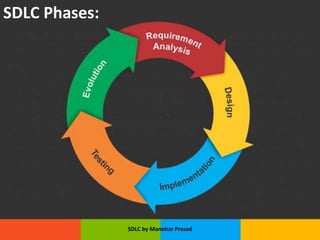
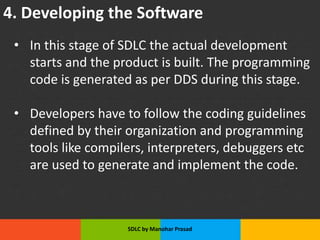
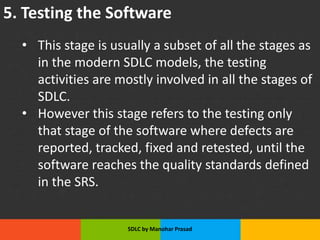
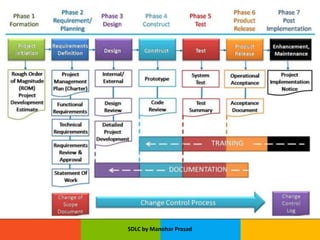
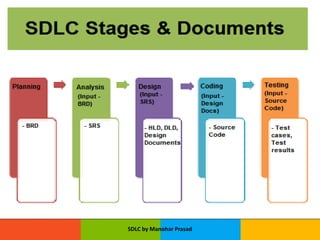
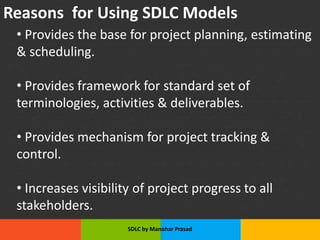
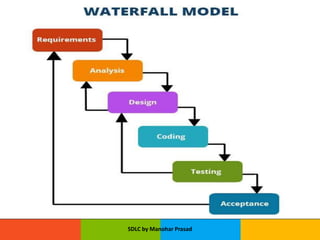
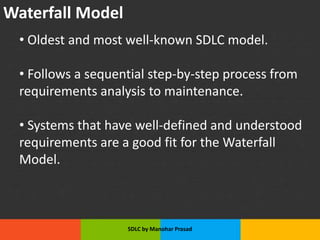
The document presents an overview of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) introduced by Manohar Prasad, outlining its phases, key models, and methodologies such as the Waterfall and Agile models. It emphasizes the importance of planning, requirements analysis, and adherence to standards like ISO/IEC 12207 for developing high-quality software. The conclusion highlights project management's role in navigating risks and ensuring successful software delivery.