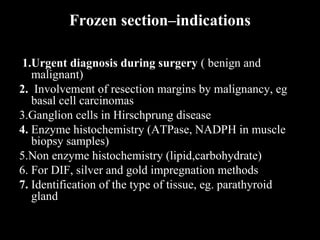
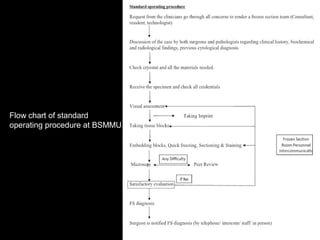
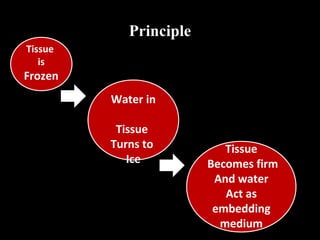
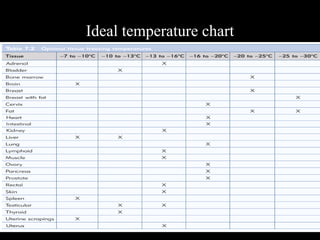
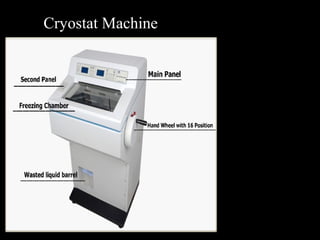
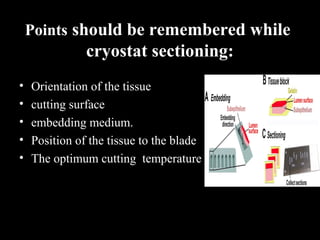
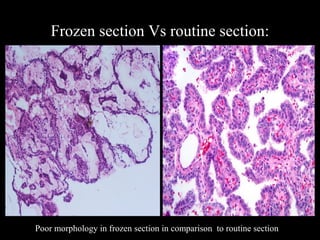
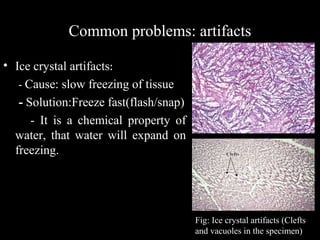
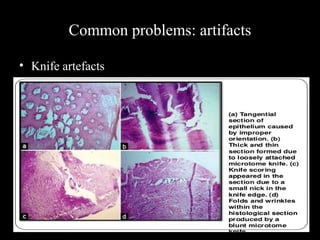
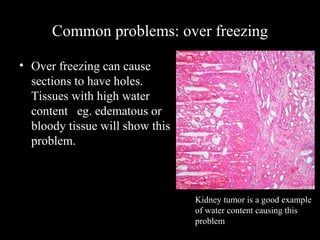
Frozen section is a pathology procedure that allows rapid microscopic examination of a specimen during surgery. Sir Louis B. Wilson pioneered the technique in 1905 at the Mayo Clinic to enable urgent intraoperative diagnosis. The procedure involves snap freezing tissue, sectioning it with a cryostat microtome, and staining for quick analysis. While fast, frozen sections can have artifacts from ice crystals and knife marks. Pathologists must communicate closely with surgeons to ensure the appropriate use of frozen sections for urgent diagnostic needs during operations.