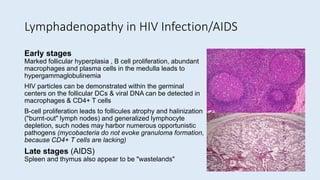
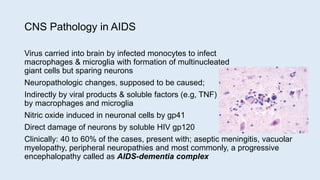
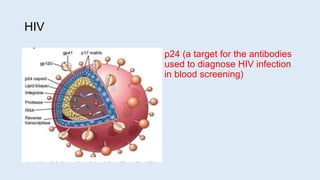
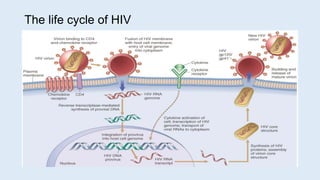
This document defines secondary immune deficiency diseases and discusses HIV/AIDS in particular. It covers the causes, pathogenesis, clinical presentations, diagnosis, and monitoring of secondary immune deficiencies, with a focus on HIV. Key points include: (1) Secondary immune deficiencies are acquired and common, caused by defects in antibodies, phagocytes, complement, or cell-mediated immunity; (2) HIV progresses through early, chronic, and crisis phases defined by declining CD4+ T-cell counts; (3) AIDS is diagnosed when CD4+ counts fall below 200 cells/μL and opportunistic infections or cancers develop.