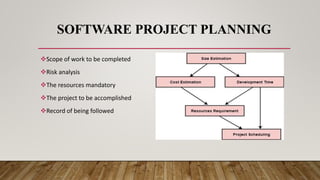
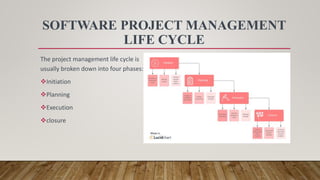
This document discusses software project management. It defines a project and software project management. Software project management involves planning, implementing, monitoring, and controlling software projects. It is important for managing resources, meeting deadlines, and maintaining quality. Key aspects of software project management include planning, leadership, execution, budgeting, and maintenance. The project manager is responsible for tasks like planning, leading the team, monitoring progress, managing risks, and ensuring proper testing. Software project management uses a standard life cycle of initiation, planning, execution, and closure phases.