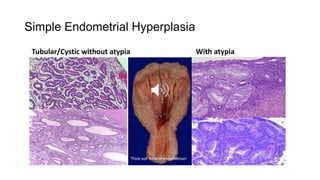
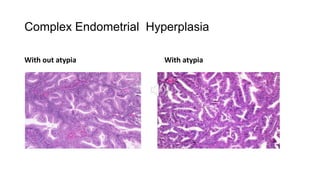
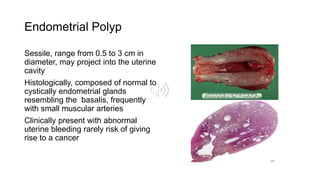
1) Uterine tumors include endometrial polyps, hyperplasia, and carcinomas. Endometrial hyperplasia is classified based on complexity and presence of atypia, with complex hyperplasia with atypia carrying the highest risk of developing into carcinoma.
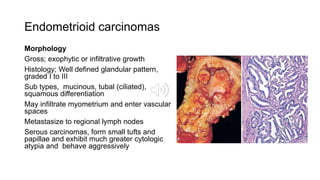
2) Endometrial carcinomas are classified into Type I (endometrioid) and Type II (non-endometrioid). Type I carcinomas are associated with estrogen excess and hyperplasia, while Type II carcinomas arise in an atrophic endometrium and have a poorer prognosis.
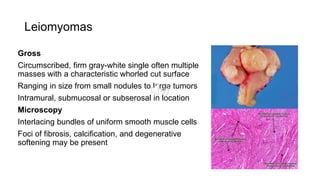
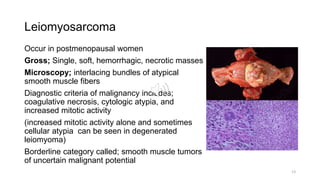
3) Leiomyomas are the most common benign uterine tumor, while leiomyosarcom