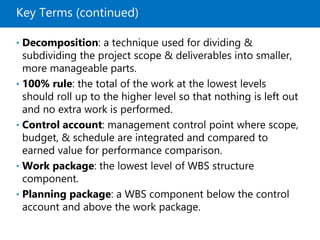
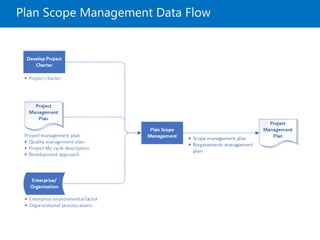
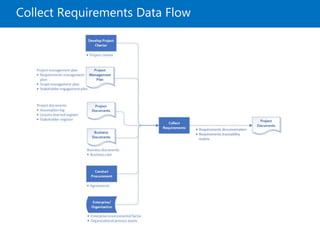
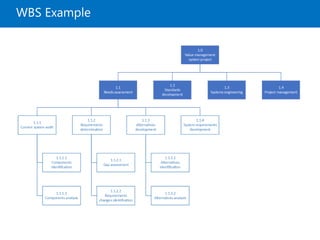
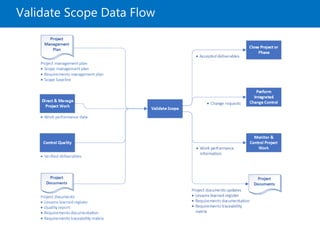
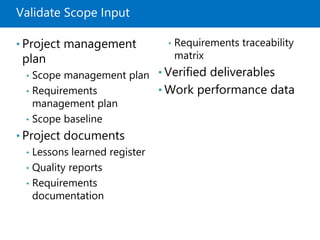
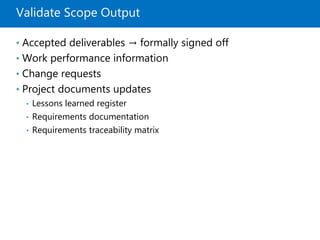
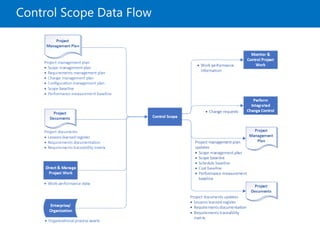
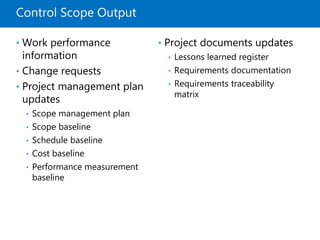
Module 5 covers project scope management, detailing the processes involved in defining and controlling project scope. It discusses key concepts such as product and project scope, requirements traceability, and the creation of a work breakdown structure (WBS). The module also addresses various lessons on planning, collecting requirements, defining scope, validating, and controlling scope throughout the project lifecycle.




![Project Scope Management
Project scope management is the processes of
defining what work is required and then making
sure all of that work –and only that work– is
completed. [RITA9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmp05-scope-180413041938/85/Project-Scope-Management-PMBOK6-5-320.jpg)































![References
• [PMBOK6] – The PMBOK 6th edition from pmi.org
• [RITA9] – Rita Mulcahy’s PMP Exam Prep 9th
edition from RMC Publications™](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmp05-scope-180413041938/85/Project-Scope-Management-PMBOK6-52-320.jpg)