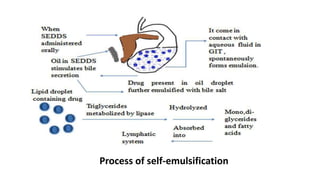
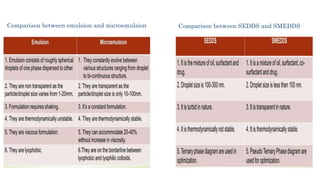
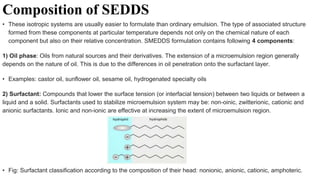
The document discusses self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS), introduced in the 1940s, focusing on their mechanisms, composition, preparation methods, advantages, and disadvantages. SEDDS improve the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs by forming microemulsions through surfactant-mediated processes. It also highlights the necessary steps for formulation optimization using ternary phase diagrams and various preparation techniques, including high-pressure homogenization and sonication.