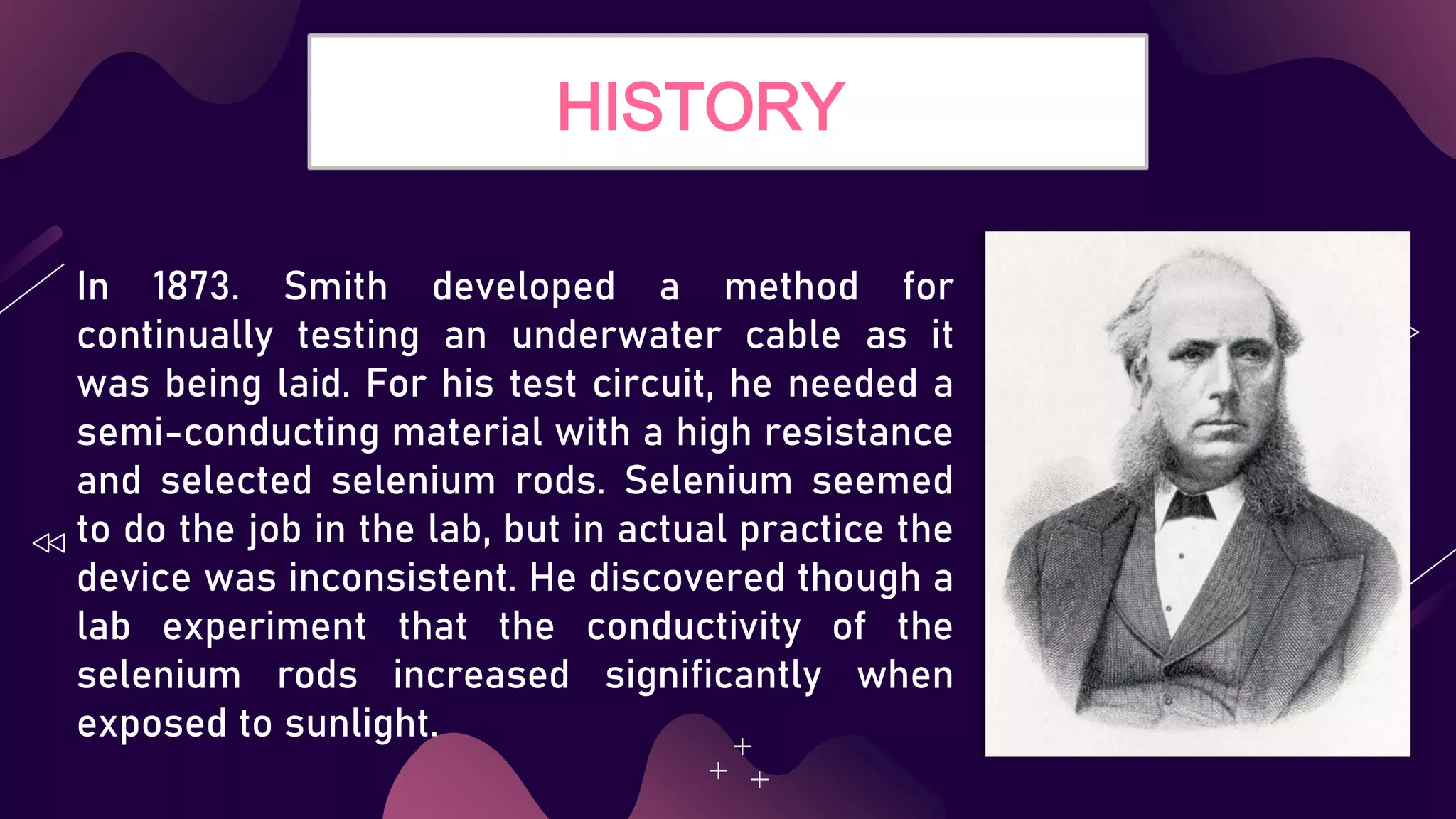
This document provides a history of solar panels from 1839 when the photovoltaic effect was first observed up until modern applications. It discusses key inventors such as Becquerel, Smith, Fritts, and Ohl who made early breakthroughs. The principles of solar panels using silicon cells are explained along with the major types of panels. Merits include being environmentally friendly and having low maintenance, while demerits include limited nighttime use and high upfront costs. Future applications include large solar farms and use in space.







![HISTORY
In 1881, the American inventor
Charles Fritts created the first
commercial solar panel, which
was reported by Fritts as
"continuous, constant and of
considerable force not only by
exposure to sunlight but also to
dim, diffused daylight."[4] However,
these solar panels were very
inefficient](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/englishpo-230118141634-7437ce20/75/english-po-pdf-9-2048.jpg)

![HISTORY
In 1939, Russell Ohl created the solar cell design that is used in many
modern solar panels. He patented his design in 1941.[5] In 1954, this
design was first used by Bell Labs to create the first commercially
viable silicon solar cell. Russell S. Ohl was an American engineer
who was a notable semiconductor researcher. In 1839, he discovered
the P-N junction (having a positive side and a negative side inside a
single crystal semiconductor). He studied the conductivity and
properties of various types of crystals. His work with
semiconductors and P-N junction led to things such as the
transistor, LEDs and laser diodes, and in 1841, his creation of the first
silicon solar cell, a design still used in today’s modern solar
photovoltaic (PV) panels!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/englishpo-230118141634-7437ce20/75/english-po-pdf-11-2048.jpg)






















