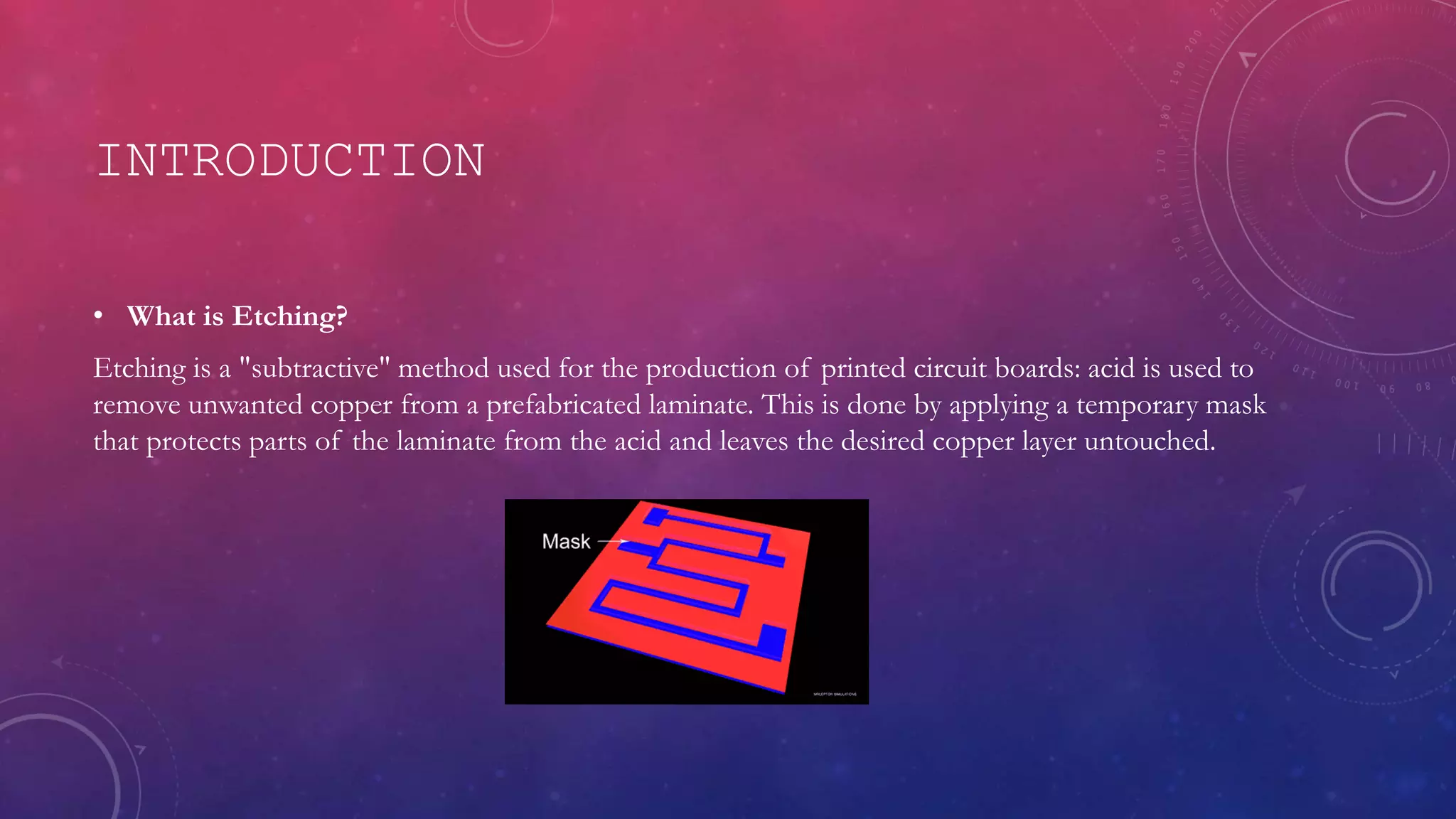
This document discusses etching techniques used in electronics manufacturing. It begins by defining etching as a subtractive process using acid to remove unwanted copper from printed circuit boards. It then discusses key metrics for etching like depth control, selectivity between materials, and degree of undercutting. The document outlines different etching types including wet etching with liquid etchants and dry etching using plasma. It describes how plasma etching works and the components of plasma etchers. Finally, it briefly mentions lithography printers used to expose photomasks in the etching process.