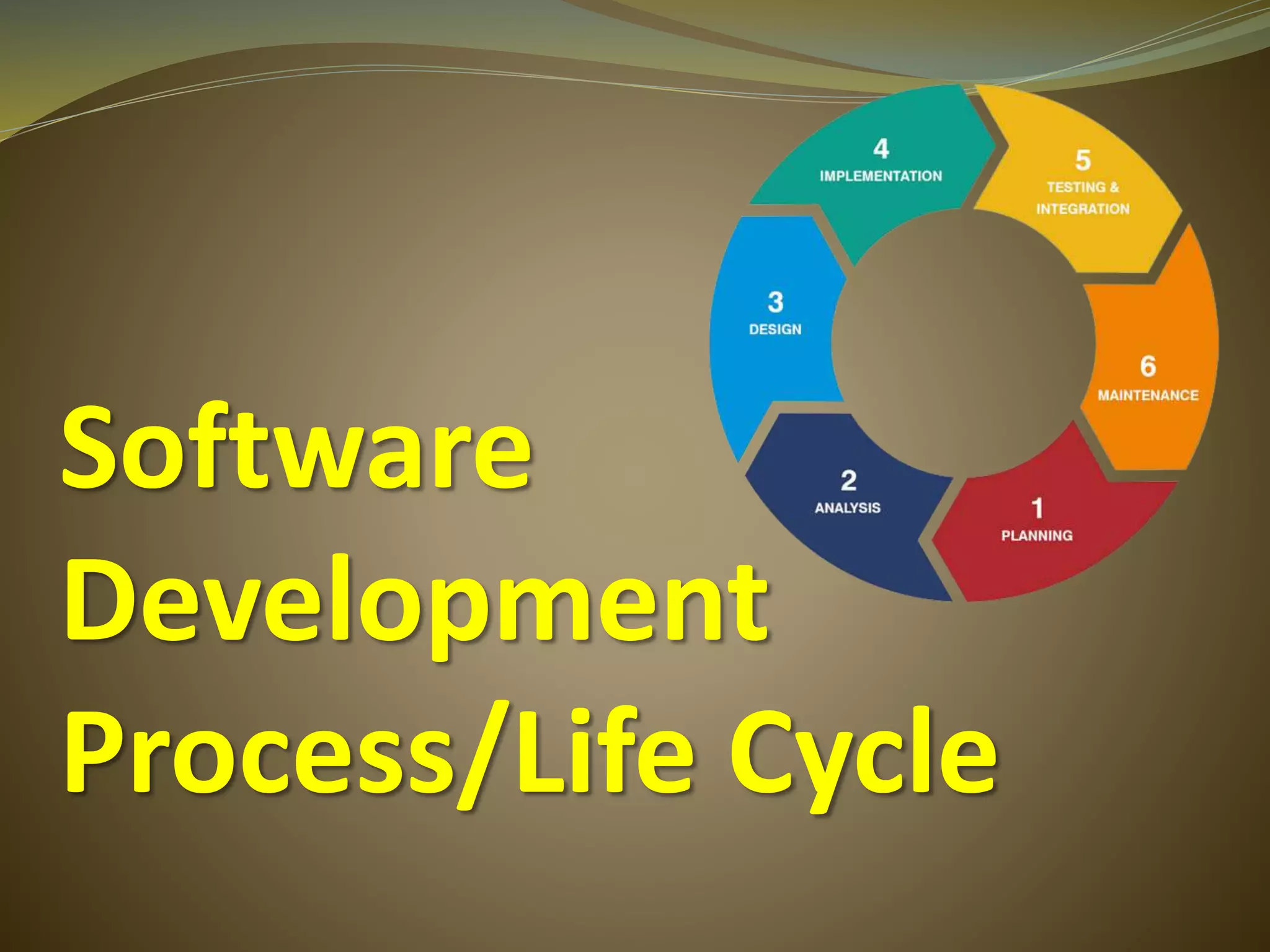
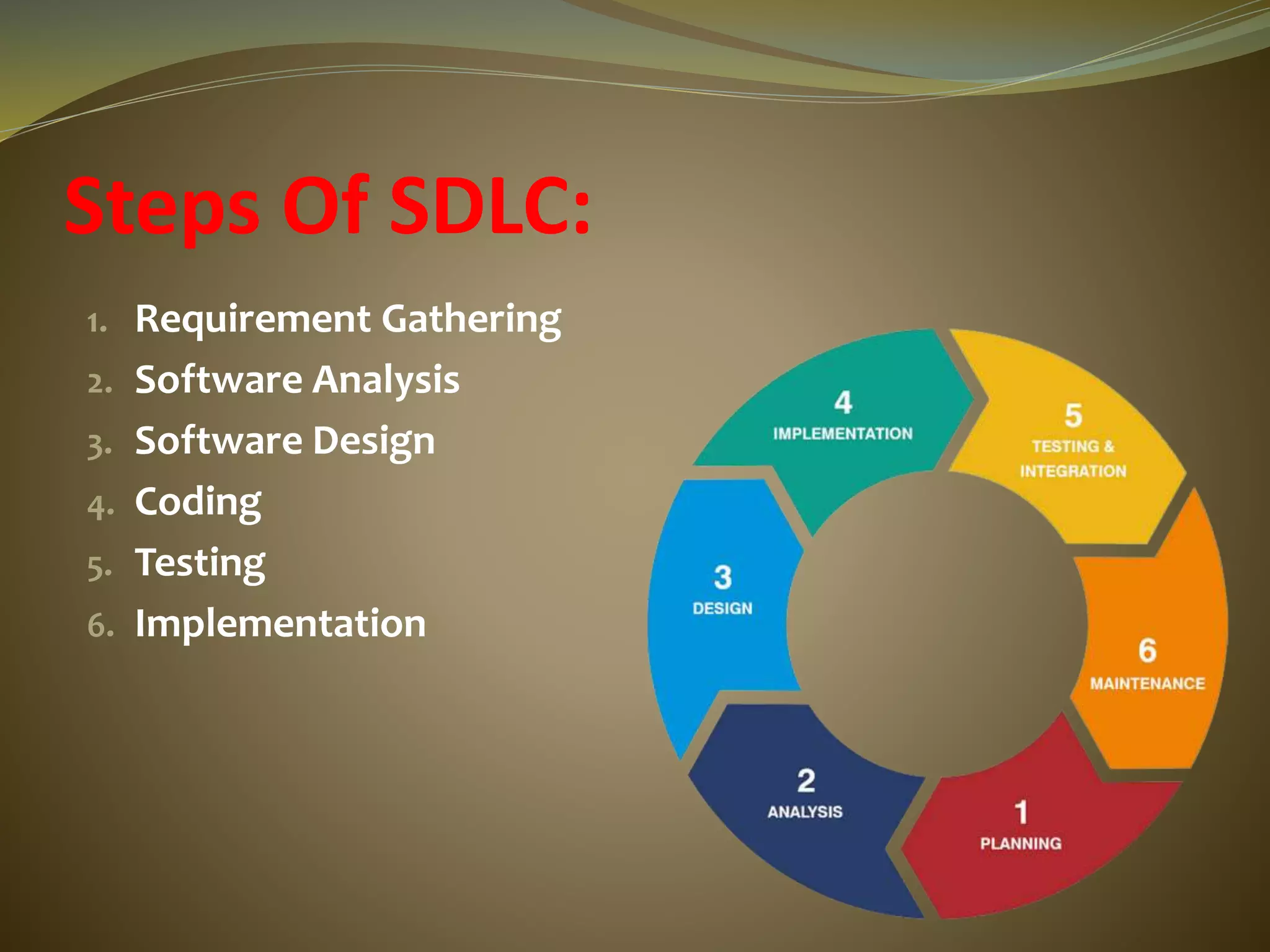
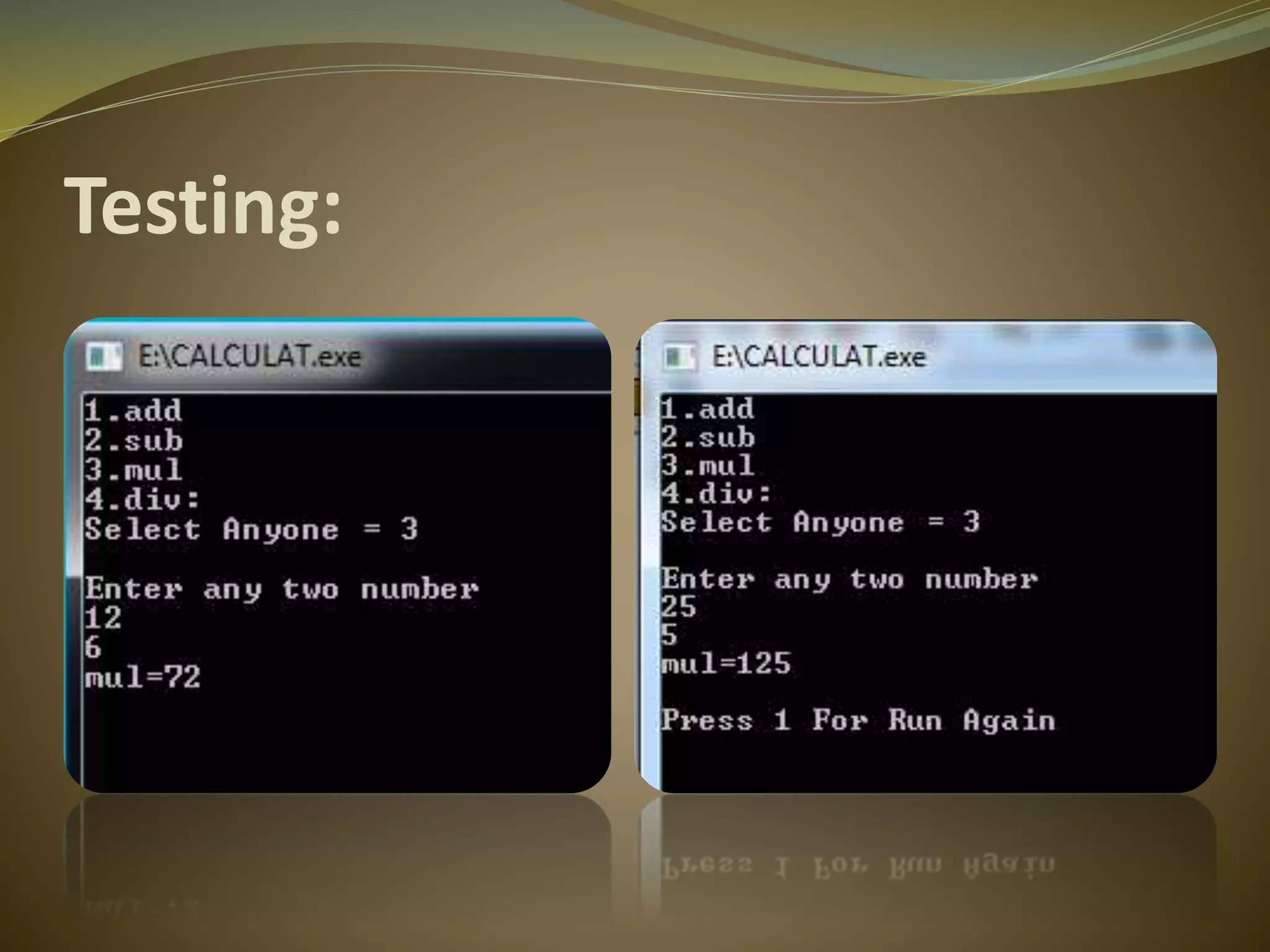
The document discusses the software development life cycle (SDLC) process. It includes 6 main steps: 1) requirement gathering, 2) software analysis, 3) software design, 4) coding, 5) testing, and 6) implementation. For each step, the document provides details on the objectives and activities involved. It also lists advantages of following the SDLC process such as increased quality, improved tracking, and decreased risks. Finally, it provides a coding example for a basic calculator application to illustrate one step of the process.