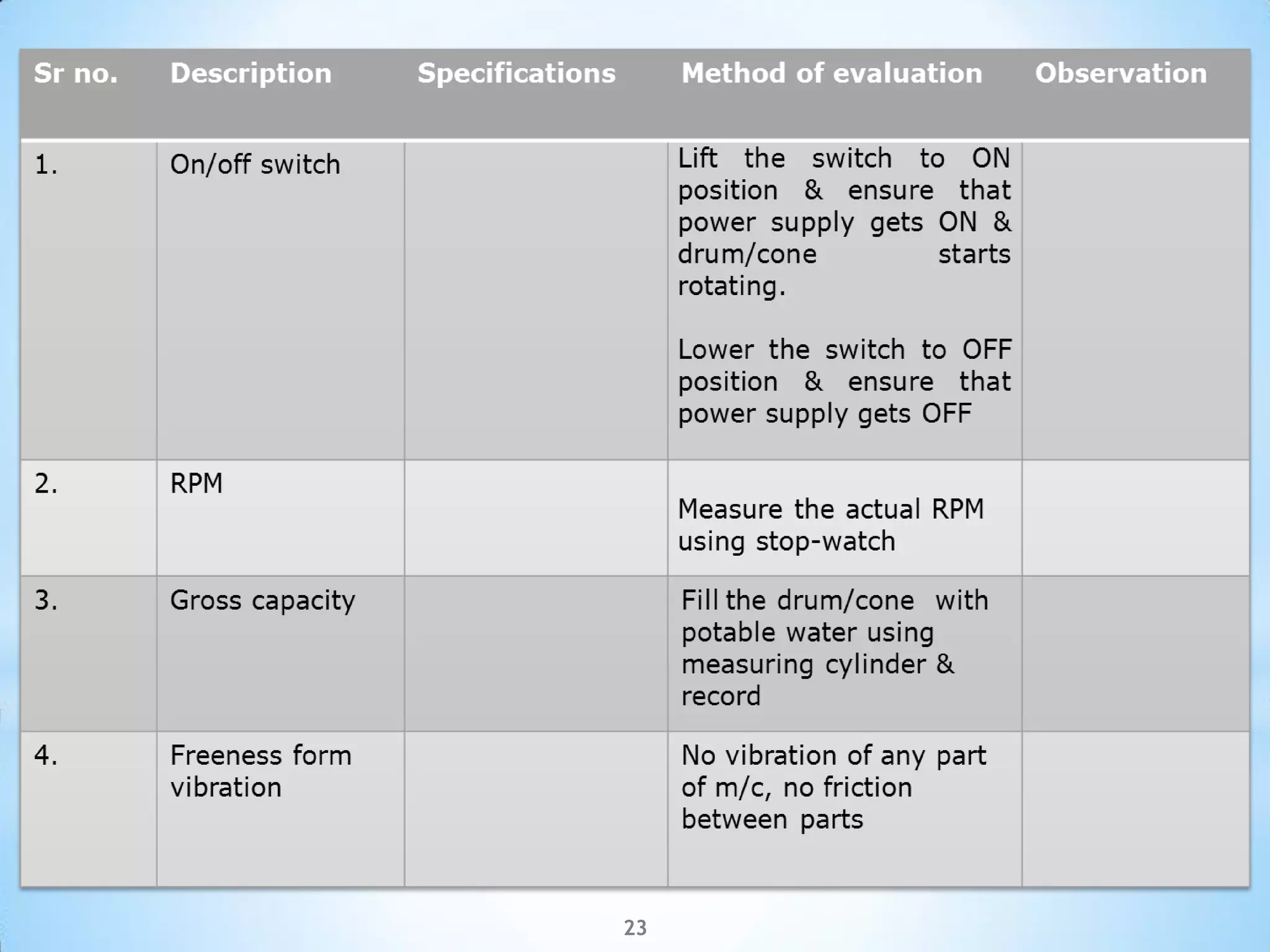
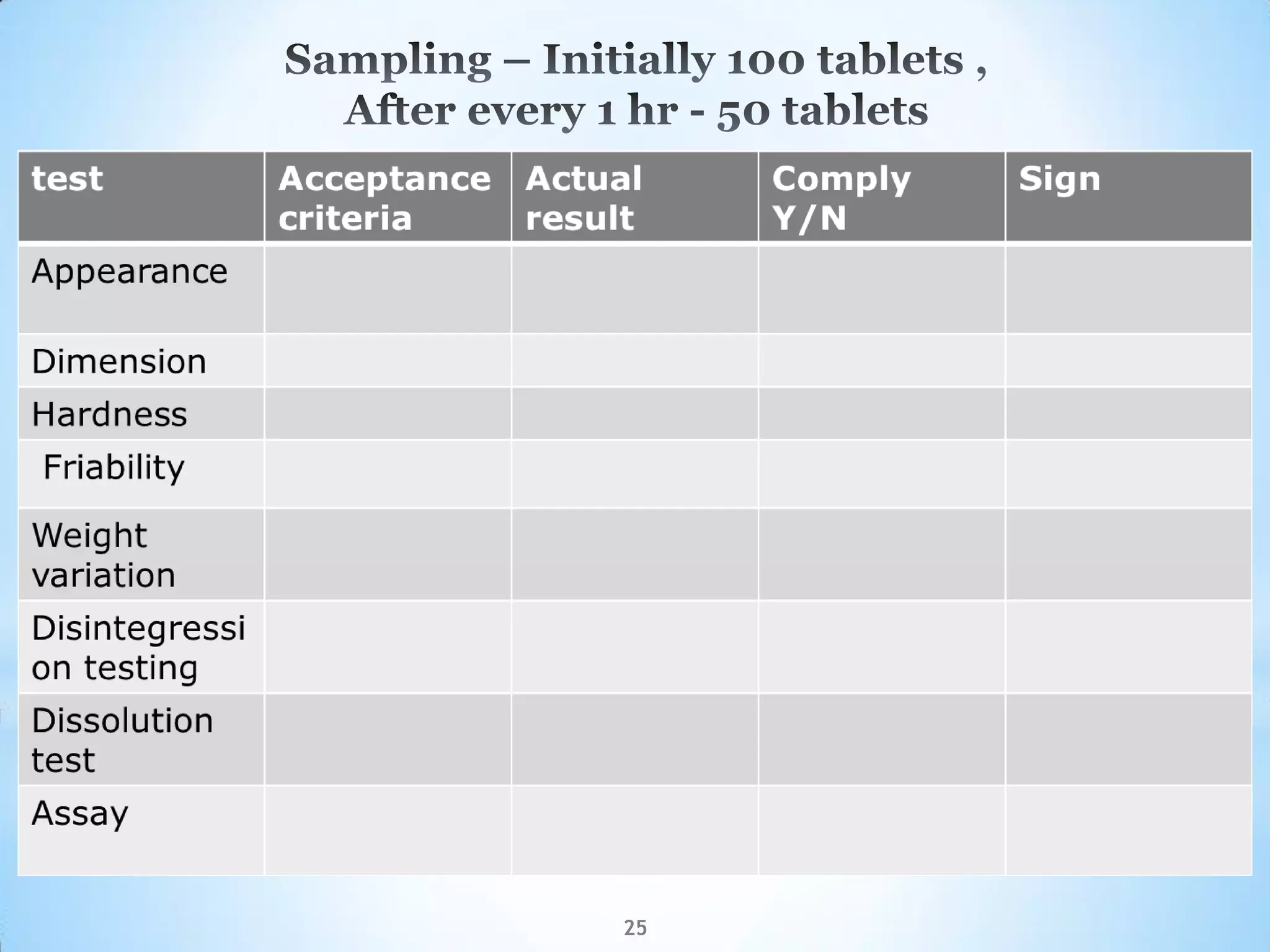
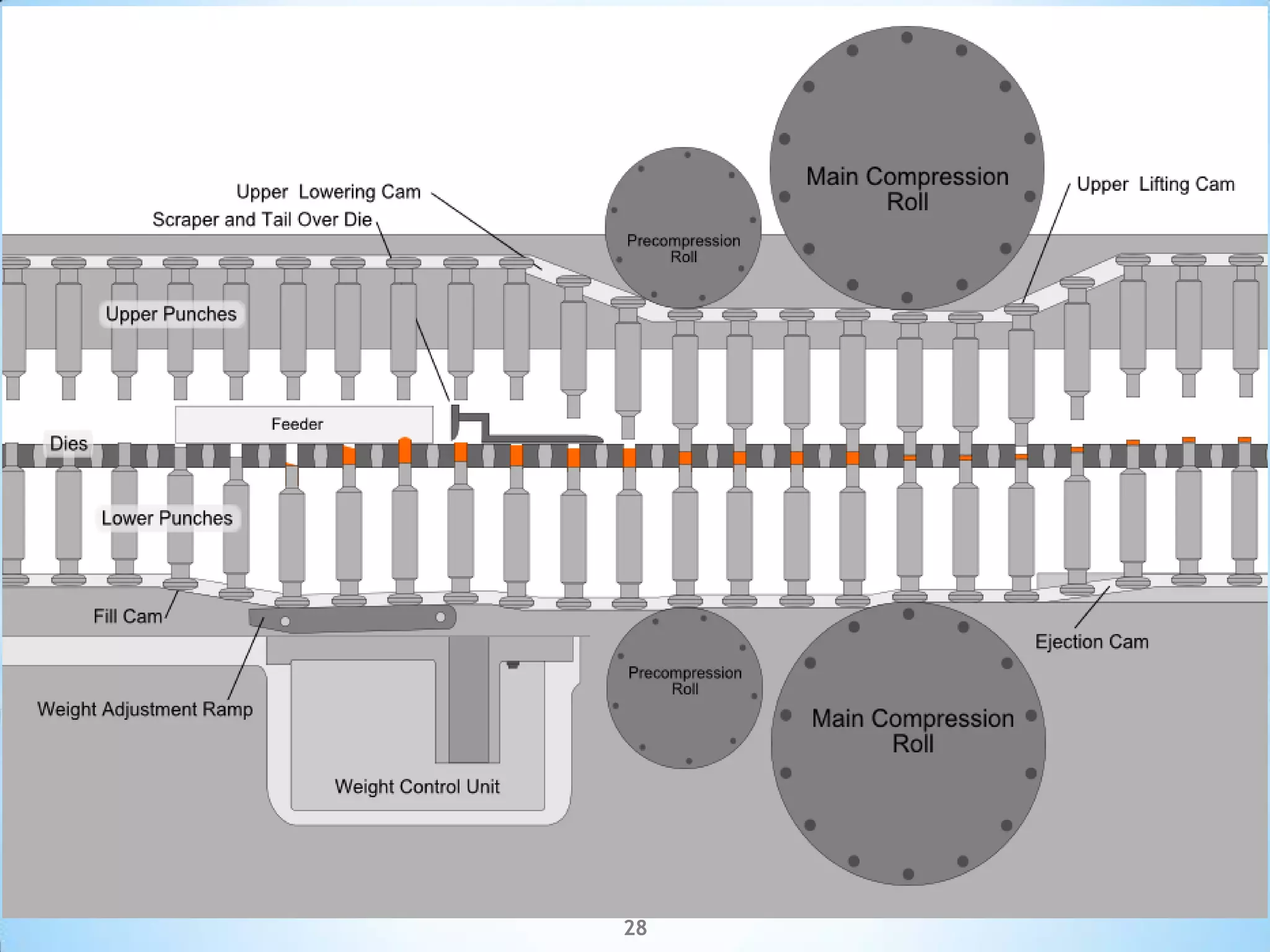
This document provides an overview of tablet compression machine validation. It begins with introducing the need and types of process validation. Then it discusses validation of tablet compression machines in particular, including the critical parameters to monitor and qualify like compression force, speed, and in-process testing. It outlines the validation protocols for installation, operational, and performance qualifications. The document emphasizes the importance of revalidating if any changes are made to equipment, location, parts, or normal schedules.