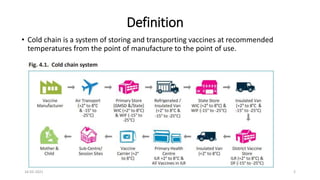
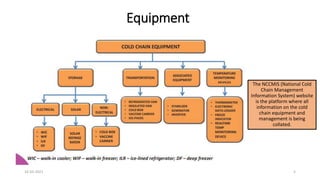
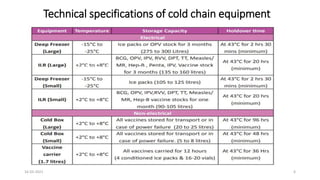
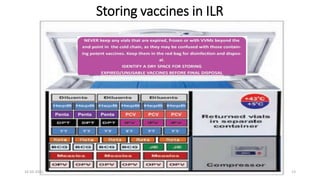
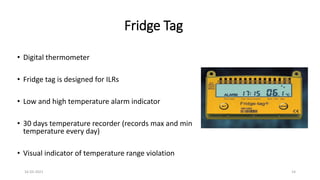
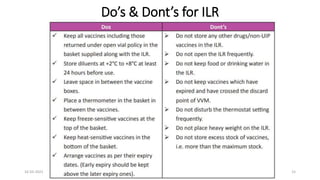
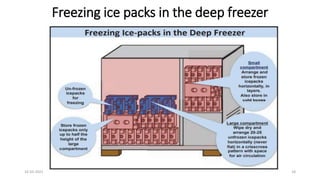
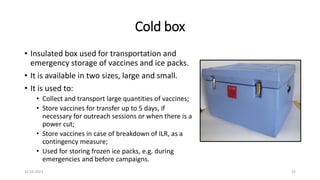
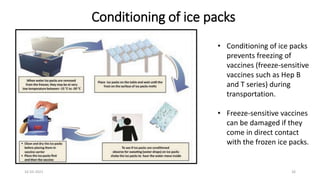
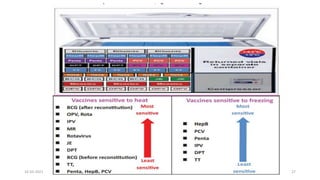
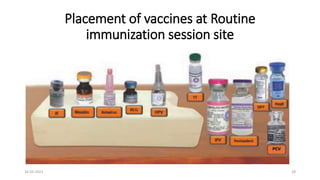
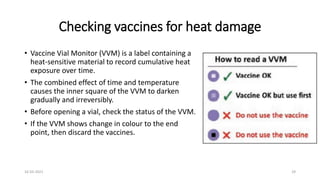
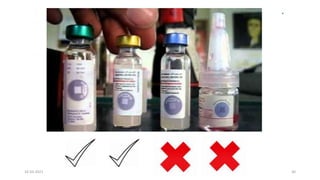
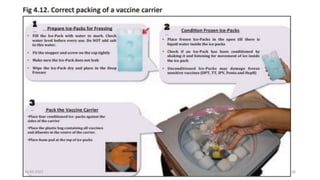
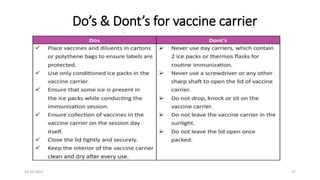
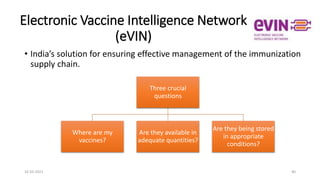
The document provides an overview of India's cold chain system for storing and transporting vaccines. It discusses the key elements which include personnel like vaccine handlers, equipment for storage and temperature monitoring, and procedures to ensure safe storage and transport. Specific equipment covered include ice-lined refrigerators, deep freezers, cold boxes, vaccine carriers, and the Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network system. Personnel roles, equipment specifications, storage guidelines, temperature monitoring, and transportation methods are described in detail. The cold chain aims to keep vaccines within the recommended temperature range from manufacture to point of use to maintain potency and safety.