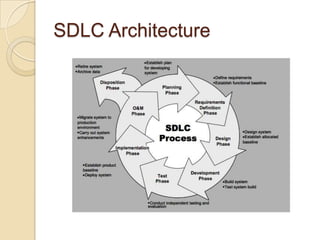
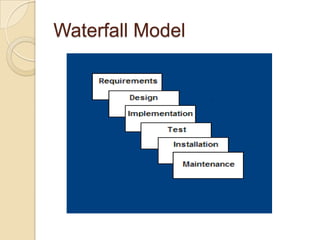
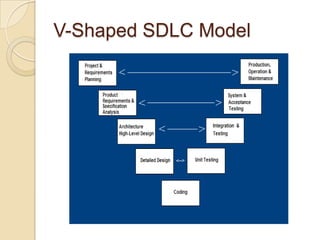
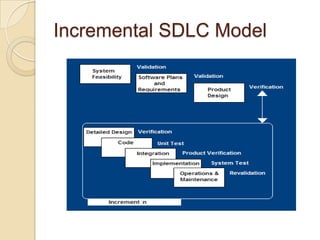
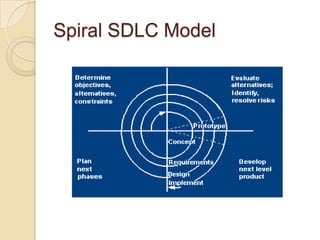
The document discusses the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), which provides an overall framework for managing the software development process. There are two main approaches to the SDLC - predictive and adaptive. All projects use some variation of the SDLC, which typically includes phases like requirements definition, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Common SDLC models discussed include waterfall, incremental, spiral, and agile methods. The strengths and weaknesses of different models are compared.