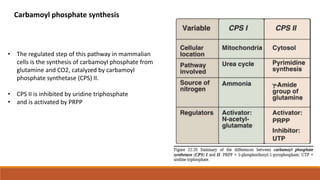
Pyrimidine synthesis begins with the formation of carbamoyl phosphate from glutamine, CO2, and aspartate. Carbamoyl aspartate is then formed from carbamoyl phosphate catalyzed by aspartate transcarbamoylase. In enteric bacteria, this enzyme represents feedback control and is inhibited by CTP and activated by ATP. Cytidine triphosphate (CTP) is produced from UTP by CTP synthetase using glutamine as the nitrogen source. Deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP) is formed from dUMP by thymidylate synthase using N5,N10-methylene-THF as the methyl group source. Inhibitors of thymidyl