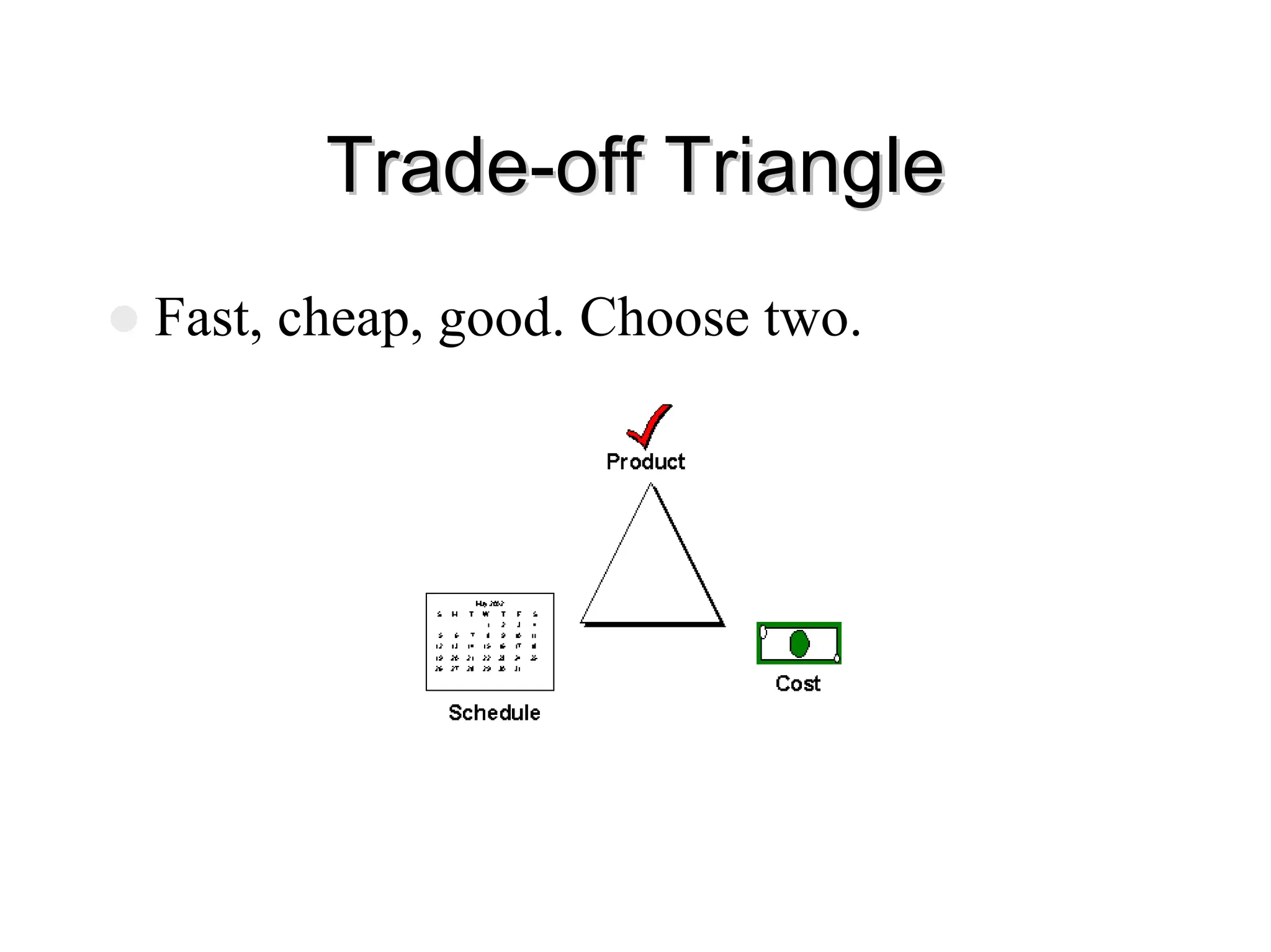
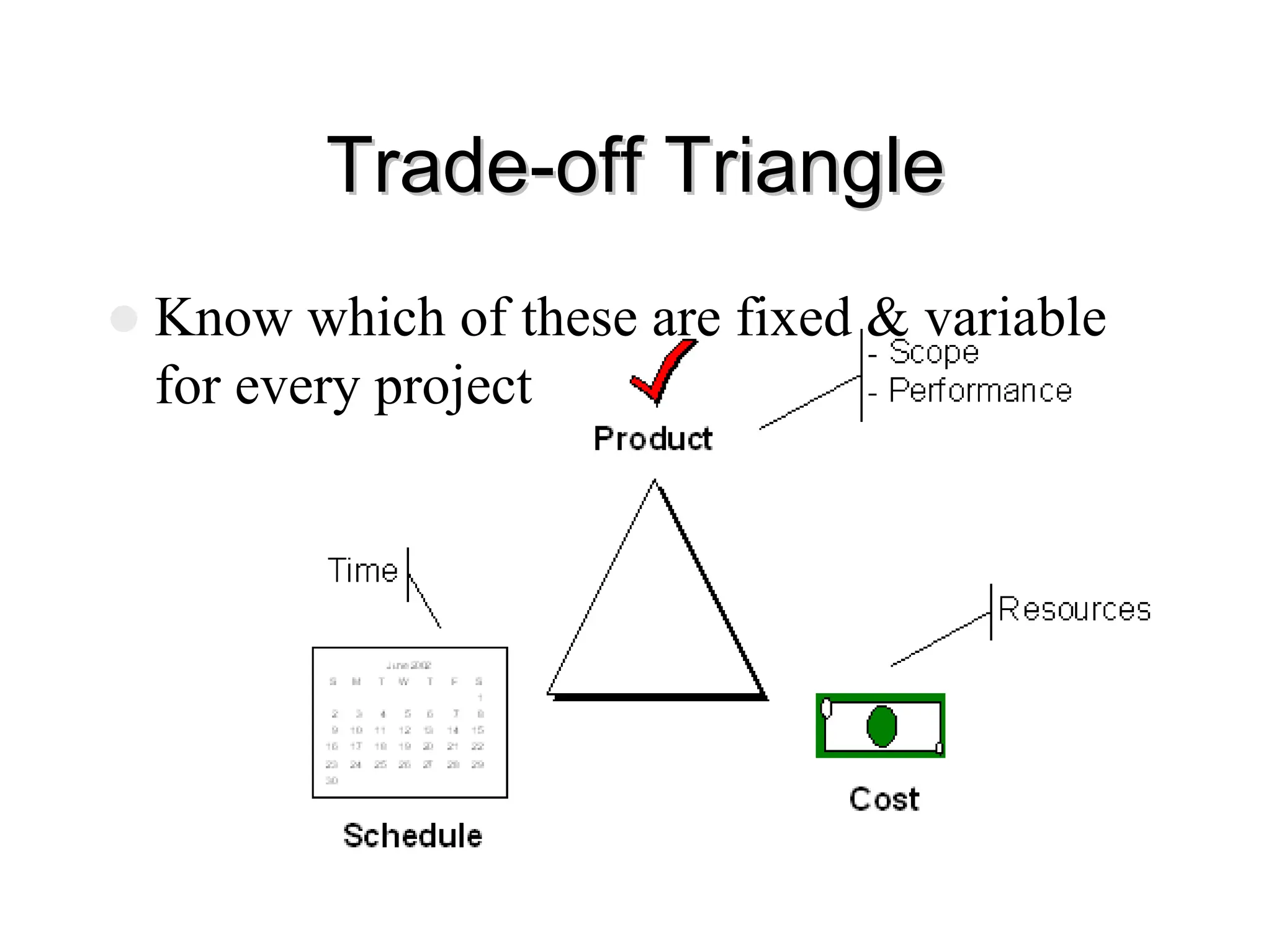
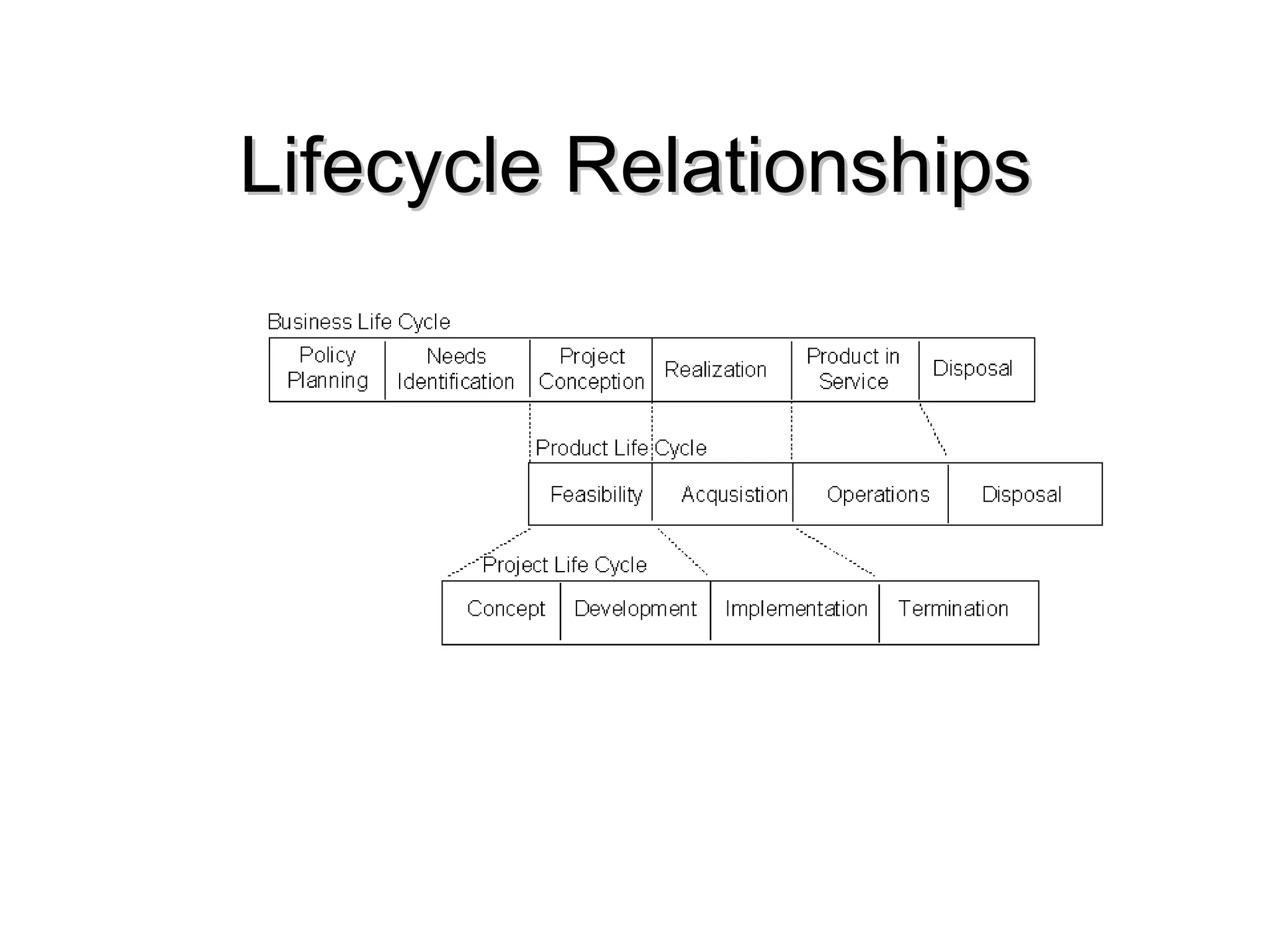
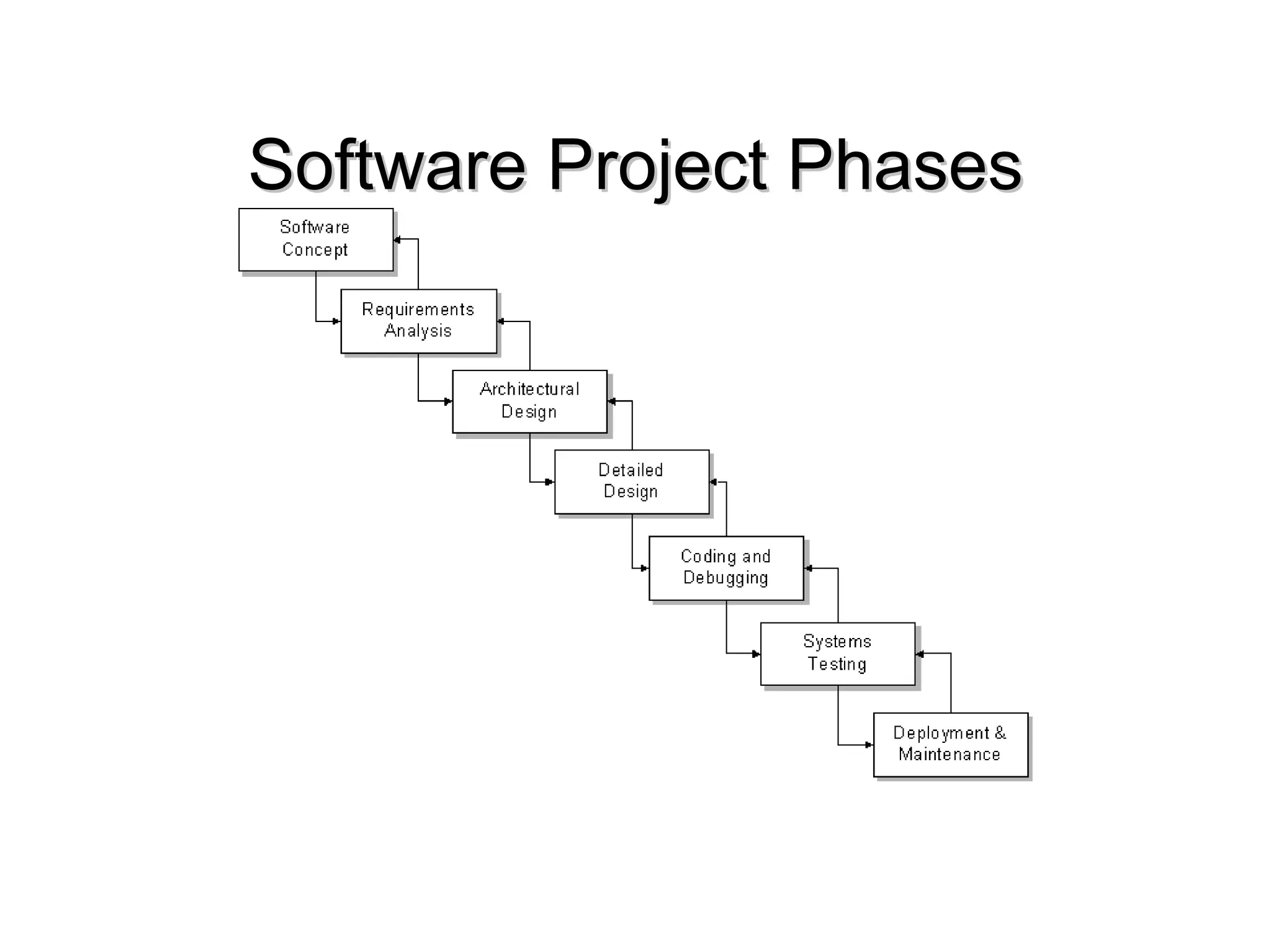
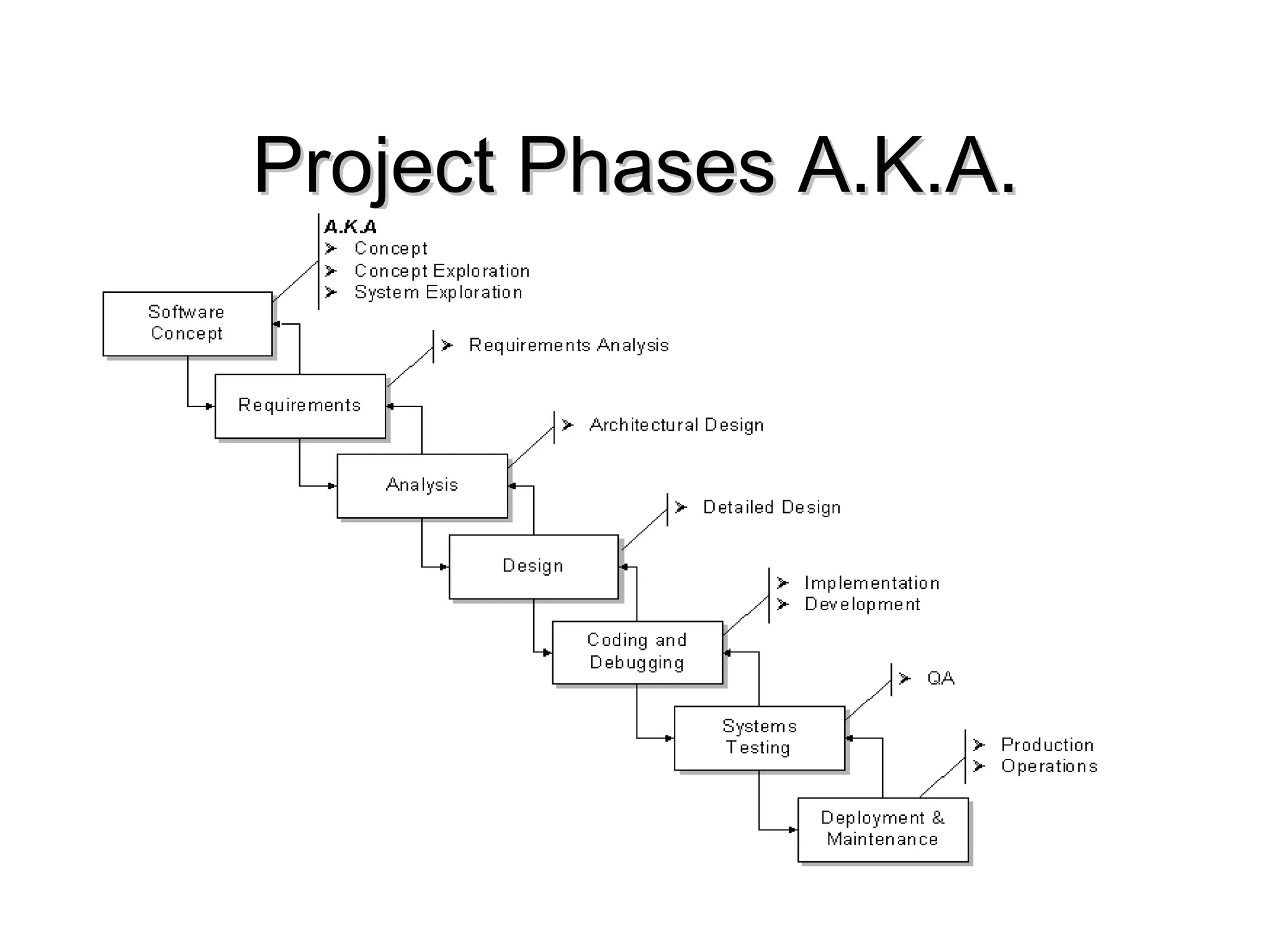
The document outlines a software project management course, covering objectives, course content, evaluation methods, and necessary resources. It discusses project management principles, tools, skills, phases, and common errors, emphasizing the importance of effective communication and planning. It also touches on various software metrics and methodologies for quality assurance and risk management.