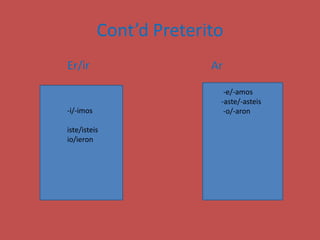
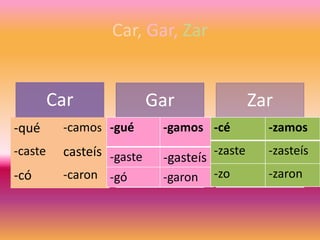
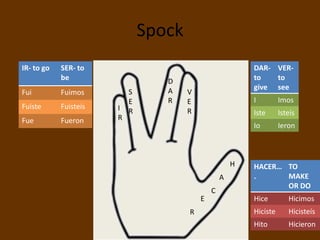
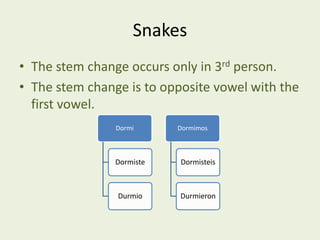
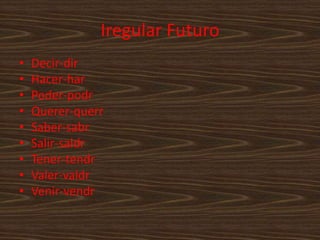
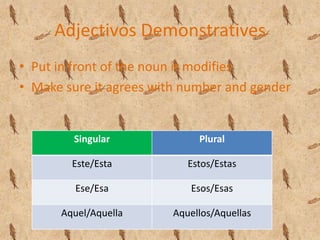
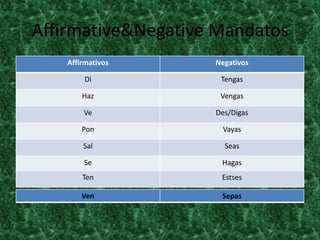
This document contains a table of contents that lists various Spanish grammar topics including verbs like ser and estar, verbs like gustar, hacer expressions, the preterite and trigger words, irregular preterite verbs, affirmative and negative commands, DOPs, IOPs, the future tense, adjectives, formal commands, modal verbs, reflexive verbs, and saber vs conocer.