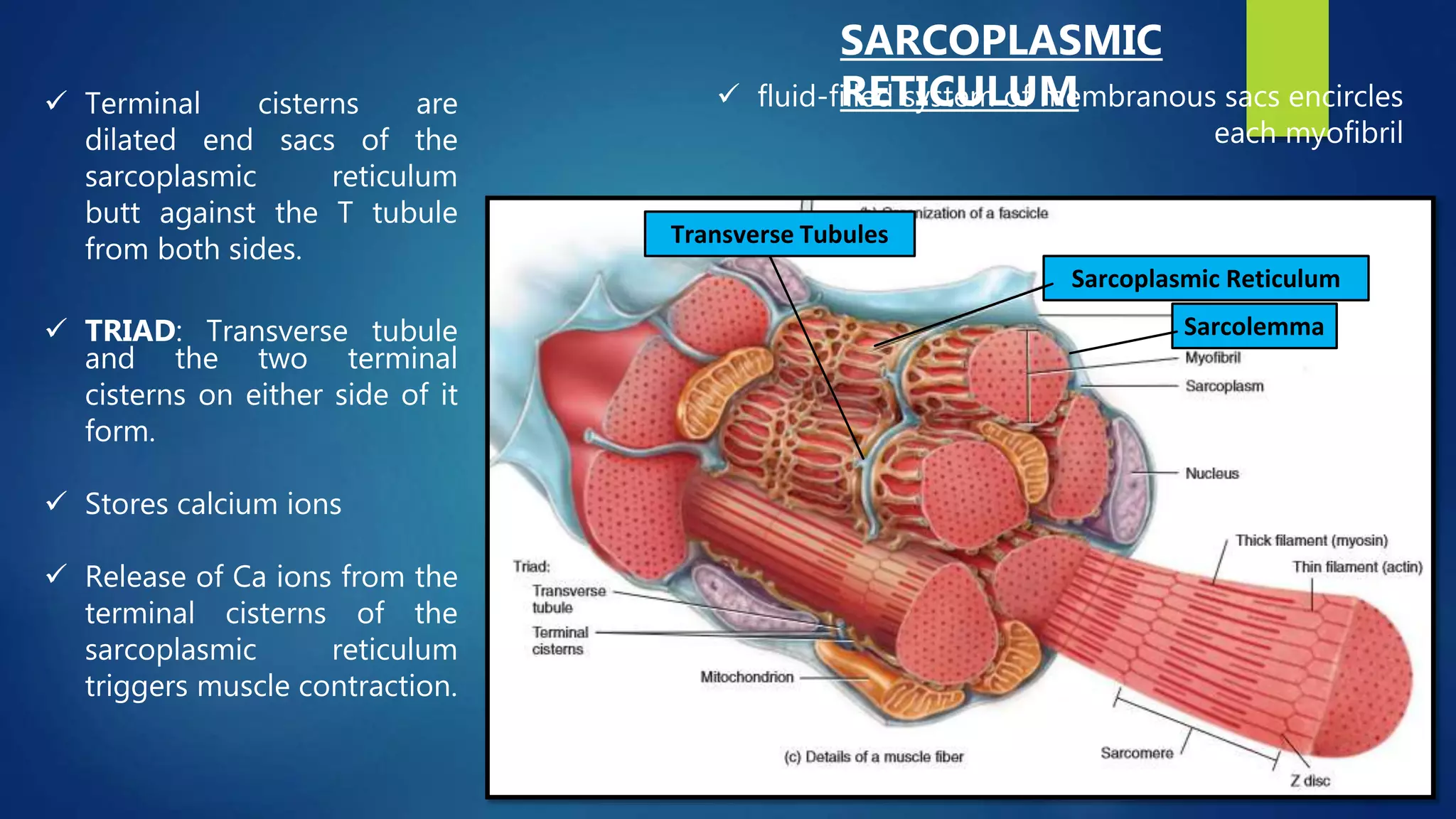
The document provides an overview of muscle physiology, detailing the three types of muscular tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. It outlines the functions of muscular tissue, including movement, stabilization, substance storage, and heat generation, as well as its key properties such as electrical excitability and contractility. Additionally, it describes the organization of skeletal muscle tissue, including connective tissue layers and the structure of muscle fibers and myofibrils.