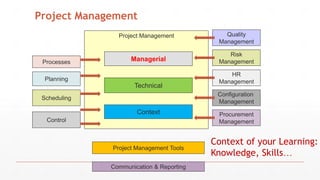
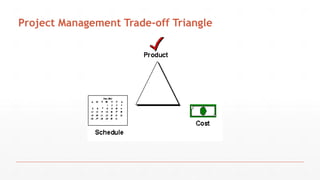
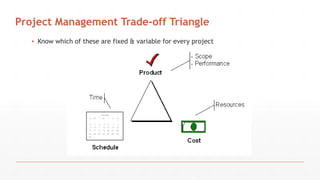
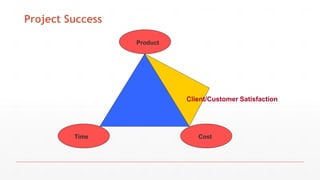
The document outlines the course structure for Software Project Management (SPM) at PMAS-Arid Agriculture University, detailing the course content, objectives, and assessment methods. It emphasizes the importance of effective management practices and introduces various project management concepts, methodologies, and the professional bodies associated with the field, such as PMI. The course aims to equip students with theoretical knowledge and practical skills essential for success in software engineering and project management.











![Management – an overview
▪ Managers: the group of individuals who make decisions about how a
business is run.
▪ A stream of decision and actions to achieve goal(s) efficiently and
effectively.
▪ Management is the process of designing and maintaining an environment
in which individuals, working together in groups, efficiently [and
effectively] accomplish selected aims.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lectureweek01-190425172305/85/Introduction-to-Software-Project-Management-17-320.jpg)