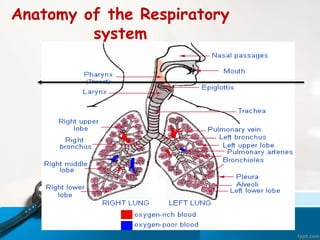
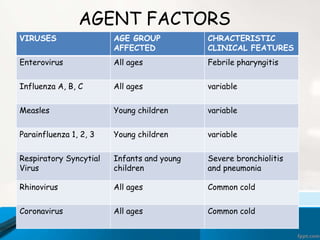
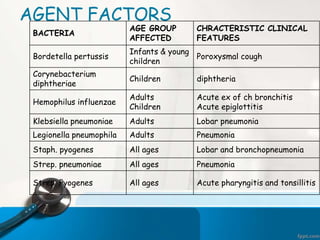
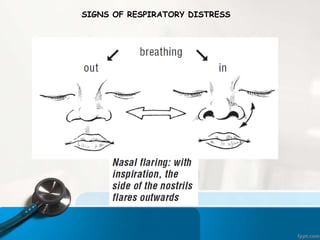
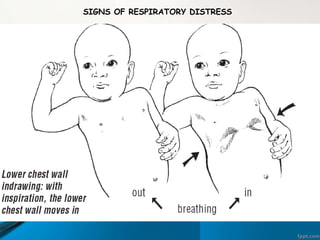
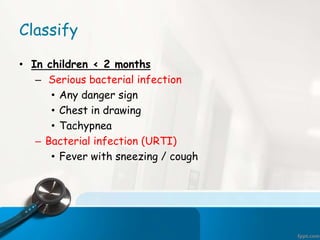
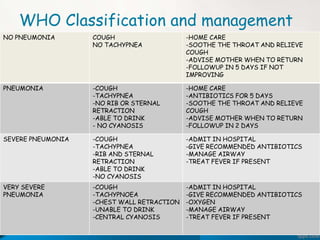
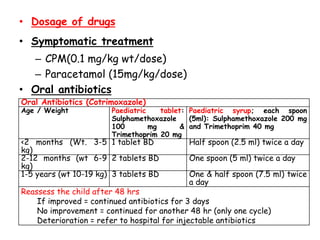
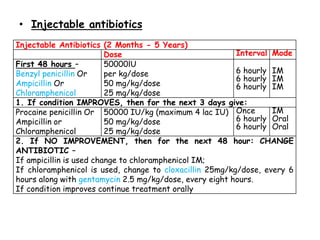
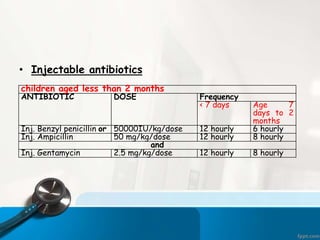
This document discusses acute respiratory infections (ARIs) which cause 20% of childhood deaths under 5 years old, with pneumonia responsible for 90% of ARI deaths. ARI mortality is highest in children who are HIV-infected, under 2 years old, malnourished, weaned early, from poorly educated families, or with difficult healthcare access. ARIs are classified as upper or lower respiratory tract infections. Treatment depends on classification and severity, ranging from symptomatic treatment at home to hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics. Prevention involves reducing risk factors through vaccination, nutrition, and treating infections early according to IMNCI guidelines.