The document provides an overview of Spanish grammar concepts including:
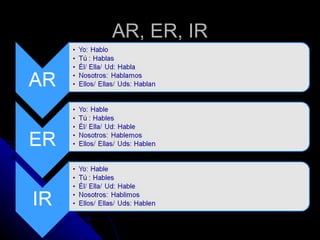
1) Present tense verbs like ar, er, ir verbs and stem changers.
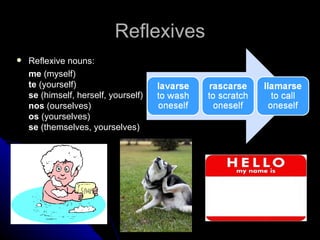
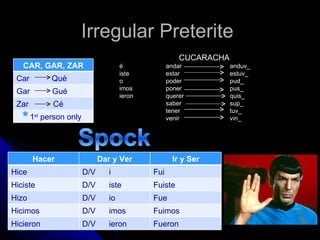
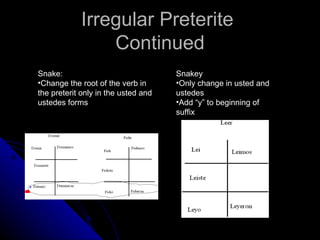
2) Other verb types like irregular verbs, saber vs conocer, reflexives, and "se" impersonal verbs.
3) Conjugations and uses of verbs like gustar, cer/cir and ger/gir verbs, and hacer expressions.
4) Uses of verb tenses including the imperfect, preterite, and future tenses.