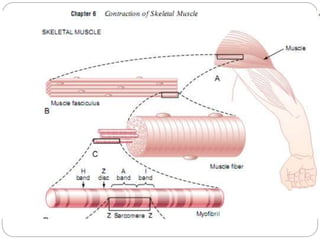
- Skeletal muscle makes up 40% of total body mass and contains long, striated muscle fibers that are multinucleated.
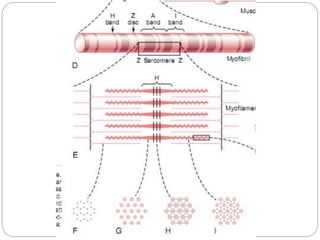
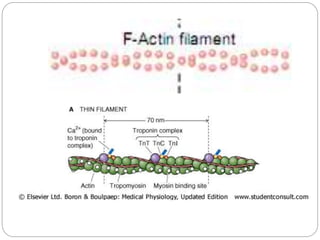
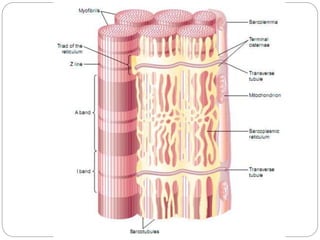
- Each muscle fiber contains numerous myofibrils composed of thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments that overlap to form dark A bands and light I bands.
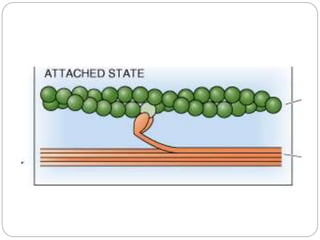
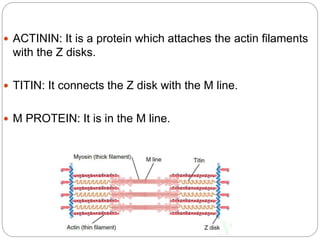
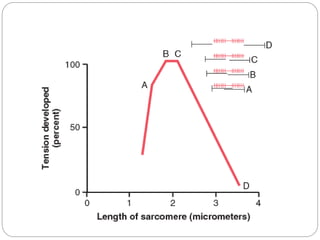
- The functional unit of skeletal muscle is the sarcomere, defined as the segment between two Z disks, which contains overlapping actin and myosin filaments that slide past each other during muscle contraction.
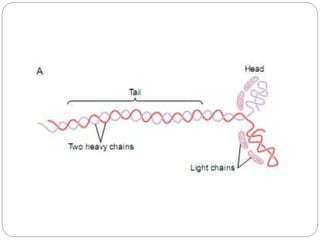
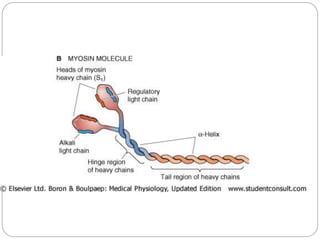
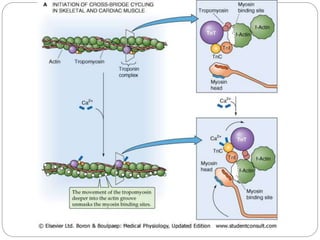
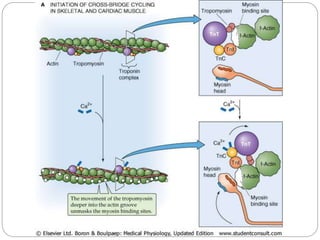
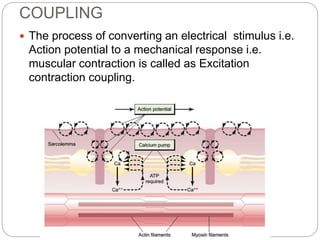
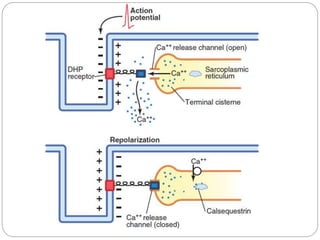
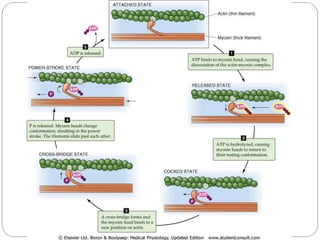
- Excitation-contraction coupling involves an action potential triggering calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, allowing calcium to bind troponin and initiate the contraction of actin and myosin