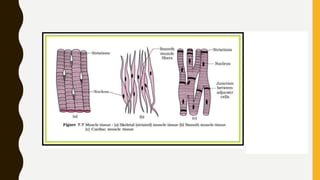
1. There are three types of muscle in the body: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle makes up about 40% of body mass.
2. Muscles are classified based on their structure and control. Skeletal and cardiac muscles are striated due to cross-striations and voluntary, while smooth muscle is non-striated and involuntary.
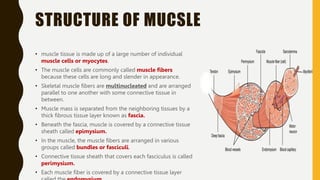
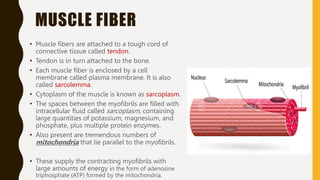
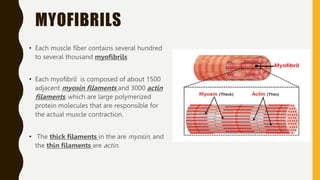
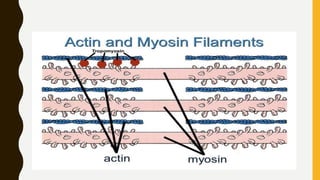
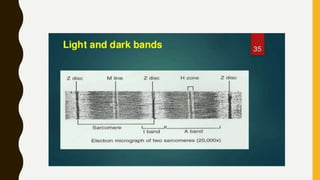
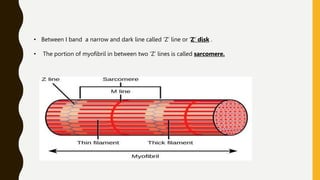
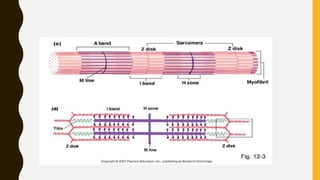
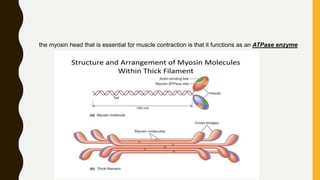
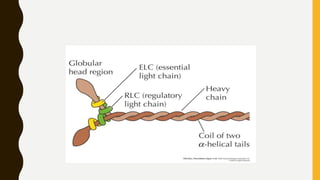
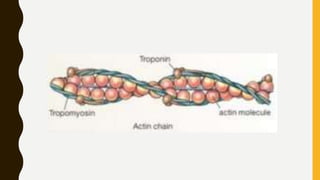
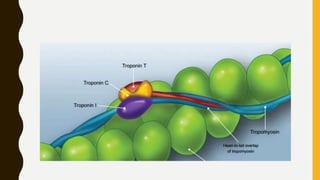
3. Each muscle fiber contains myofibrils which are made up of repeating sarcomere units consisting of actin and myosin filaments that overlap to enable contraction.