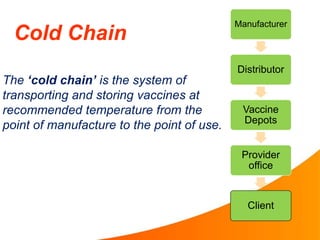
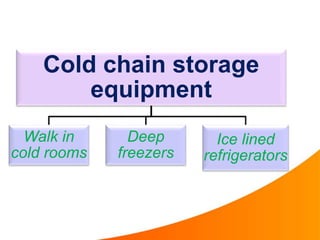
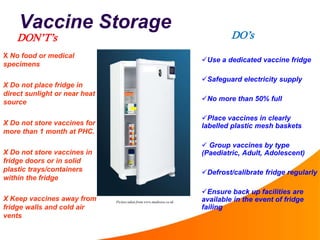
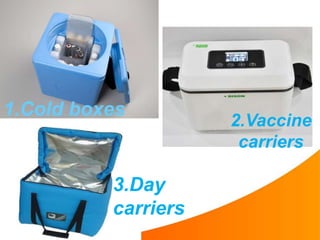
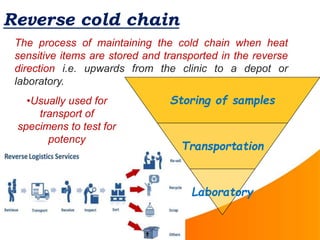
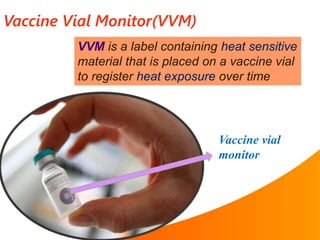
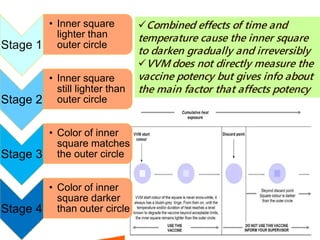
1. The cold chain refers to the system used to transport and store vaccines at temperatures between 2-8°C from manufacture to point of use to maintain potency. Proper cold chain storage using equipment like walk-in cold rooms, deep freezers, and ice-lined refrigerators is important for vaccine effectiveness and compliance with regulations.
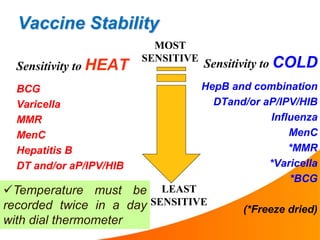
2. Vaccines are biological products that lose potency over time if not stored at proper temperatures. Maintaining the cold chain ensures vaccines provide maximum benefit and protects scarce health resources by preventing wastage from temperature excursions.
3. The immunization schedule approved by the Indian Academy of Pediatrics outlines the vaccines recommended to accelerate control of vaccine-preventable diseases and