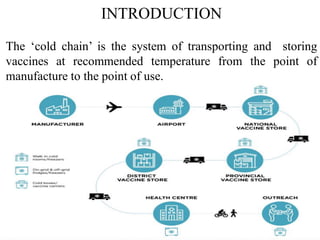
The document discusses India's cold chain system for transporting and storing vaccines. It defines the cold chain as maintaining vaccines at recommended temperatures from manufacture to point of use. Key components of the cold chain system include equipment like walk-in freezers and coolers, refrigerators, cold boxes, vaccine carriers and day carriers. Vaccines are stored at different levels from national stores down to local health centers. Proper temperature maintenance is important to preserve vaccine potency and effectiveness of immunization programs.