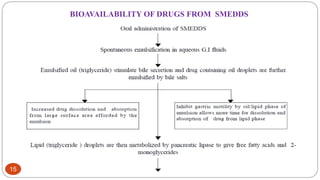
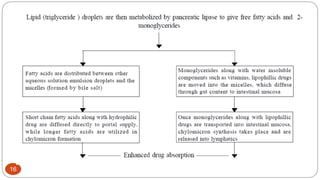
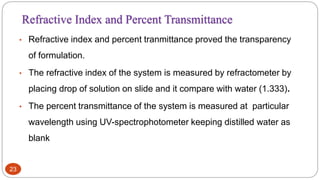
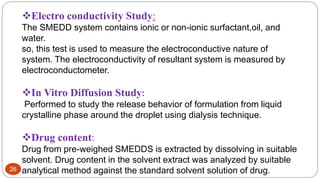
This document discusses self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS). It begins with an introduction to SMEDDS and explains they are isotropic mixtures that can form microemulsions upon mild agitation and dilution in the GI tract. It then covers the definition of SMEDDS, the difference between SMEDDS and self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS), the composition of SMEDDS including oils, surfactants, co-solvents and polymers. The document discusses the mechanism of emulsification for SMEDDS and factors affecting SMEDDS. It provides details on characterizing and solidifying SMEDDS before concluding with advantages and recent advances.