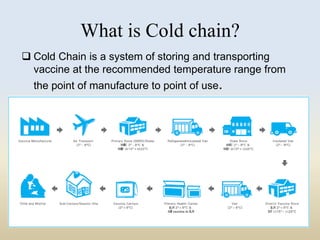
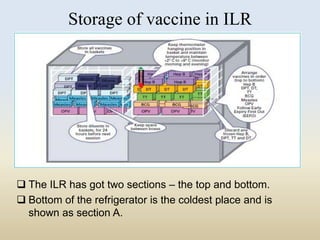
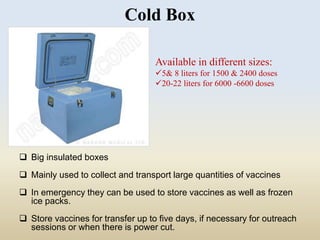
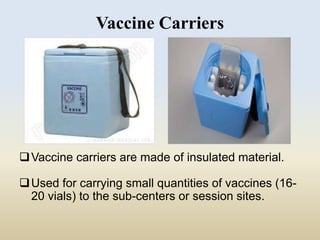
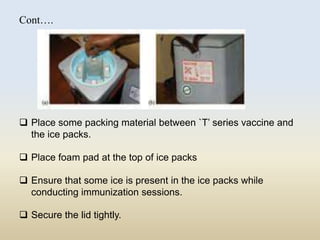
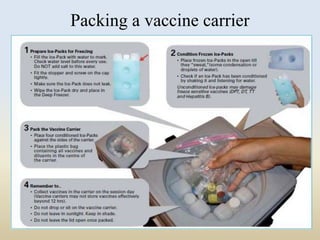
This document discusses the importance of maintaining a cold chain for vaccines in India's Universal Immunization Program. It explains that vaccines must be stored and transported within a specific temperature range to maintain potency. The cold chain involves a system using equipment like walk-in freezers, walk-in coolers, ice-lined refrigerators, deep freezers, cold boxes, and vaccine carriers to store and transport vaccines from manufacturers to immunization sites while keeping them within the proper temperature range. Proper cold chain maintenance is critical to ensure vaccine safety and efficacy.