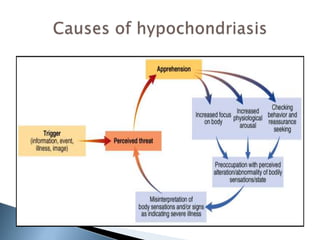
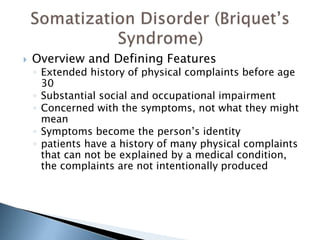
This document discusses somatoform and dissociative disorders as defined in the DSM-IV. Somatoform disorders involve physical symptoms that cannot be fully explained by medical factors and are thought to be linked to psychological issues. Dissociative disorders involve disruptions or breakdowns in consciousness, memory, identity or perception. The document provides overviews of specific disorders including their defining features, causes, prevalence and treatment approaches. These include conversion disorder, pain disorder, hypochondriasis and dissociative disorders like dissociative identity disorder.