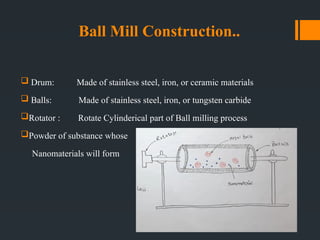
The document discusses the production of nanomaterials through the ball milling method, covering its history, construction, parameters, and applications. Ball milling, a top-down approach, efficiently synthesizes metallic and ceramic nanomaterials, although it has disadvantages such as energy consumption and limited control over particle size. The conclusion emphasizes the cost-effectiveness and potential for future developments in this area.