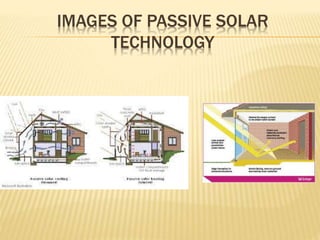
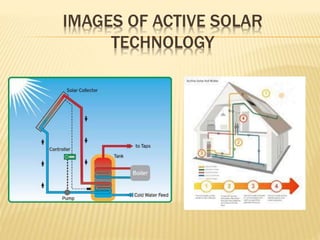
This document provides an overview of solar energy sources and technology. It defines solar energy as energy obtained from radiation emitted by the sun. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells made of silicon semiconductors. Passive solar uses sunlight without equipment to warm buildings, while active solar uses collectors and fluid/air transfer to store solar heat. Advantages include reducing global warming, energy reliability and independence, while disadvantages include high initial costs and needing batteries for nighttime use.