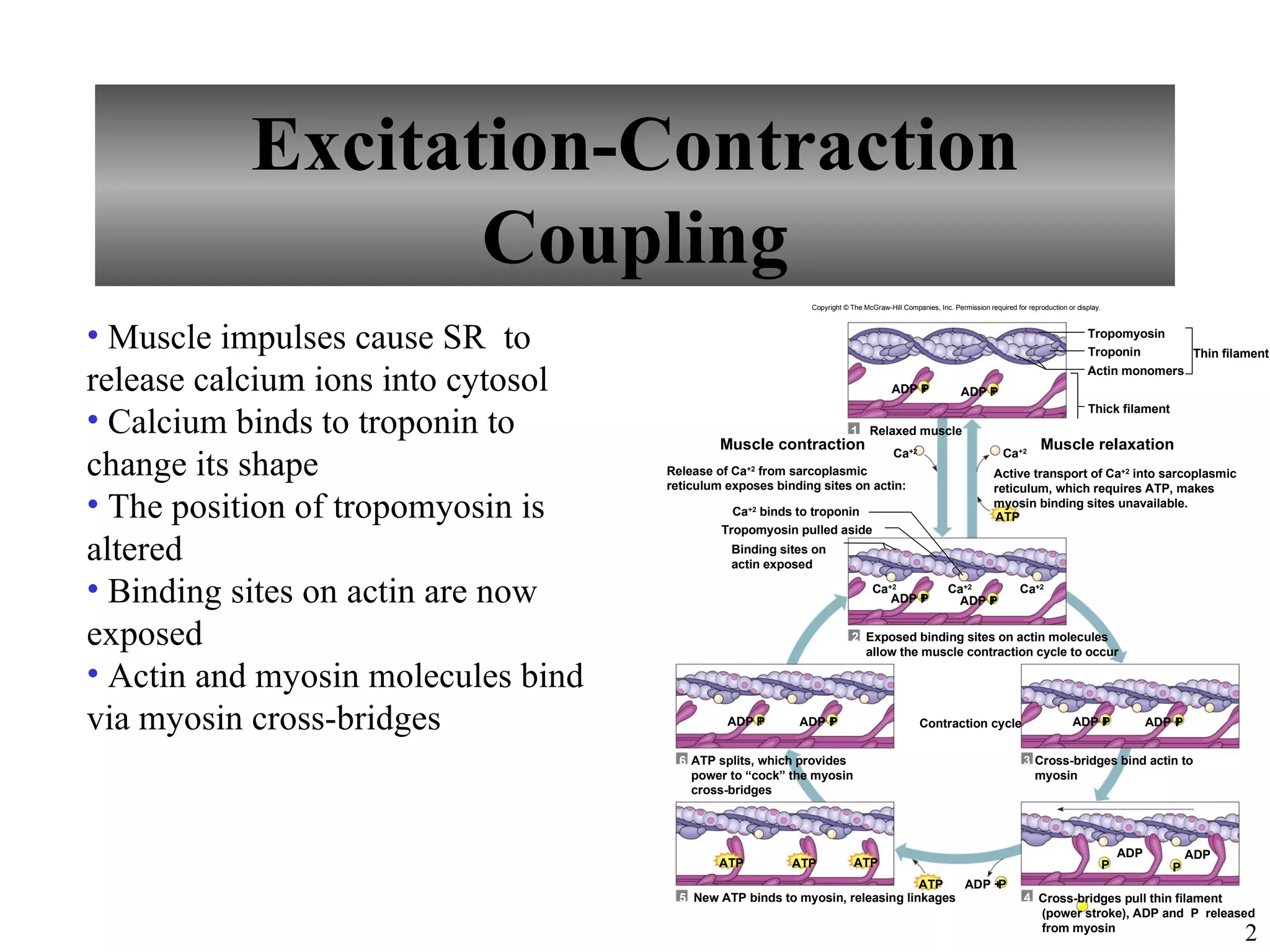
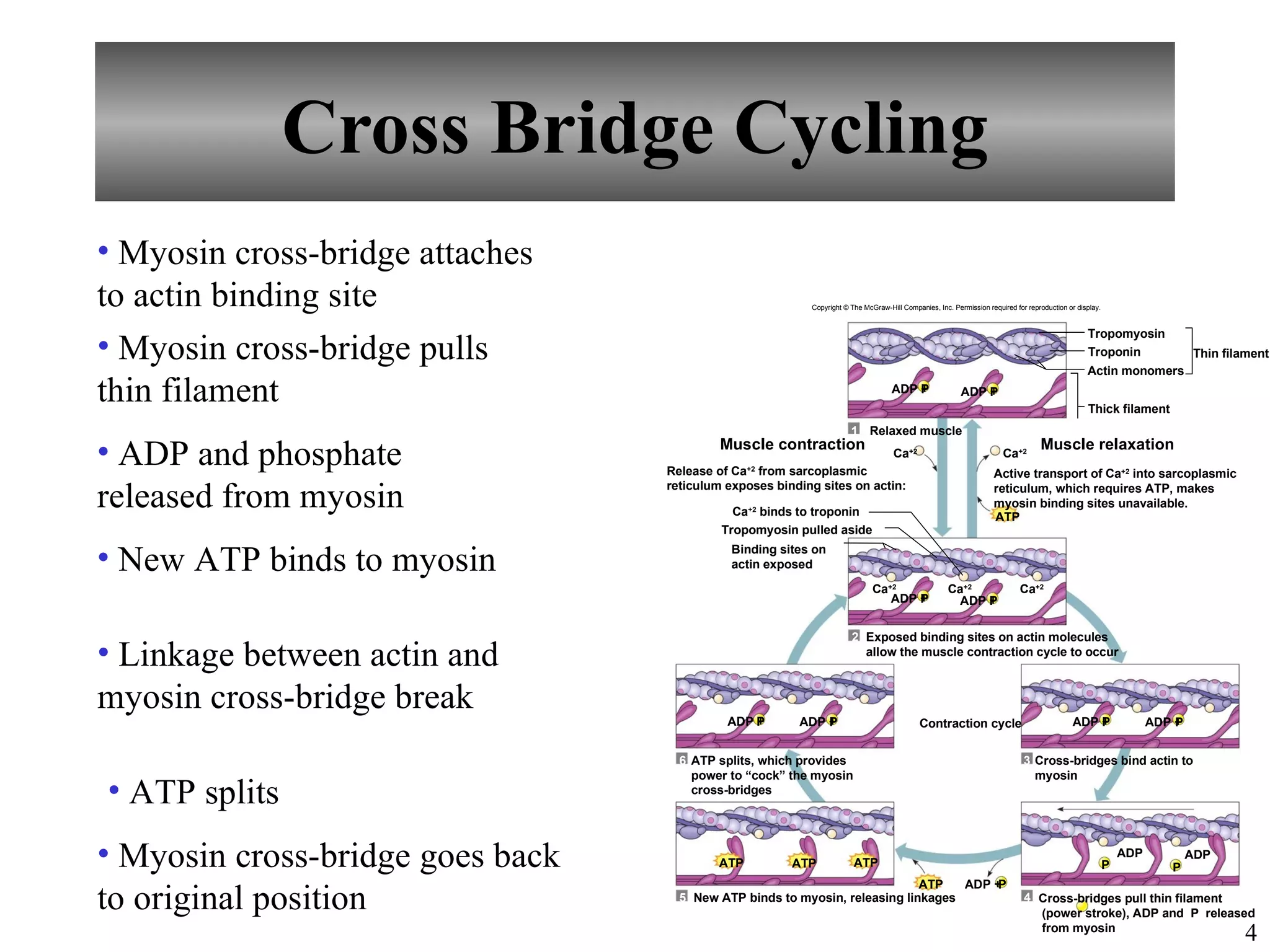
The document describes the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. It explains that (1) muscle impulses cause calcium ions to be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which then bind to troponin and alter the position of tropomyosin, exposing binding sites on actin. (2) Actin and myosin can then bind via cross-bridges, causing contraction. (3) Muscle relaxation occurs when calcium is actively transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, making the binding sites on actin unavailable again.