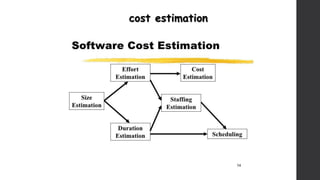
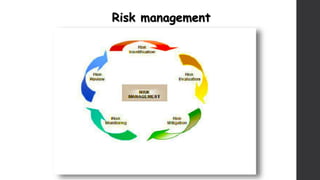
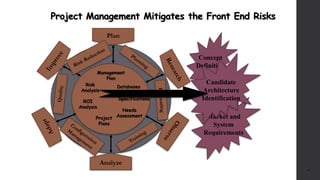
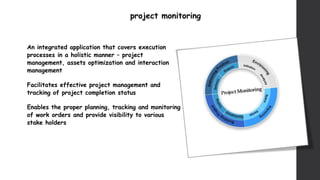
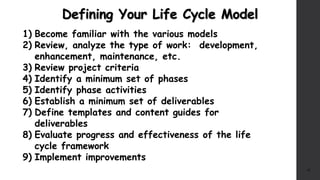
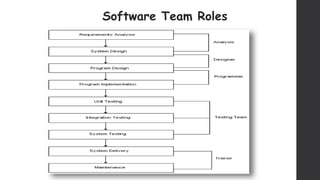
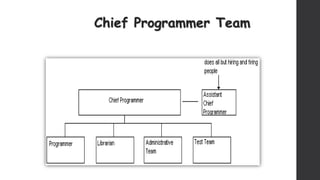
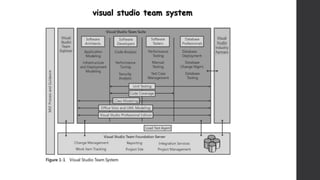
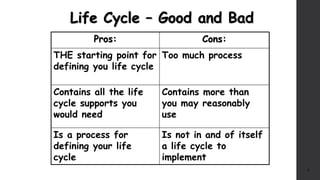
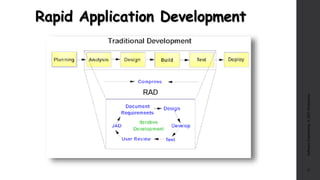
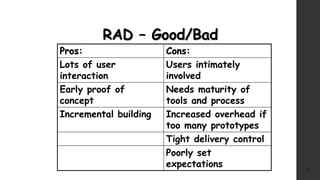
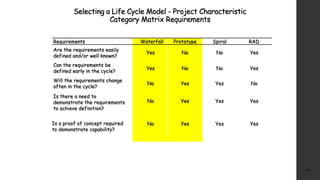
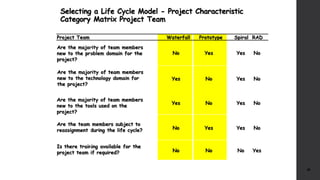
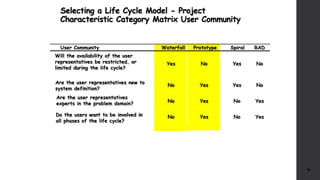
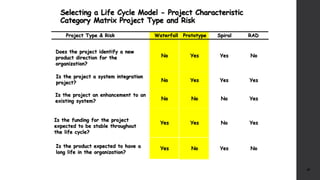
The document discusses software project management. It defines what a project and project management are, and describes the key characteristics of a software project. It outlines several software development lifecycles and methodologies including waterfall, prototype, spiral, agile, Scrum, extreme programming (XP), and rapid application development (RAD). It also discusses software project roles, risk management, project monitoring, defining a lifecycle model, software team organization structures, communication and coordination practices, and factors to consider when selecting a lifecycle model.