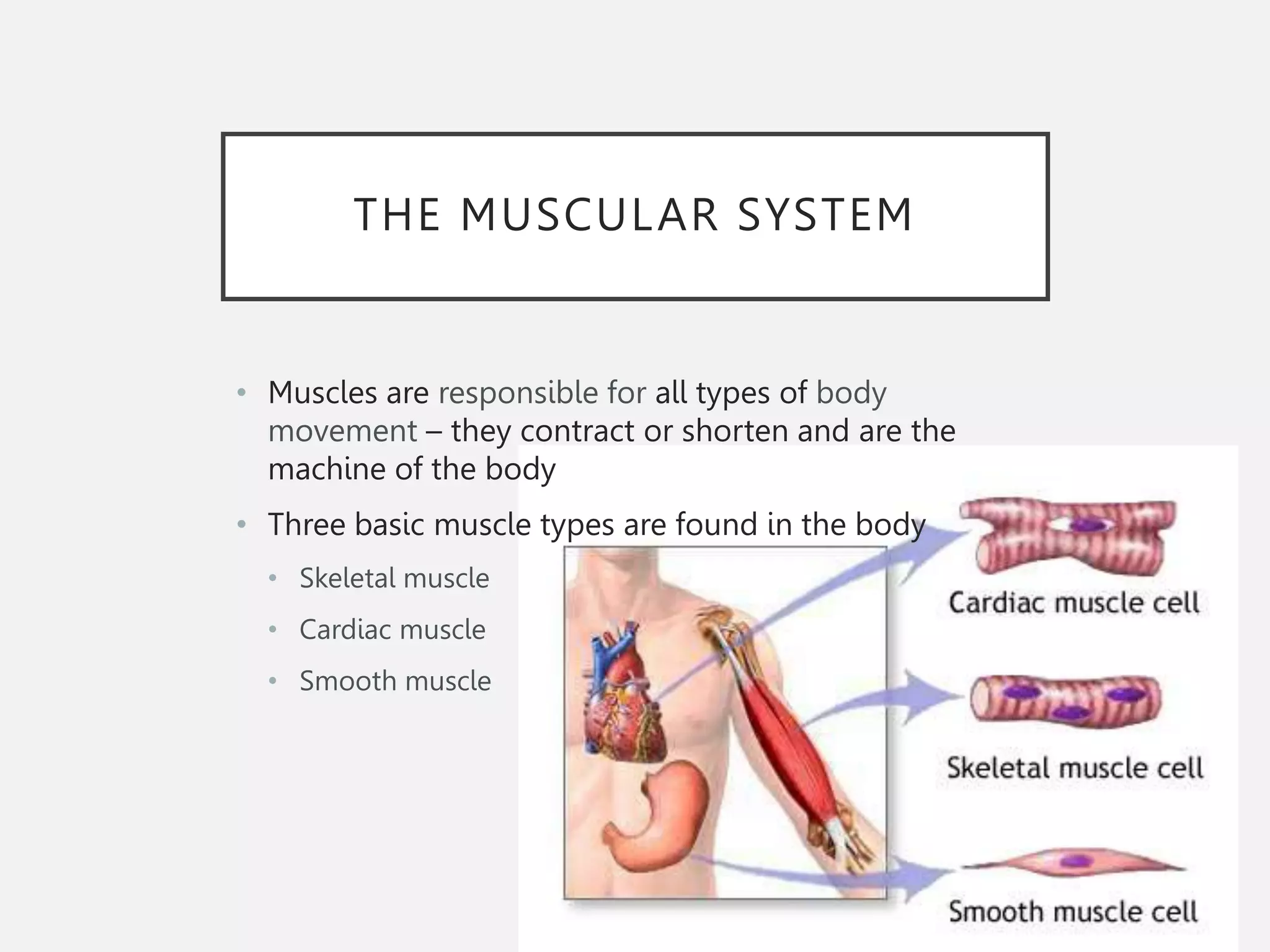
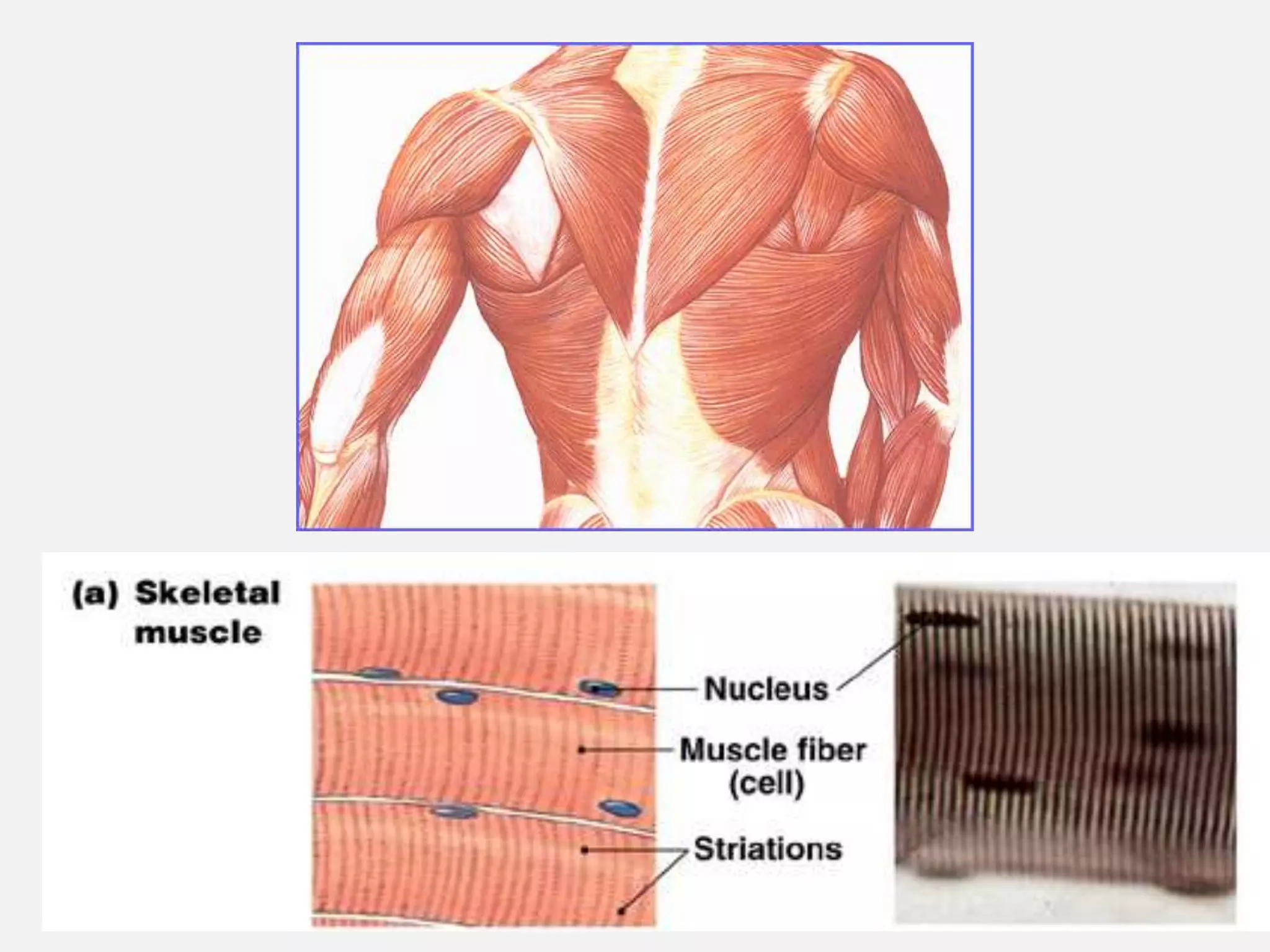
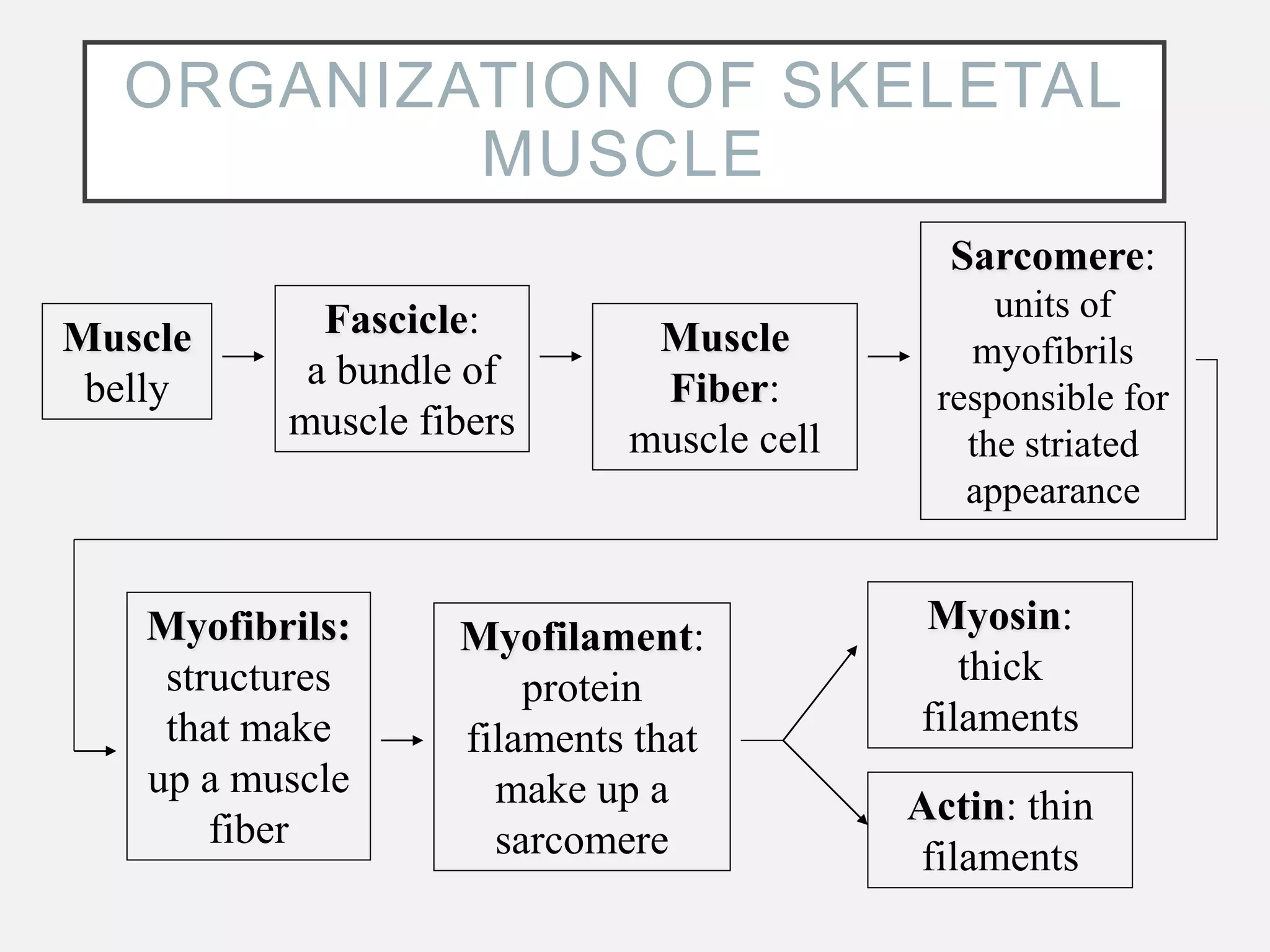
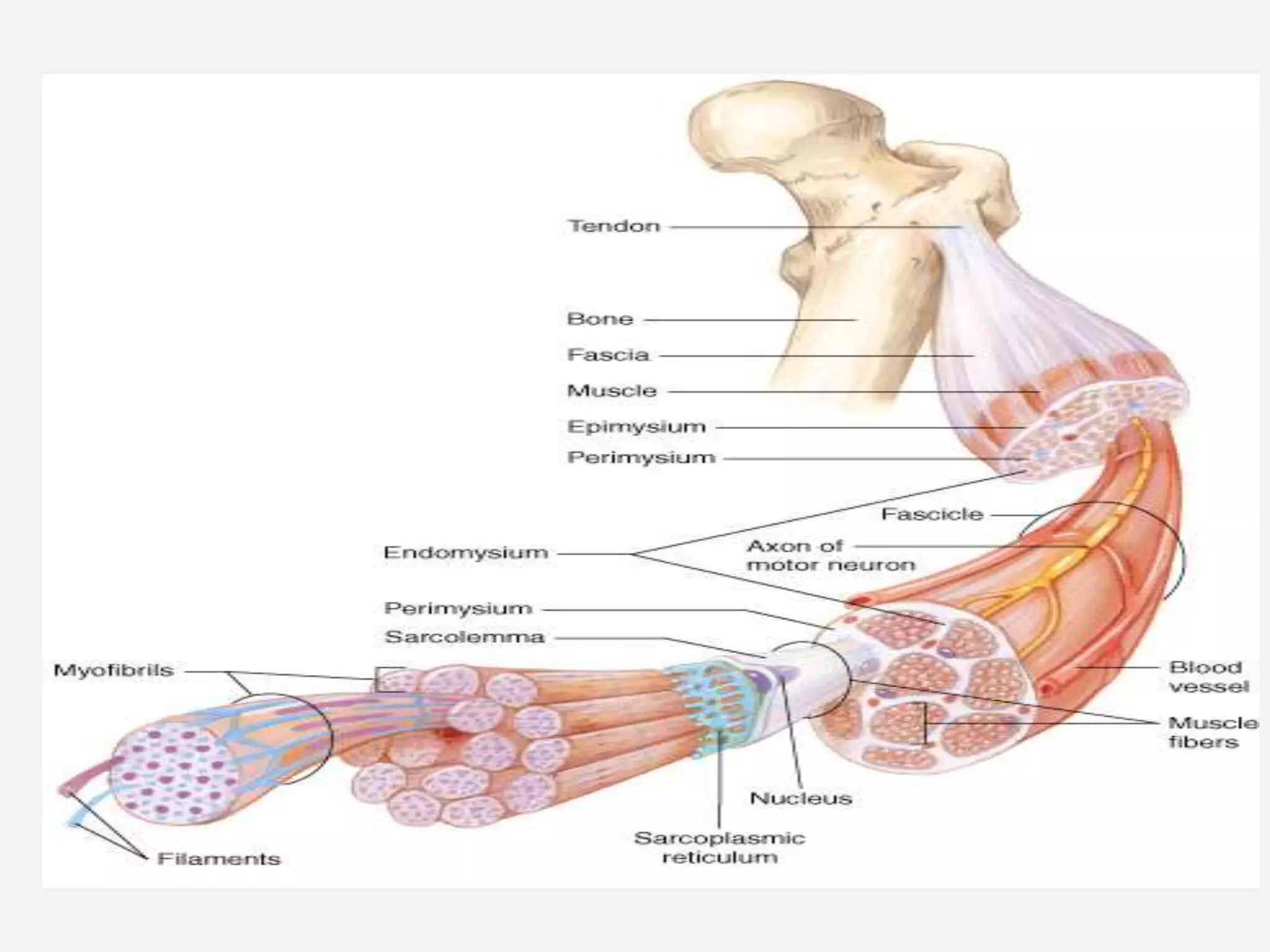
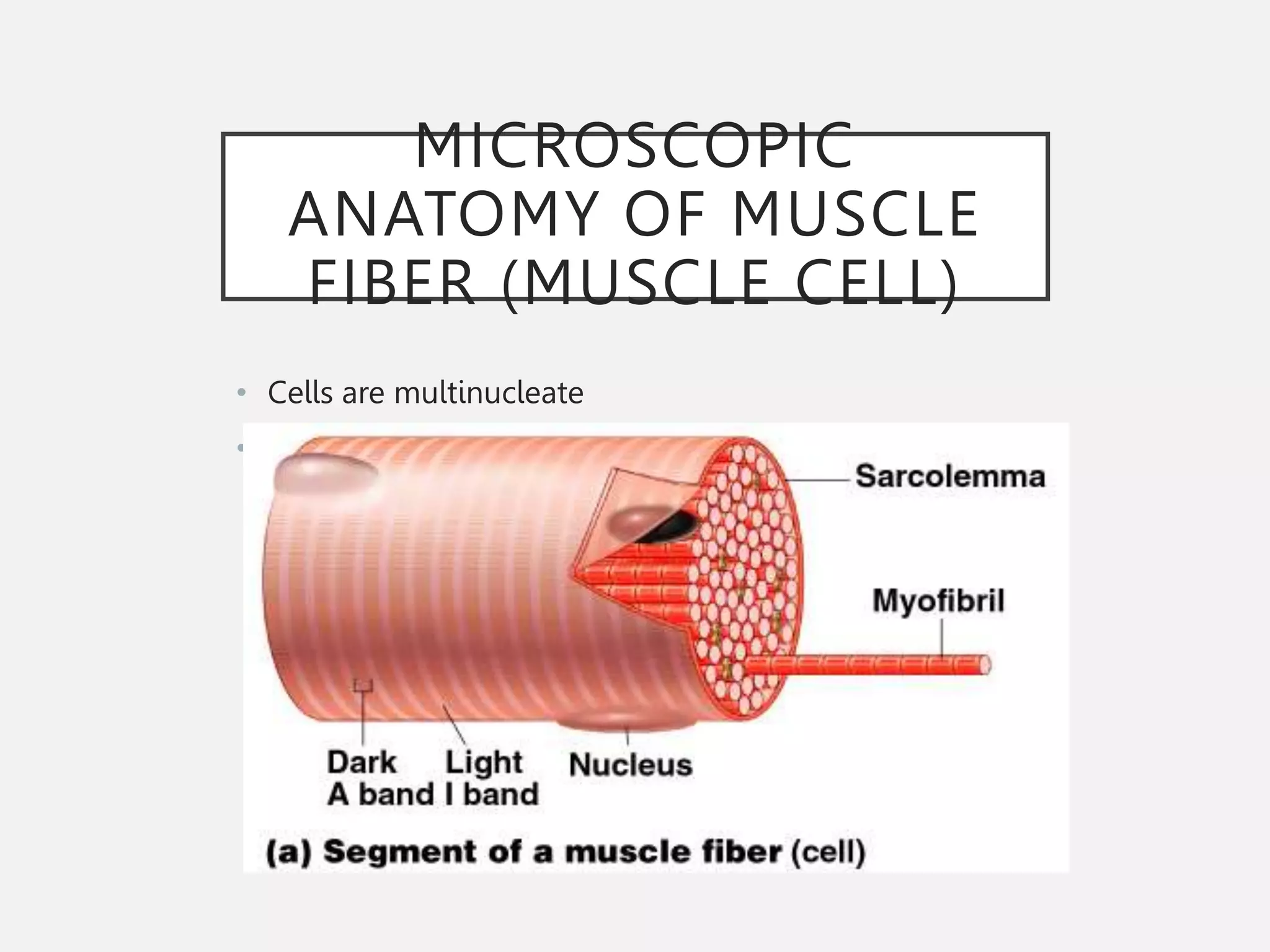
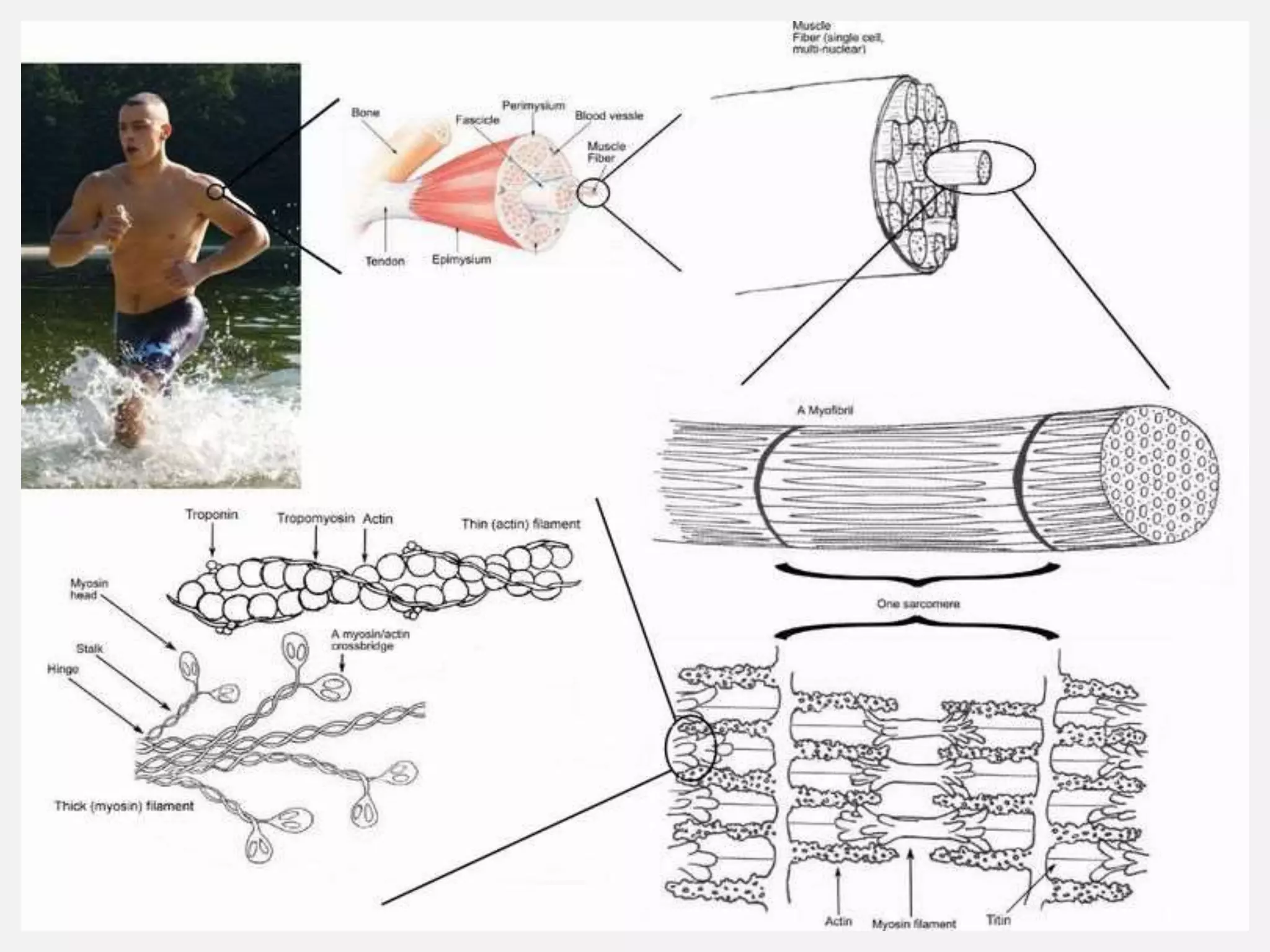
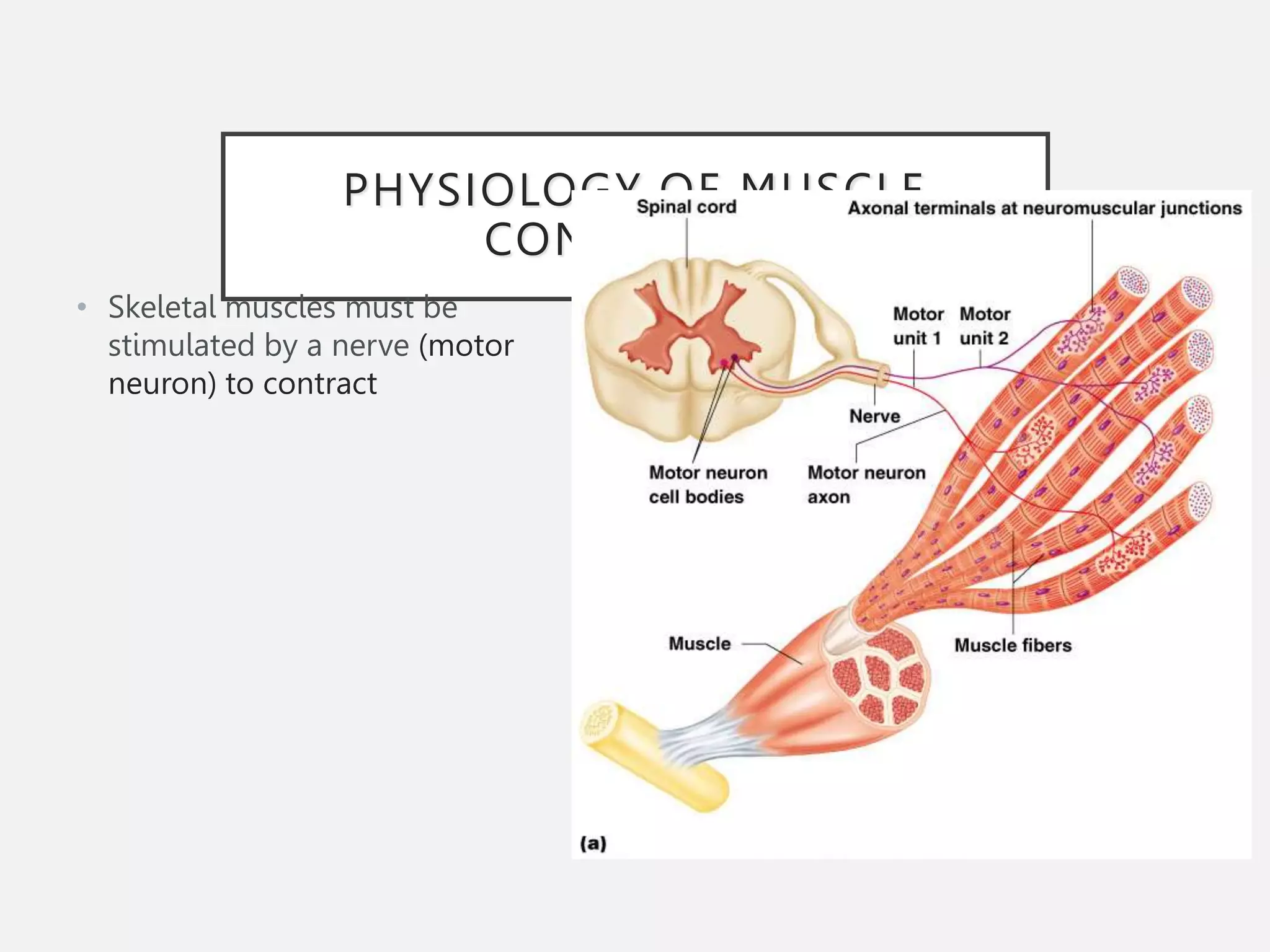
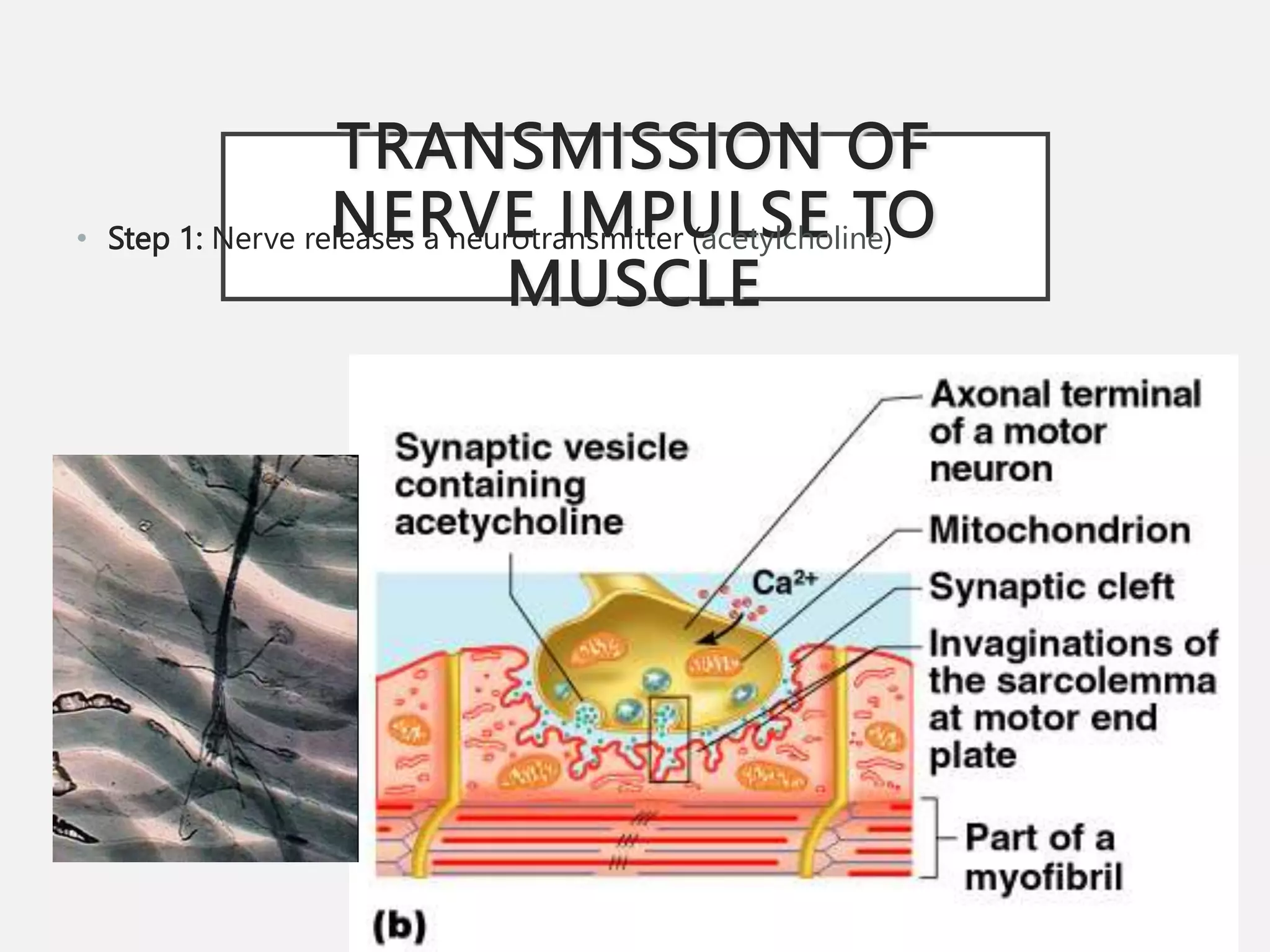
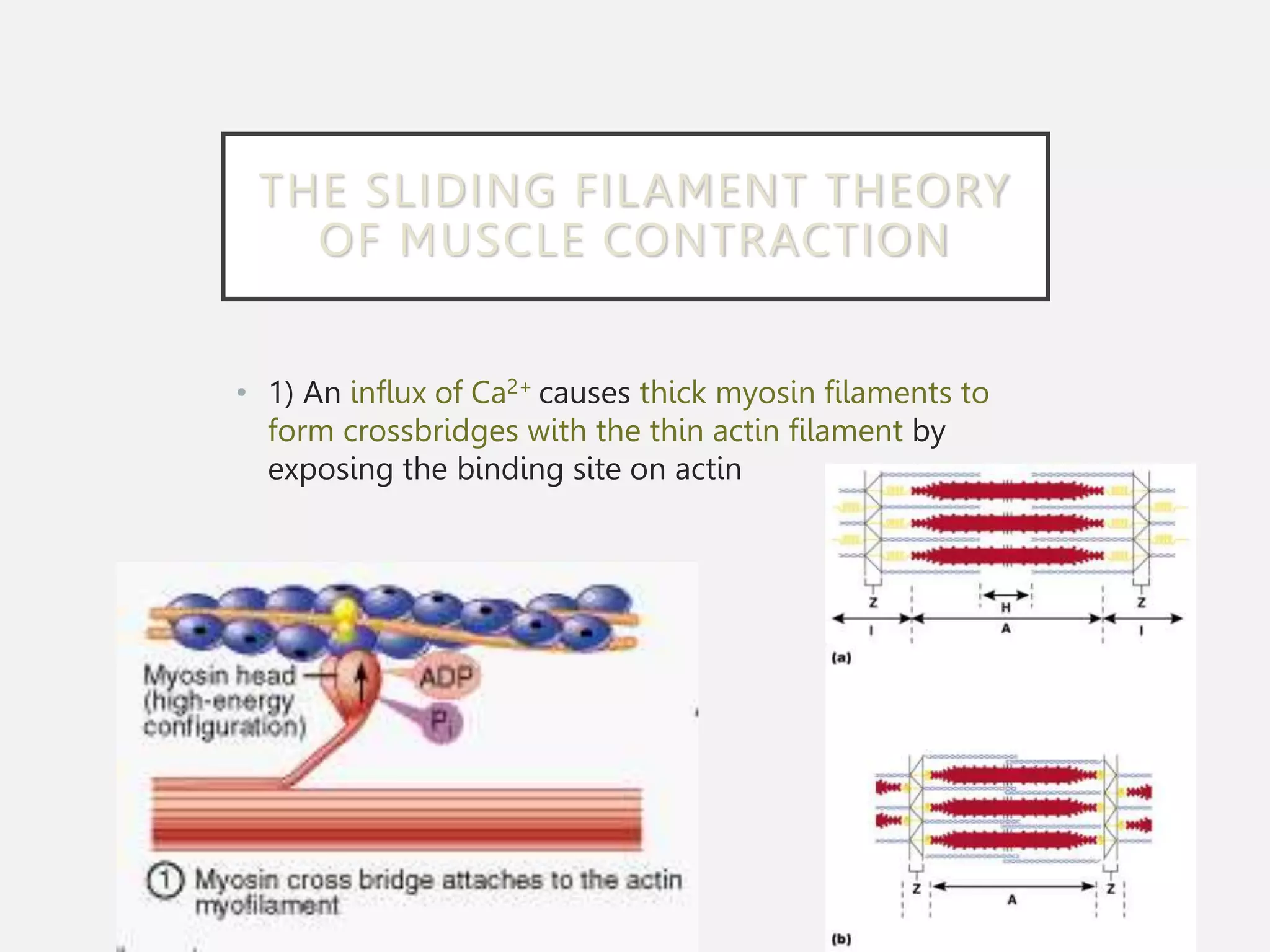
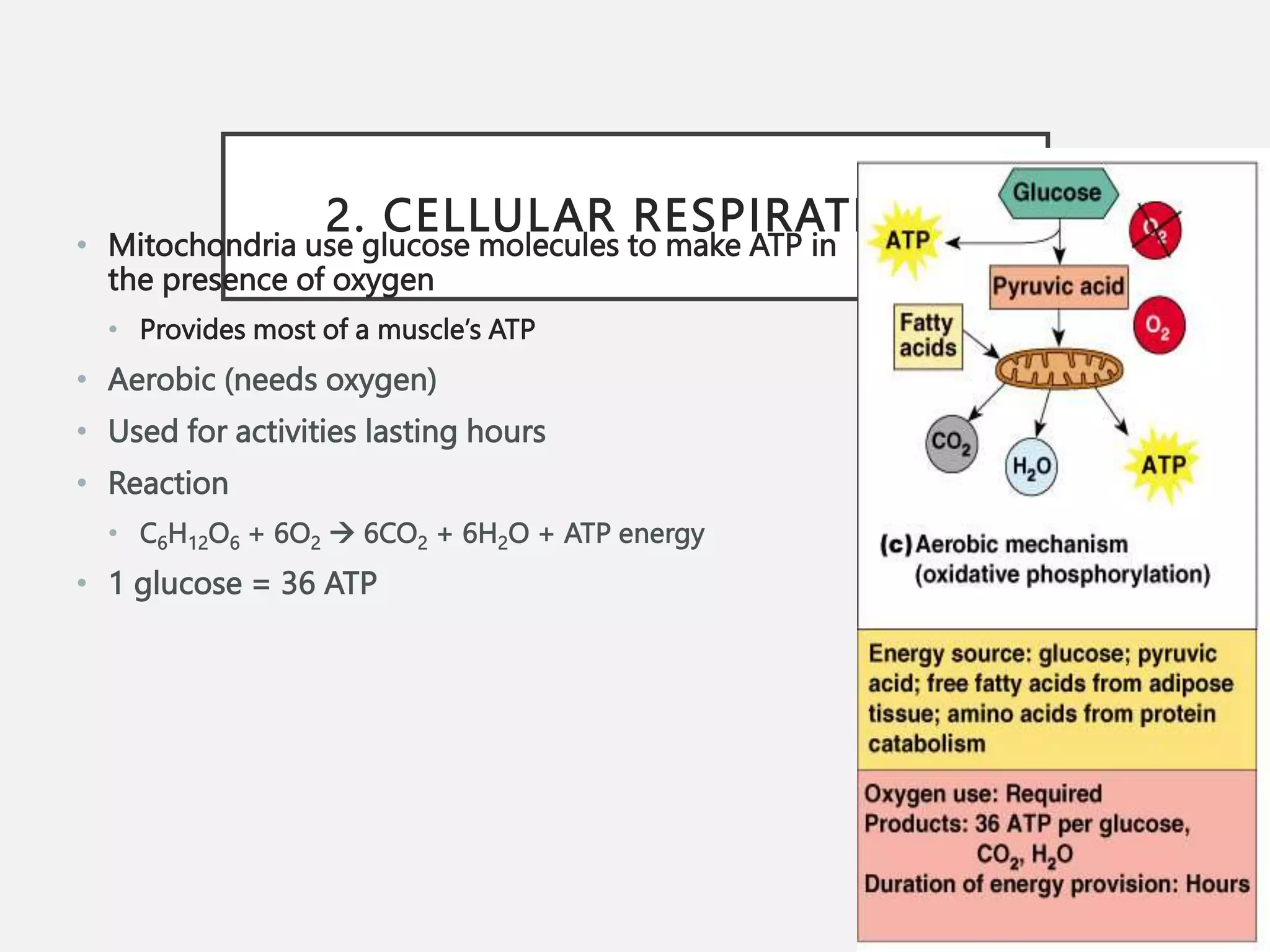
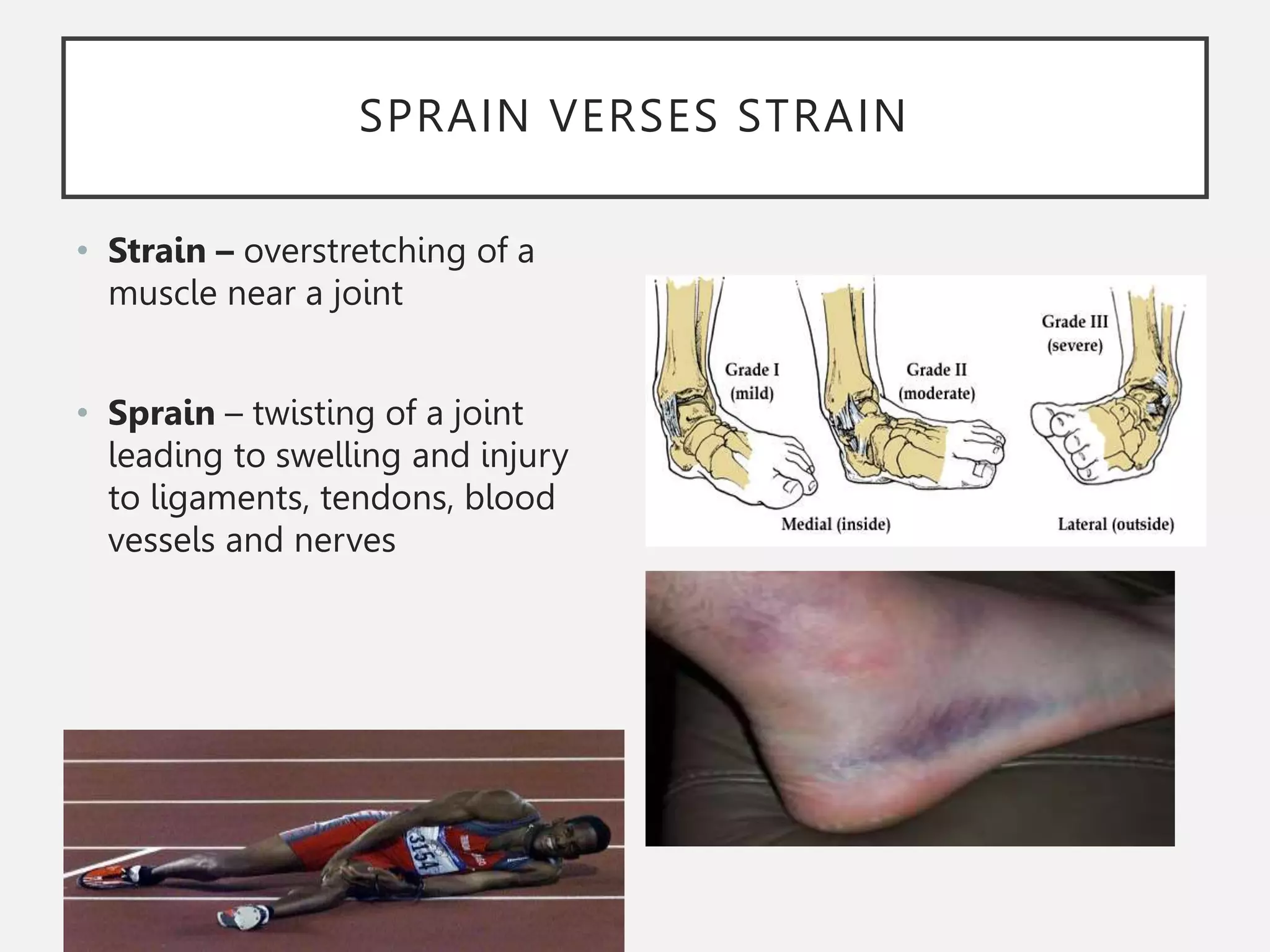
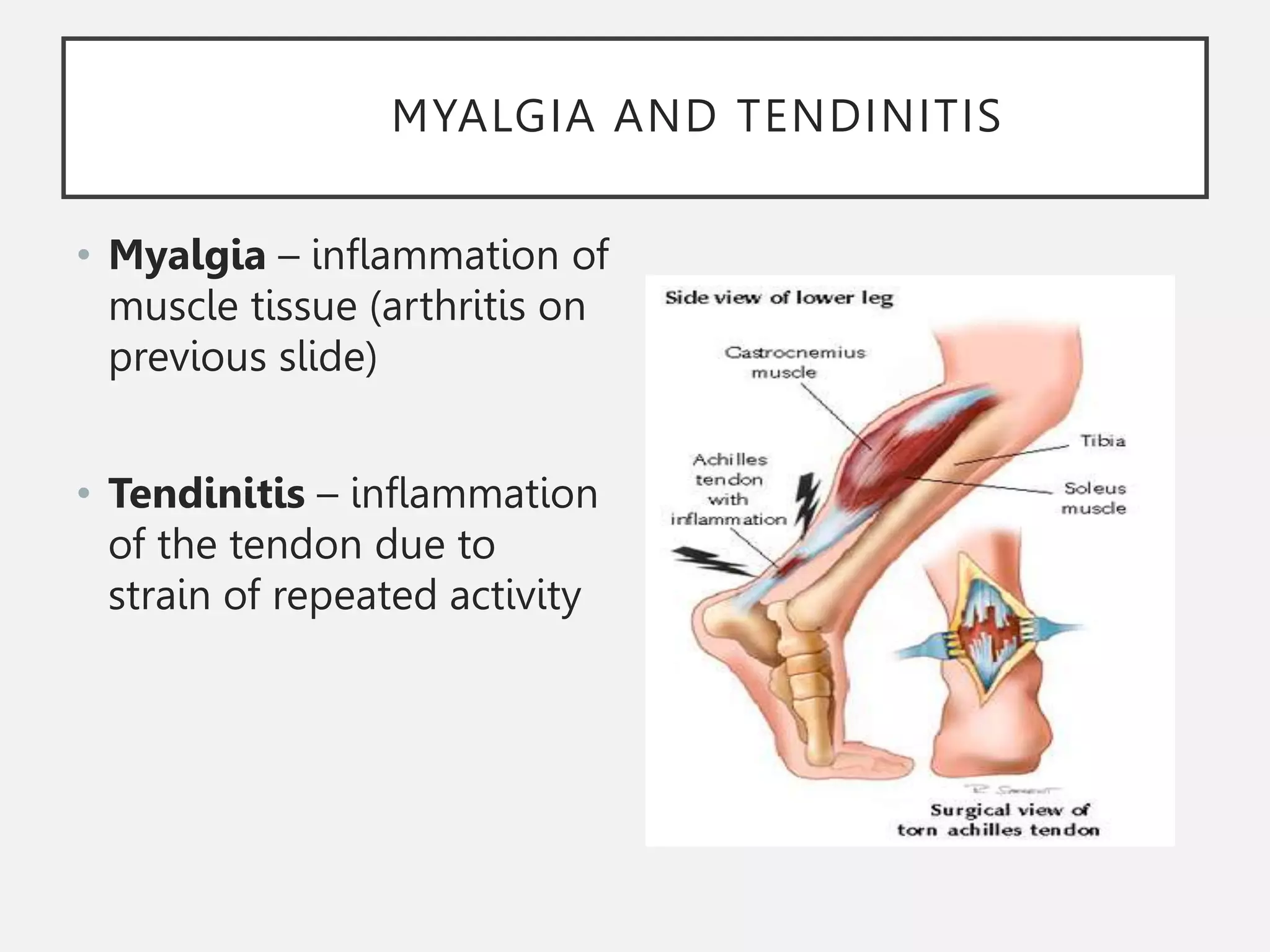
The muscular system is composed of three types of muscles - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle allows for movement by contracting and shortening. It is organized into fascicles containing bundles of striated muscle fibers. Muscle fibers contain myofibrils made up of overlapping actin and myosin filaments that slide past each other during contraction. Contraction is initiated when a nerve impulse causes calcium release and the heads of myosin filaments form cross-bridges with actin to generate force through the hydrolysis of ATP. Aging can lead to muscle loss but exercise can help build muscle mass. Disorders of muscle include muscular dystrophy and myasthenia gravis.