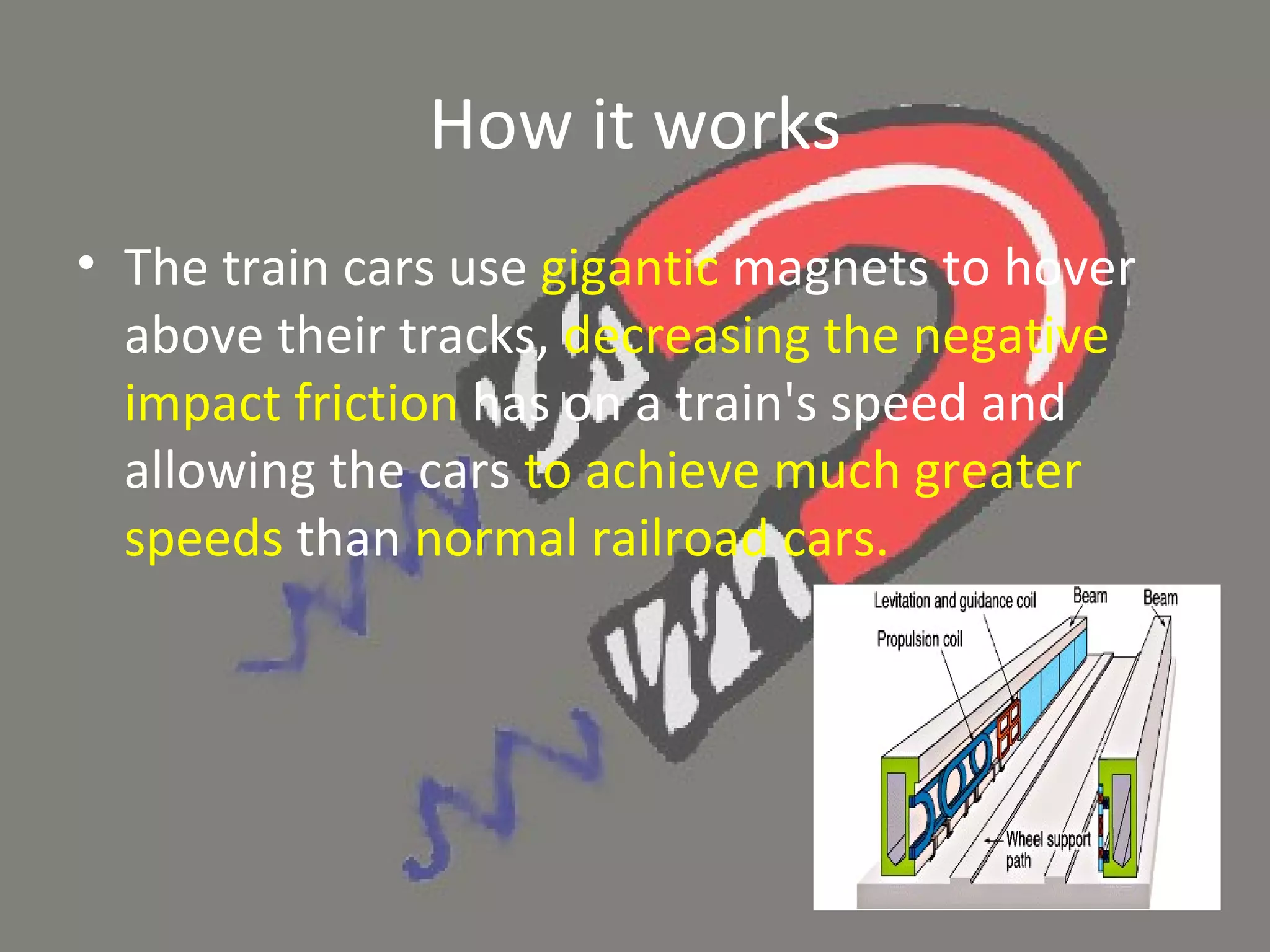
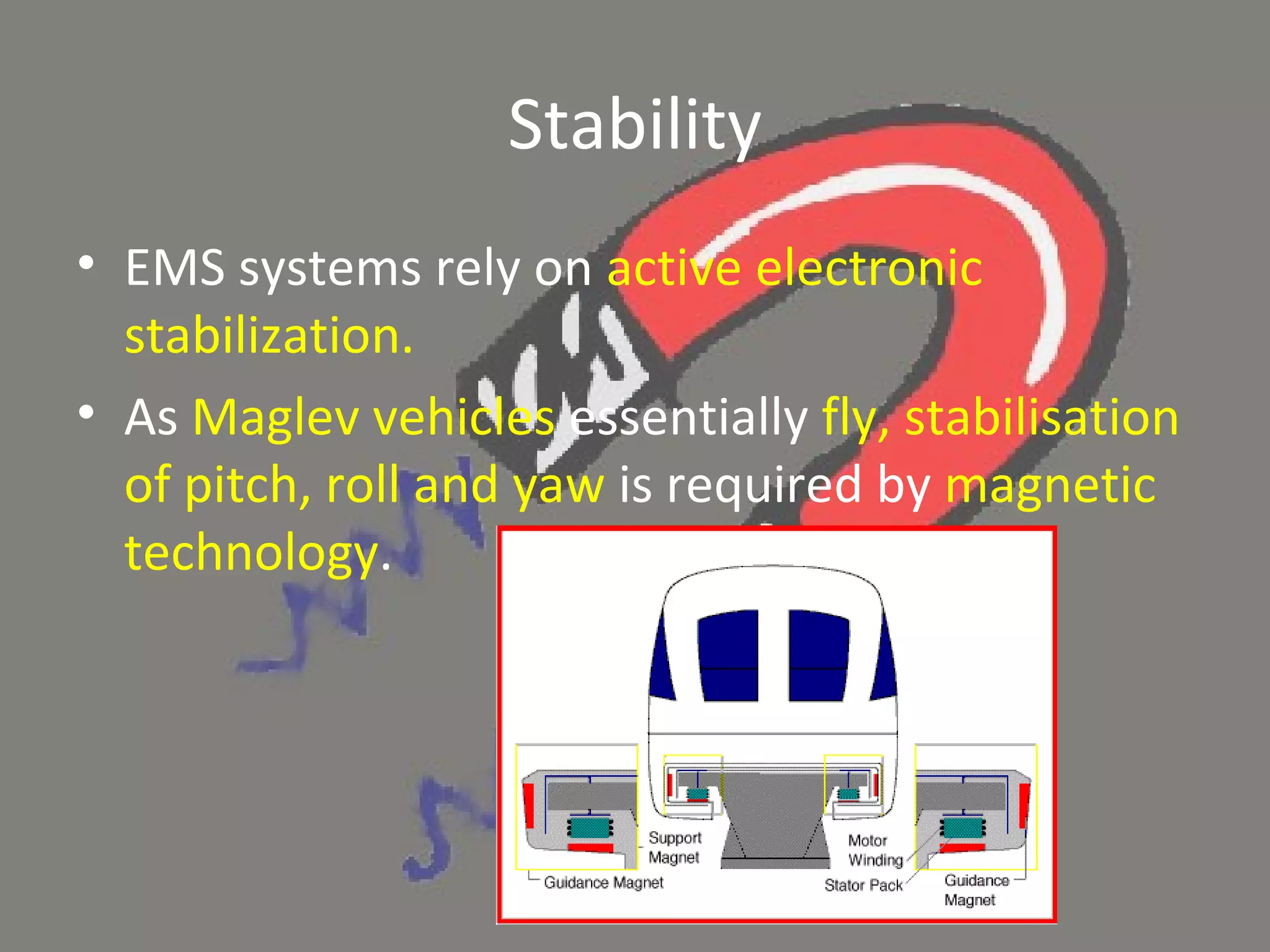
Maglev trains use magnetic levitation powered by electromagnets to float above guideways without touching and to propel trains at very high speeds up to 250 mph. There are two main types of maglev technology - electromagnetic suspension which uses electromagnets to levitate the train above the track, and electrodynamic suspension which uses both electromagnets on the train and induced magnetic fields in the track for levitation and propulsion. While maglev trains offer advantages like very high speeds and less energy usage than wheeled trains, they also present challenges including very high infrastructure costs to build new exclusive guideways.