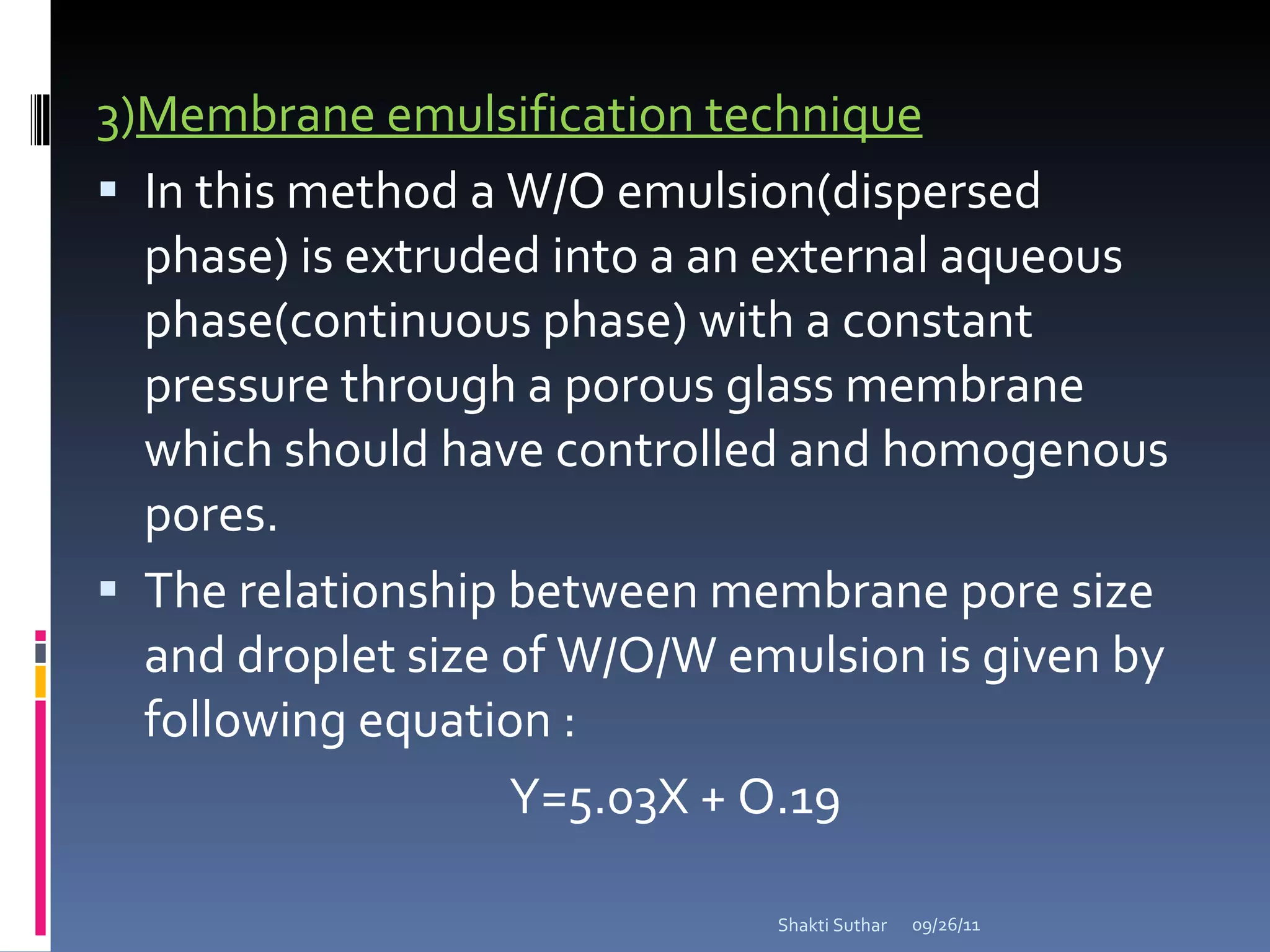
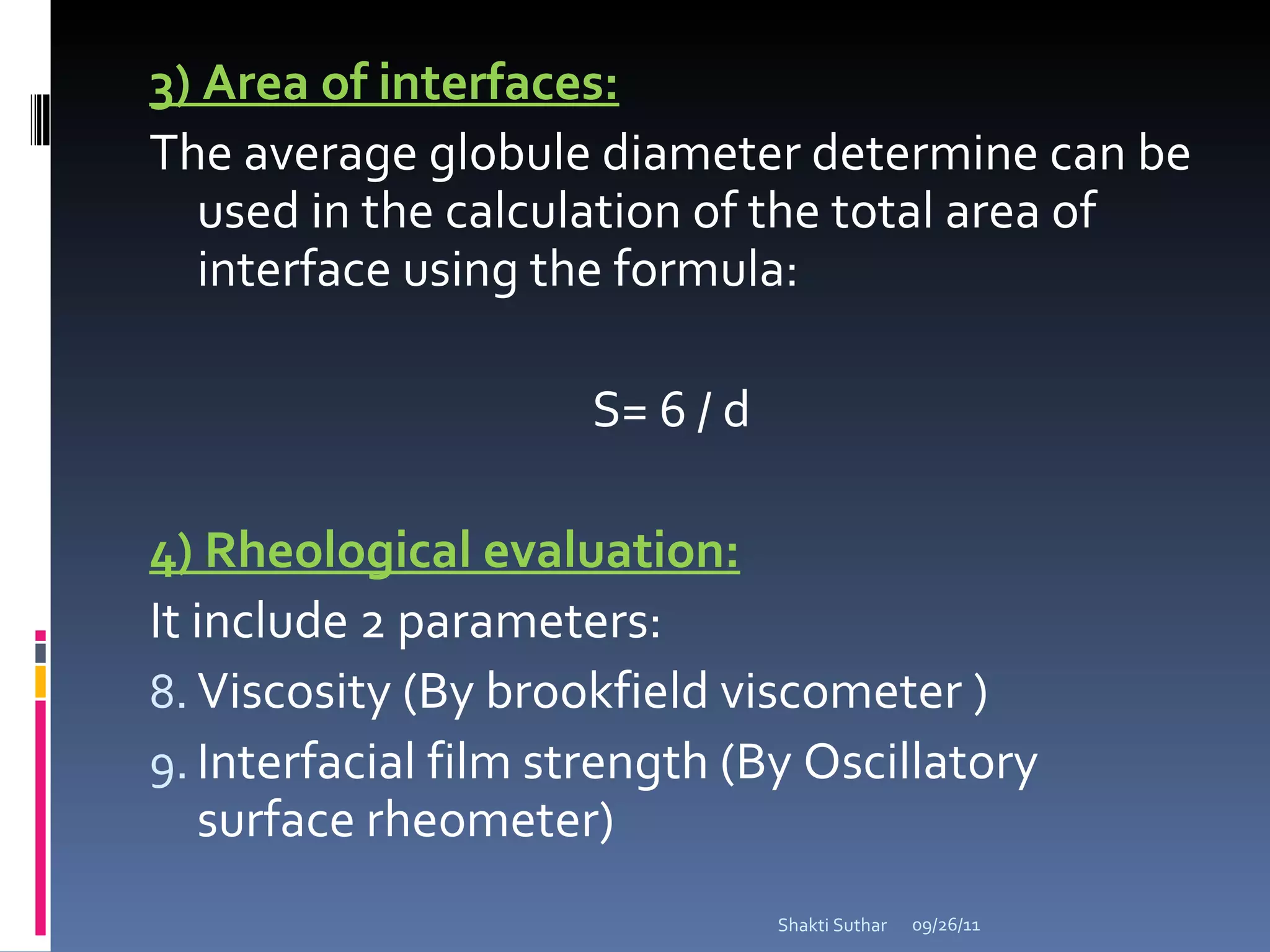
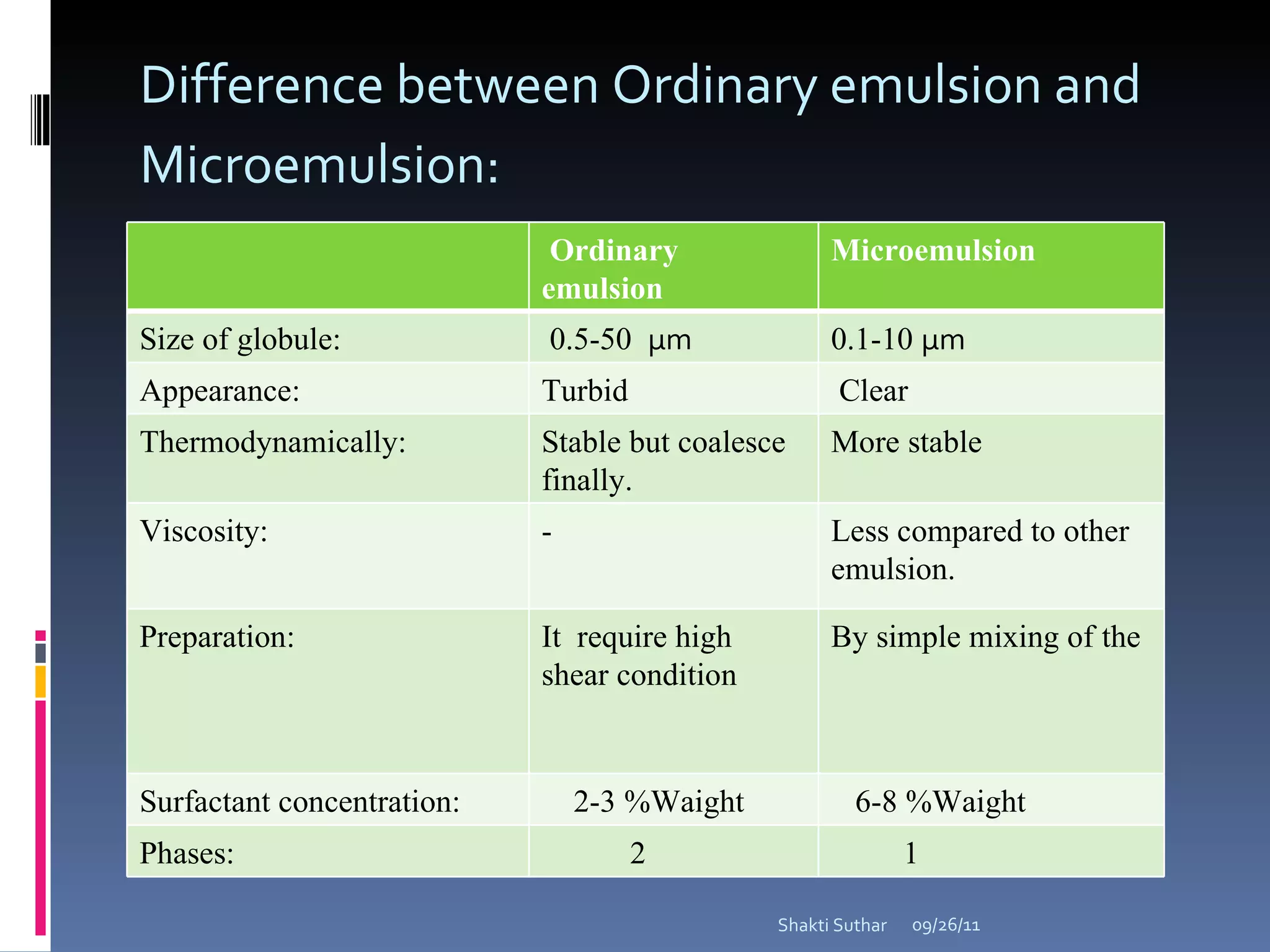
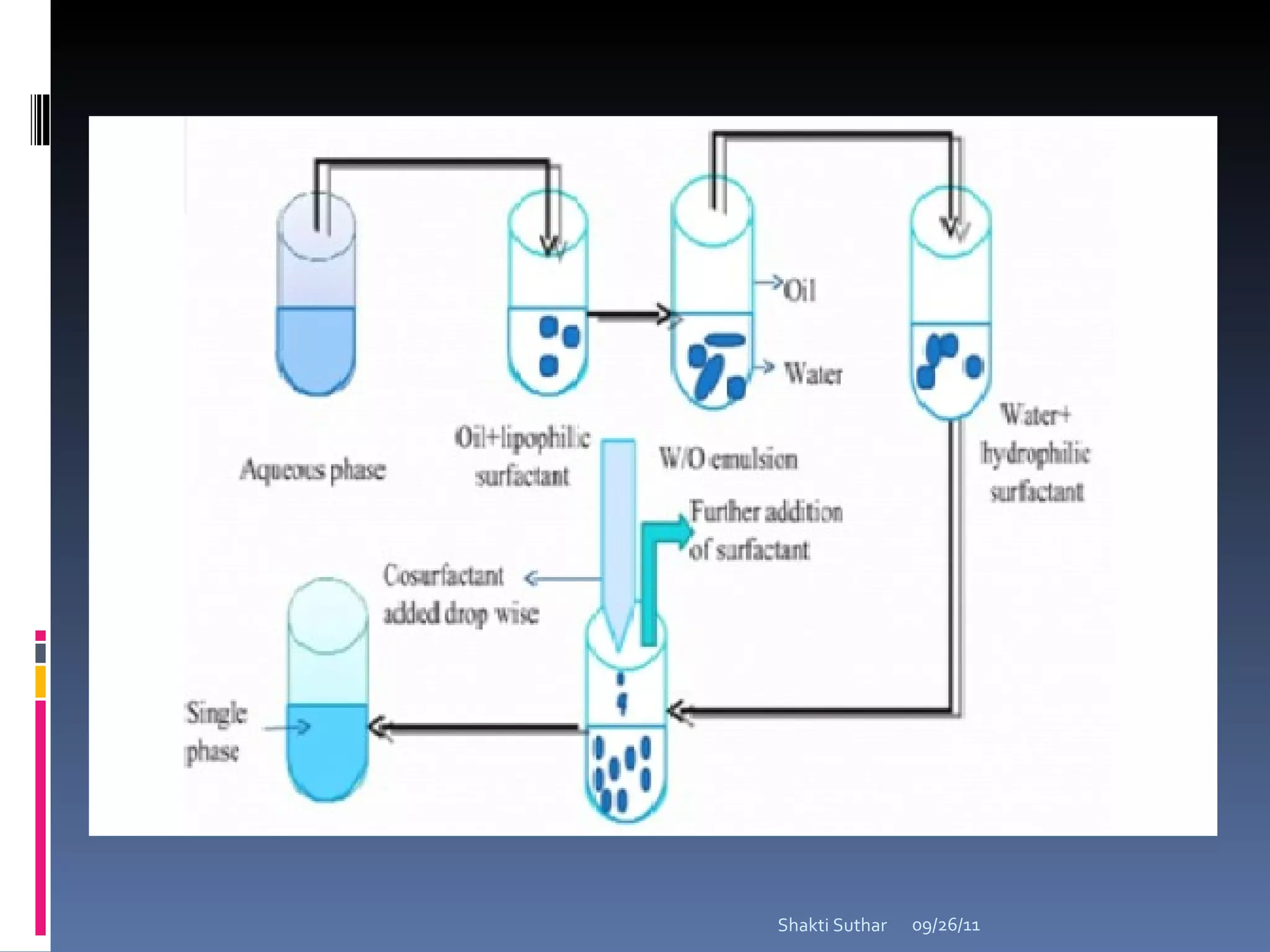
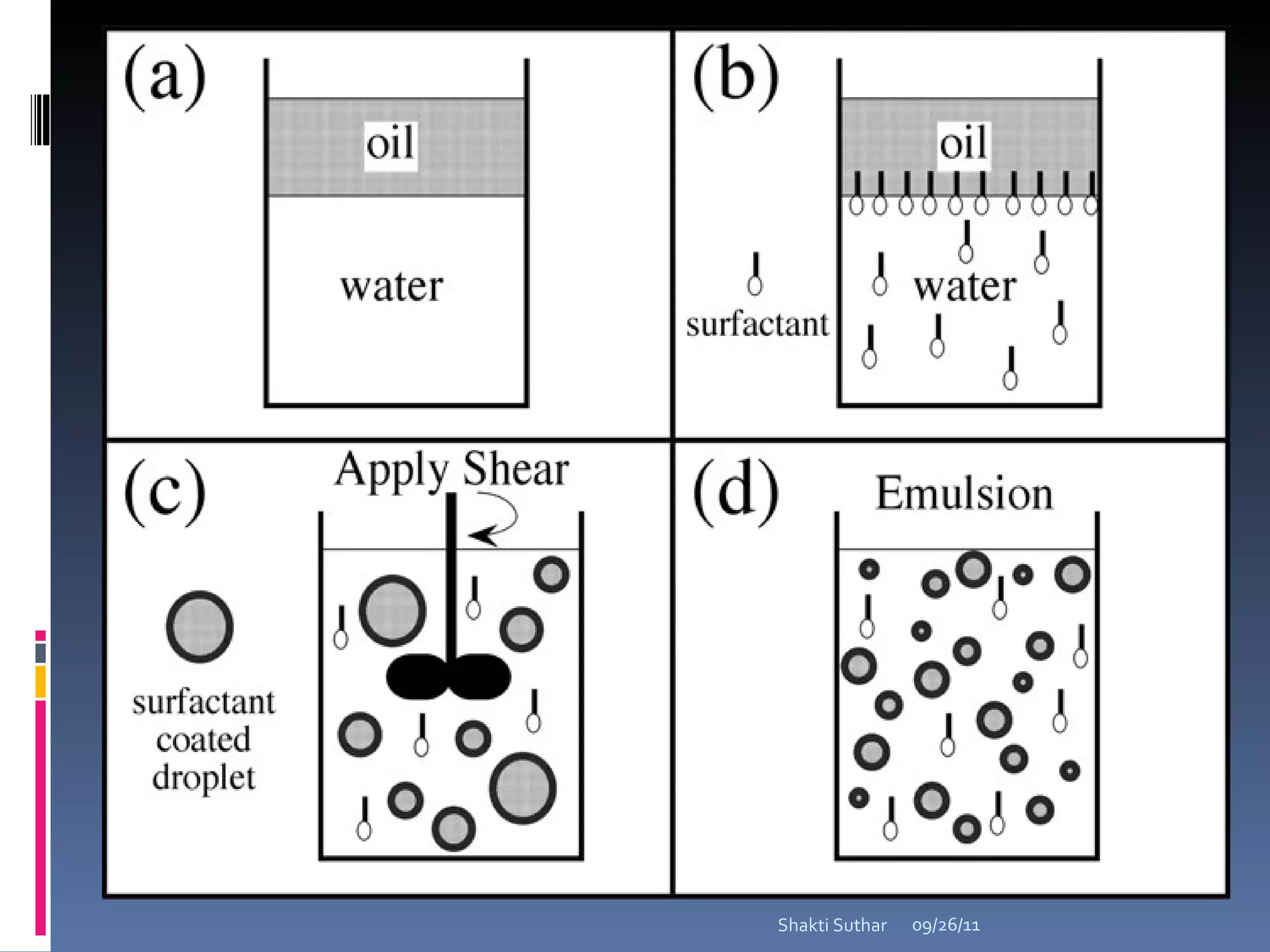
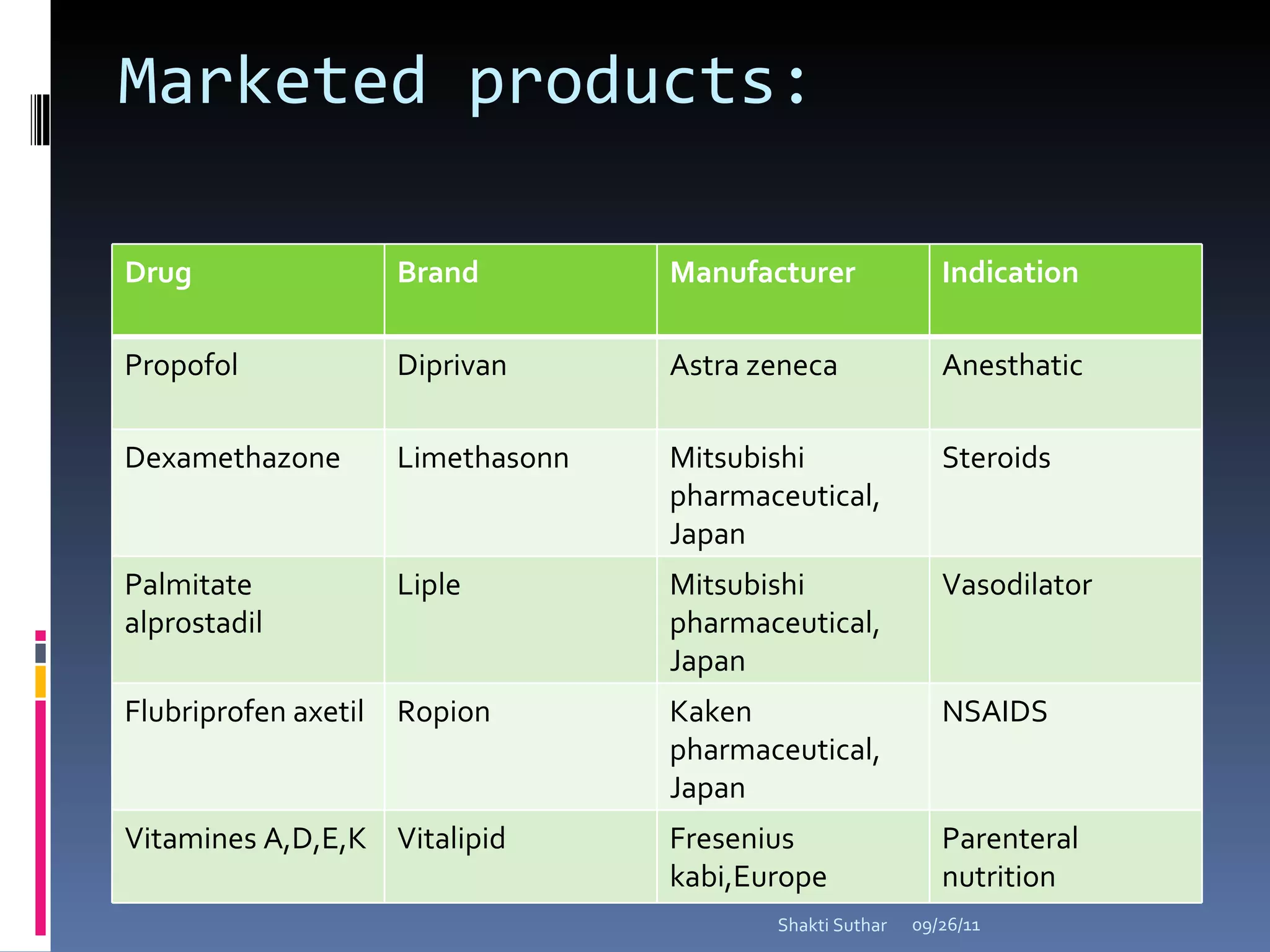
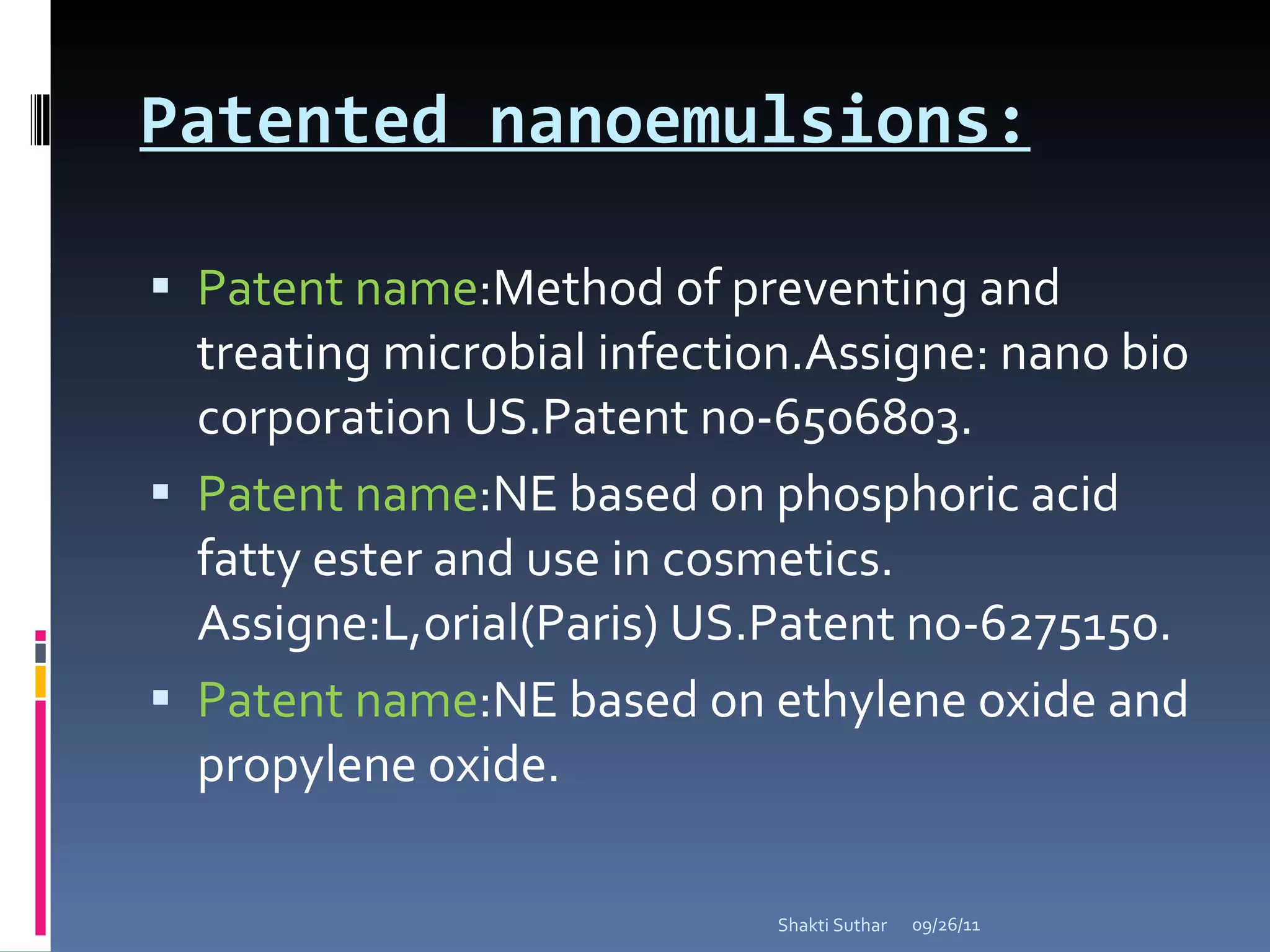
The document summarizes recent advances in emulsion technology, including multiple emulsions, microemulsions, self-emulsifying drug delivery systems, and nanoemulsions. It discusses the introduction, advantages, methods of preparation, characterization, and applications of each type of emulsion system.