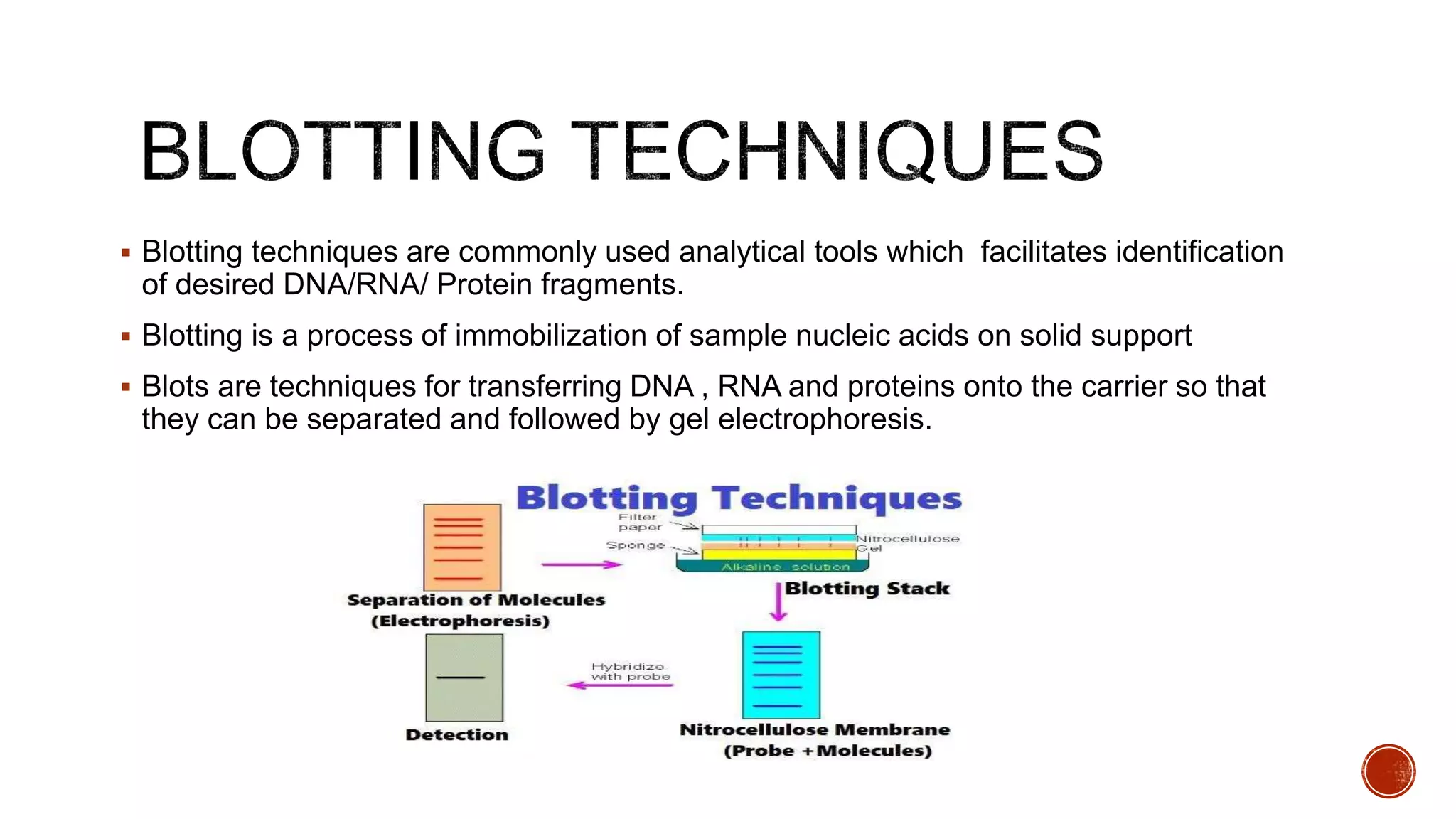
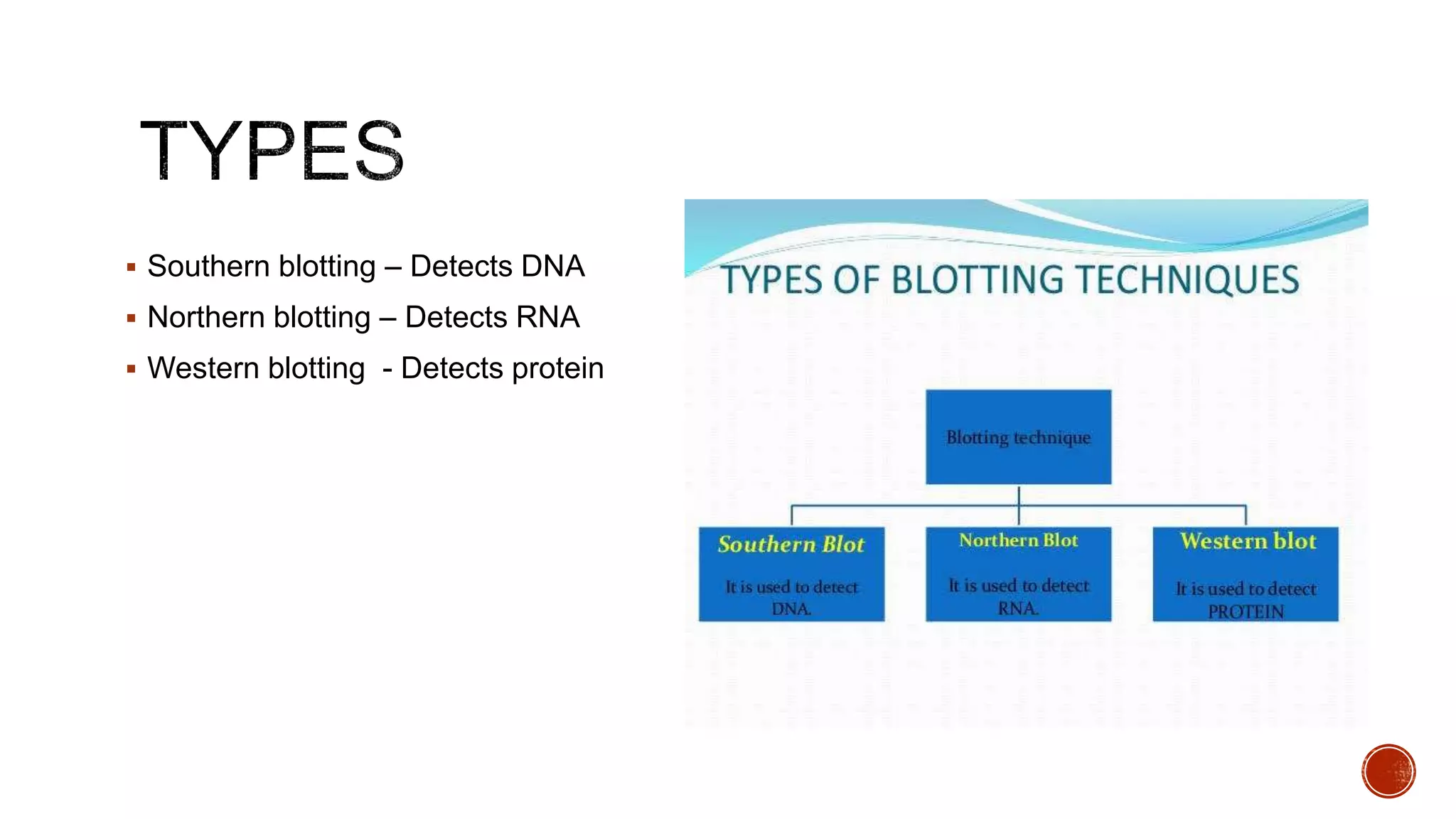
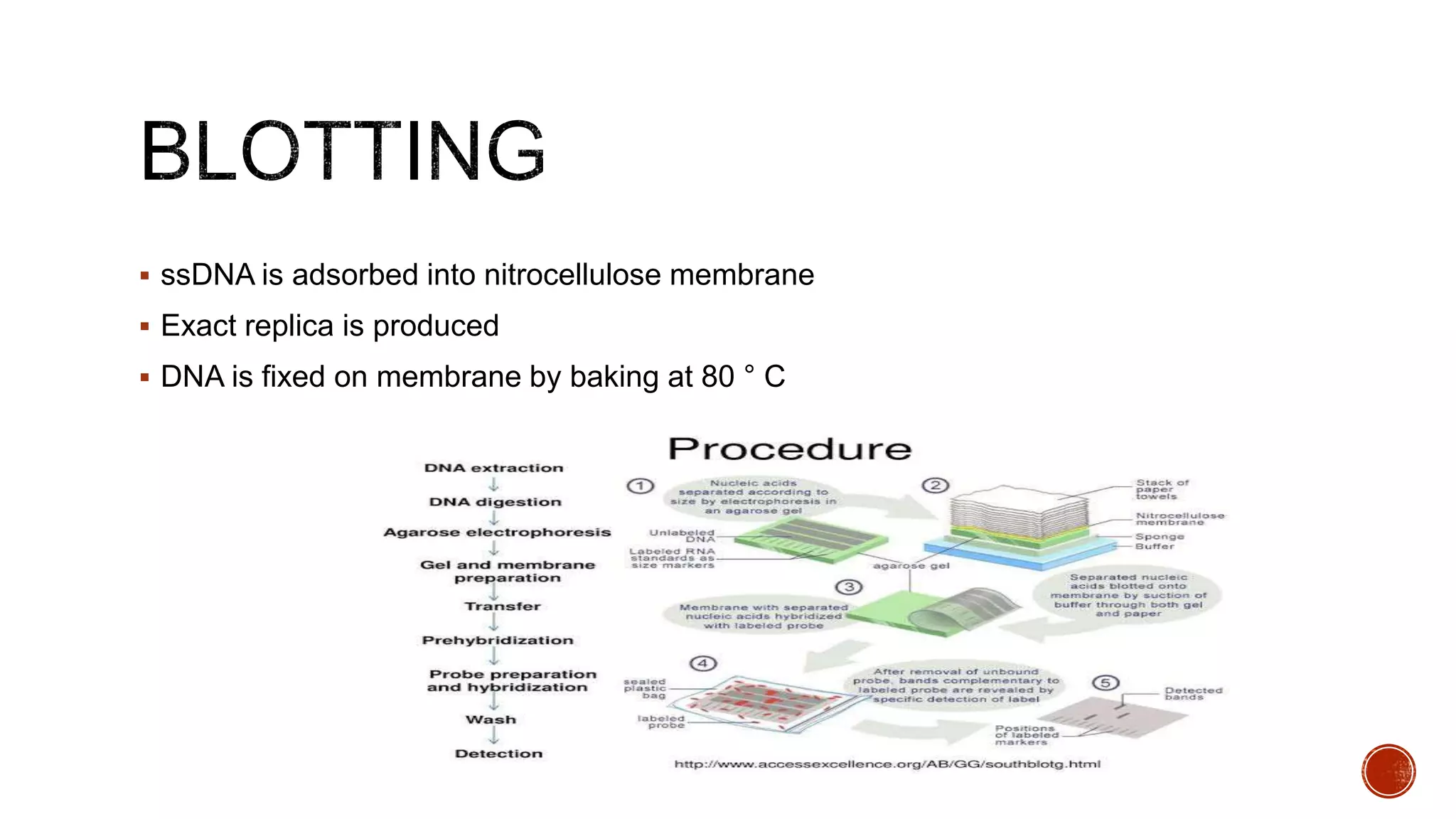
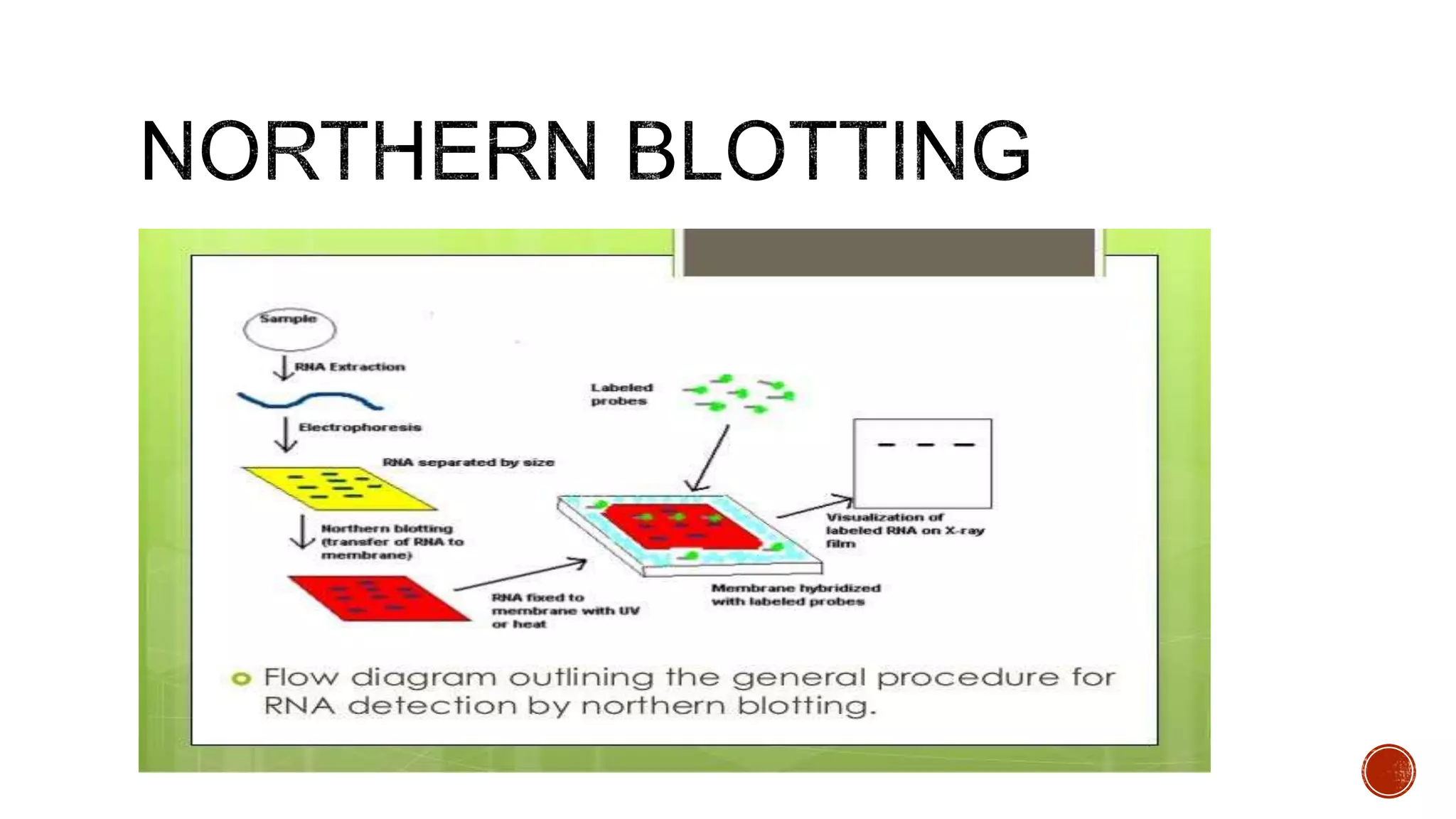
The document discusses various blotting techniques used to detect DNA, RNA, and proteins. It describes Southern blotting for detecting DNA, Northern blotting for detecting RNA, and Western blotting for detecting proteins. It provides details on the steps involved in each technique, including separating biomolecules by electrophoresis, transferring them to a membrane, and using probes for detection through hybridization or antibody binding.