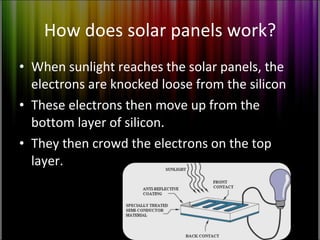
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells. There are different types of solar panels including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and amorphous silicon panels. Solar panels are made of layers of semiconductor materials that produce a flow of electrons when struck by sunlight. Proper positioning of solar panels maximizes sunlight exposure. Benefits of solar panels include being pollution-free, renewable, and requiring little maintenance.