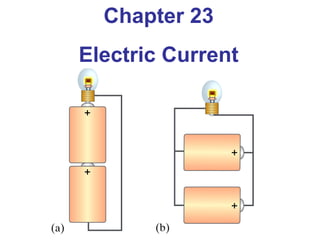
This document provides an overview of electric current and some key concepts:
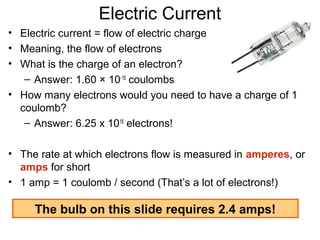
- Electric current is the flow of electric charge, specifically electrons. The rate of electron flow is measured in amps.
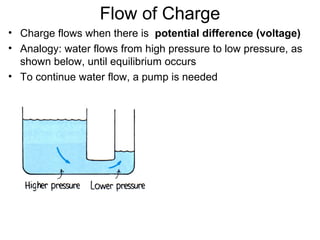
- A voltage or potential difference is needed to cause electric current to flow, similar to how water needs pressure to flow. Voltage is measured in volts.
- Electrical resistance opposes the flow of electric current. Resistance is measured in ohms and can be decreased by using shorter, thicker wires.
- Ohm's Law states that voltage equals current times resistance (V=IR). It shows the relationship between these three key electrical concepts.